Practice Free N10-009 Exam Online Questions
A network administrator’s device is experiencing severe Wi-Fi interference within the corporate headquarters causing the device to constantly drop off the network.
Which of the following is most likely the cause of the issue?
- A . Too much wireless reflection
- B . Too much wireless absorption
- C . Too many wireless repeaters
- D . Too many client connections
A
Explanation:
Reference: CompTIA Network+ Certification Exam Objectives – Wireless Networks section.
Which of the following is most closely associated with a dedicated link to a cloud environment and may not include encryption?
- A . Direct Connect
- B . Internet gateway
- C . Captive portal
- D . VPN
A
Explanation:
Direct Connect refers to a dedicated network connection between an on-premises network and a cloud service provider (such as AWS Direct Connect). This link bypasses the public internet, providing a more reliable and higher-bandwidth connection. It may not inherently include encryption because it relies on the security measures of the dedicated physical connection itself. In contrast, other options like VPN typically involve encryption as they traverse the public internet.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ full course material indicates that Direct Connect type services offer dedicated, private connections which might not include encryption due to the dedicated and secure nature of the link itself.
SIMULATION
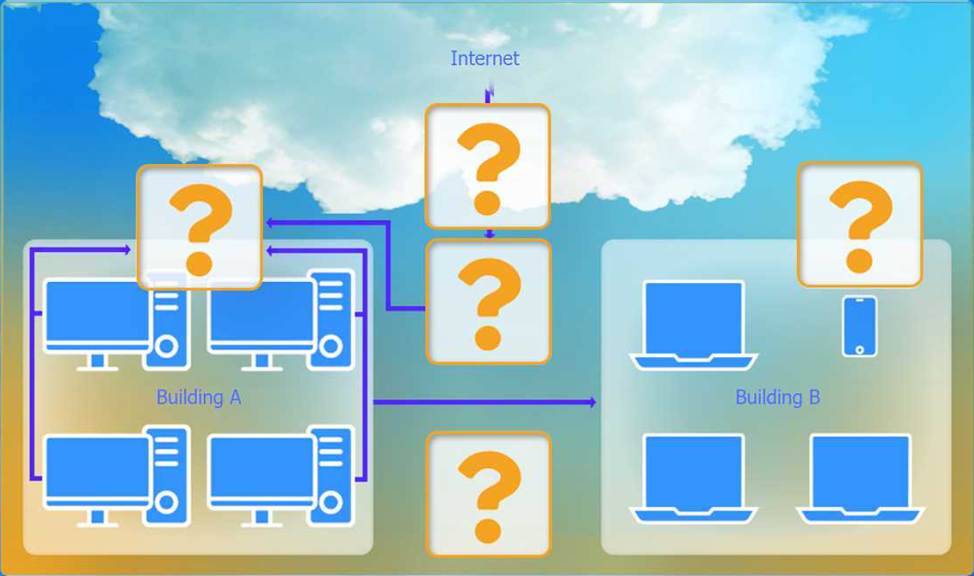
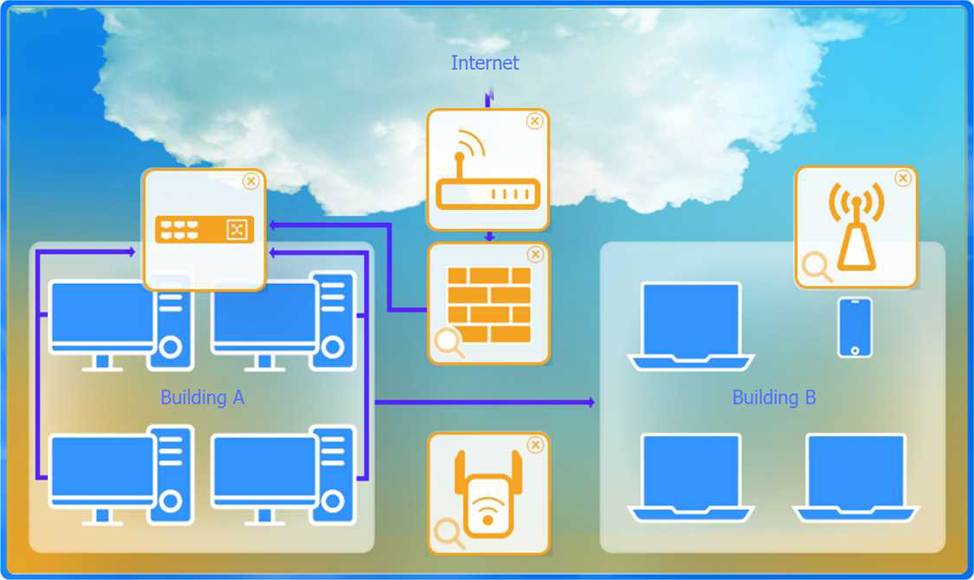
A network administrator has been tasked with configuring a network for a new corporate office. The office consists of two buildings, separated by 50 feet with no physical connectivity.
The configuration must meet the following requirements:
. Devices in both buildings should be able to access the Internet.
. Security insists that all Internet traffic be inspected before entering the network.
. Desktops should not see traffic destined for other devices.
INSTRUCTIONS
Select the appropriate network device for each location. If applicable, click on the magnifying glass next to any device which may require configuration updates and make any necessary changes.
Not all devices will be used, but all locations should be filled.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.

Security insists that all Internet traffic be inspected before entering the network.
Desktops should not see traffic destined for other devices.
Here is the corrected layout with explanation:
Building A:
Switch: Correctly placed to connect all desktops.
Firewall: Correctly placed to inspect all incoming and outgoing traffic.
Building B:
Switch: Not needed. Instead, place a Wireless Access Point (WAP) to provide wireless connectivity for laptops and mobile devices.
Between Buildings:
Wireless Range Extender: Correctly placed to provide connectivity between the buildings wirelessly.
Connection to the Internet:
Router: Correctly placed to connect to the Internet and route traffic between the buildings and the Internet.
Firewall: The firewall should be placed between the router and the internal network to inspect all traffic before it enters the network.
Corrected Setup:
Top-left (Building A): Switch
Bottom-left (Building A): Firewall (inspect traffic before it enters the network)
Top-middle (Internet connection): Router
Bottom-middle (between buildings): Wireless Range Extender
Top-right (Building B): Wireless Access Point (WAP)
In this corrected setup, the WAP in Building B will connect wirelessly to the Wireless Range Extender, which is connected to the Router. The Router is connected to the Firewall to ensure all traffic is inspected before it enters the network.
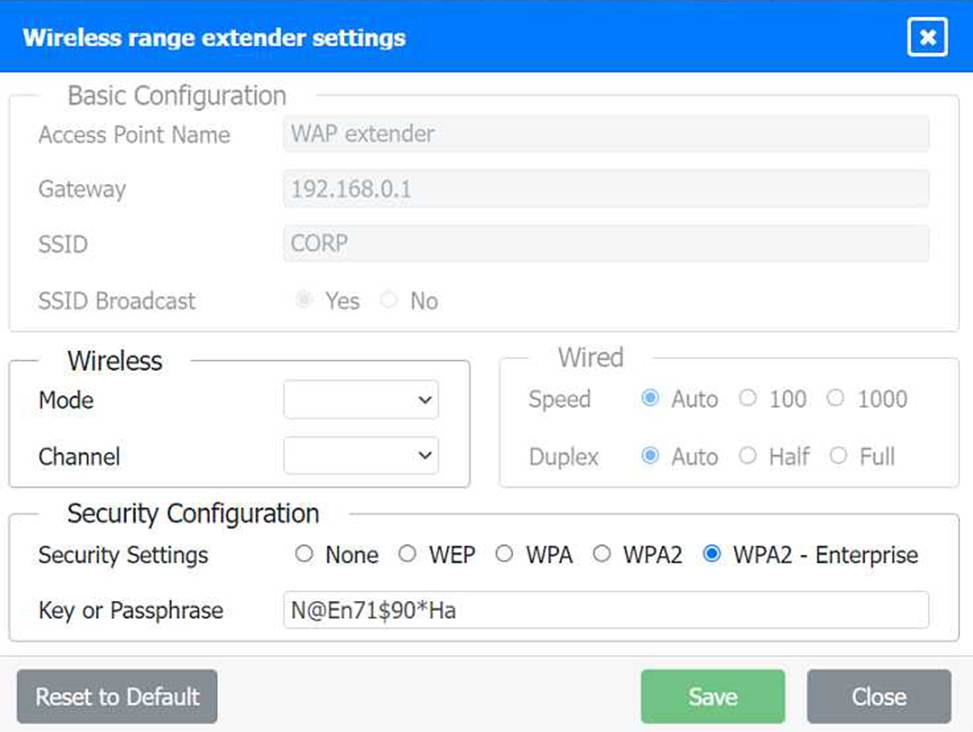
Configuration for Wireless Range Extender:
SSID: CORP
Security Settings: WPA2 or WPA2 – Enterprise
Key or Passphrase: [Enter a strong passphrase]
Mode: [Set based on your network plan]
Channel: [Set based on your network plan]
Speed: Auto
Duplex: Auto
With these settings, both buildings will have secure access to the Internet, and all traffic will be inspected by the firewall before entering the network. Desktops and other devices will not see traffic intended for others, maintaining the required security and privacy.
To configure the wireless range extender for security, follow these steps:
SSID (Service Set Identifier):
Ensure the SSID is set to "CORP" as shown in the exhibit.
Security Settings:
WPA2 or WPA2 – Enterprise: Choose one of these options for stronger security. WPA2-Enterprise provides more robust security with centralized authentication, which is ideal for a corporate environment.
Key or Passphrase:
If you select WPA2, enter a strong passphrase in the "Key or Passphrase" field.
If you select WPA2 – Enterprise, you will need to configure additional settings for authentication servers, such as RADIUS, which is not shown in the exhibit.
Wireless Mode and Channel:
Set the appropriate mode and channel based on your network design and the environment to avoid
interference. These settings are not specified in the exhibit, so set them according to your network plan.
Wired Speed and Duplex:
Set the speed to "Auto" unless you have specific requirements for 100 or 1000 Mbps.
Set the duplex to "Auto" unless you need to specify half or full duplex based on your network equipment.
Save Configuration:
After making the necessary changes, click the "Save" button to apply the settings.
Here is how the configuration should look after adjustments:
SSID: CORP
Security Settings: WPA2 or WPA2 – Enterprise
Key or Passphrase: [Enter a strong passphrase]
Mode: [Set based on your network plan]
Channel: [Set based on your network plan]
Speed: Auto
Duplex: Auto
Once these settings are configured, your wireless range extender will provide secure connectivity for devices in both buildings.
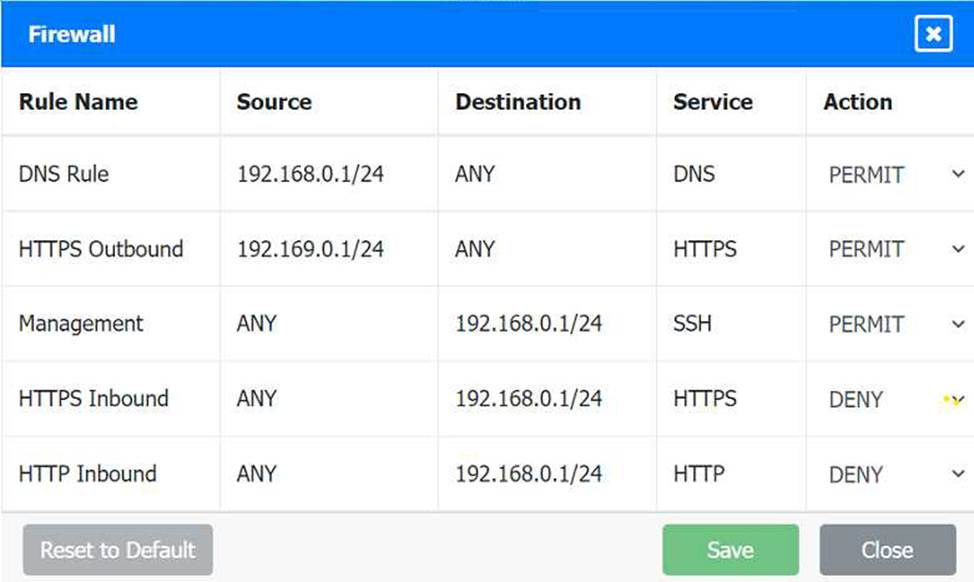
Firewall setting to to ensure complete compliance with the requirements and best security practices, consider the following adjustments and additions:
DNS Rule: This rule allows DNS traffic from the internal network to any destination, which is fine.
HTTPS Outbound: This rule allows HTTPS traffic from the internal network (assuming 192.169.0.1/24 is a typo and should be 192.168.0.1/24) to any destination, which is also good for secure web browsing.
Management: This rule allows SSH access to the firewall for management purposes, which is necessary for administrative tasks.
HTTPS Inbound: This rule denies inbound HTTPS traffic to the internal network, which is good unless you have a web server that needs to be accessible from the internet.
HTTP Inbound: This rule denies inbound HTTP traffic to the internal network, which is correct for security purposes.
Suggested Additional Settings:
Permit General Outbound Traffic: Allow general outbound traffic for web access, email, etc.
Block All Other Traffic: Ensure that all other traffic is blocked to prevent unauthorized access.
Firewall Configuration Adjustments:
Correct the Network Typo:
Ensure that the subnet 192.169.0.1/24 is corrected to 192.168.0.1/24.
Permit General Outbound Traffic:
Rule Name: General Outbound
Source: 192.168.0.1/24
Destination: ANY
Service: ANY
Action: PERMIT
Deny All Other Traffic:
Rule Name: Block All
Source: ANY
Destination: ANY
Service: ANY
Action: DENY
Here is how your updated firewall settings should look:
Rule Name Source Destination Service Action
DNS Rule 192.168.0.1/24 ANY DNS PERMIT
HTTPS Outbound 192.168.0.1/24 ANY HTTPS PERMIT
Management ANY 192.168.0.1/24 SSH PERMIT
HTTPS Inbound ANY 192.168.0.1/24 HTTPS DENY
HTTP Inbound ANY 192.168.0.1/24 HTTP DENY
General Outbound 192.168.0.1/24 ANY ANY PERMIT
Block All ANY ANY ANY DENY
These settings ensure that:
Internal devices can access DNS and HTTPS services externally.
Management access via SSH is permitted.
Inbound HTTP and HTTPS traffic is denied unless otherwise specified.
General outbound traffic is allowed.
All other traffic is blocked by default, ensuring a secure environment.
Make sure to save the settings after making these adjustments.
Which of the following explains what happens if a packet is lost in transit when using UDP?
- A . The data link layer will recognize the error and resend the packet.
- B . IP uses the TTL field to track packet hops and will resend the packet if necessary.
- C . If the sender does not receive a UDP acknowledgement, the packet will be resent.
- D . Some applications will recognize the loss and initiate a resend of the packet if necessary.
D
Explanation:
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless protocol that does not provide built-in mechanisms for error detection, retransmission, or acknowledgments. If a UDP packet is lost in transit, the protocol itself does not handle retransmission. However, some applications using UDP (e.g., TFTP or custom streaming protocols) may implement their own mechanisms to detect packet loss and request retransmission if needed.
Why not A? The data link layer (Layer 2) handles frame-level errors within a single network segment, not end-to-end packet loss across networks.
Why not B? The IP TTL (Time to Live) field prevents routing loops by decrementing with each hop, but IP does not handle retransmission.
Why not C? UDP does not use acknowledgments, so the sender does not expect or receive them.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ N10-009 Objective 1.4: Explain the characteristics of network topologies and protocols. The CompTIA Network+ Study Guide (e.g., Chapter 4: Network Protocols) explains that UDP is a “fire-and-forget” protocol, and any retransmission logic must be handled by the application layer.
Which of the following technologies are X.509 certificates most commonly associated with?
- A . PKI
- B . VLAN tagging
- C . LDAP
- D . MFA
A
Explanation:
X.509 certificates are most commonly associated with Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). These certificates are used for a variety of security functions, including digital signatures, encryption, and authentication.
PKI: X.509 certificates are a fundamental component of PKI, used to manage encryption keys and authenticate users and devices.
Digital Certificates: They are used to establish secure communications over networks, such as SSL/TLS for websites and secure email communication.
Authentication and Encryption: X.509 certificates provide the means to securely exchange keys and verify identities in various applications, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality. Network
Reference: CompTIA Network+ N10-007 Official Certification Guide: Covers PKI and the role of X.509 certificates in network security.
Cisco Networking Academy: Provides training on PKI, certificates, and secure communications. Network+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide: Explains PKI, X.509 certificates, and their applications in securing network communications.
SIMULATION
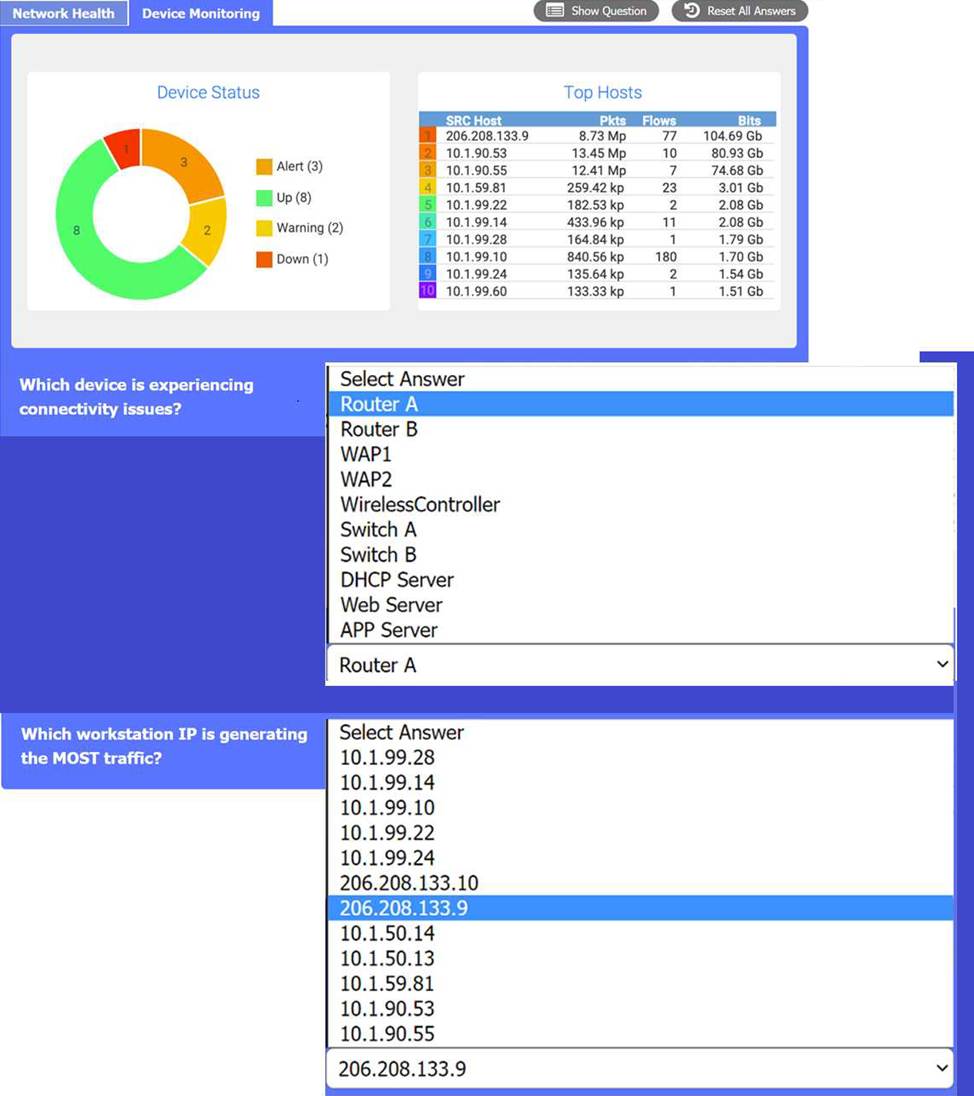
After a recent power outage, users are reporting performance issues accessing the application servers. Wireless users are also reporting intermittent Internet issues.
INSTRUCTIONS
Click on each tab at the top of the screen. Select a widget to view information, then use the drop-down menus to answer the associated questions. If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.
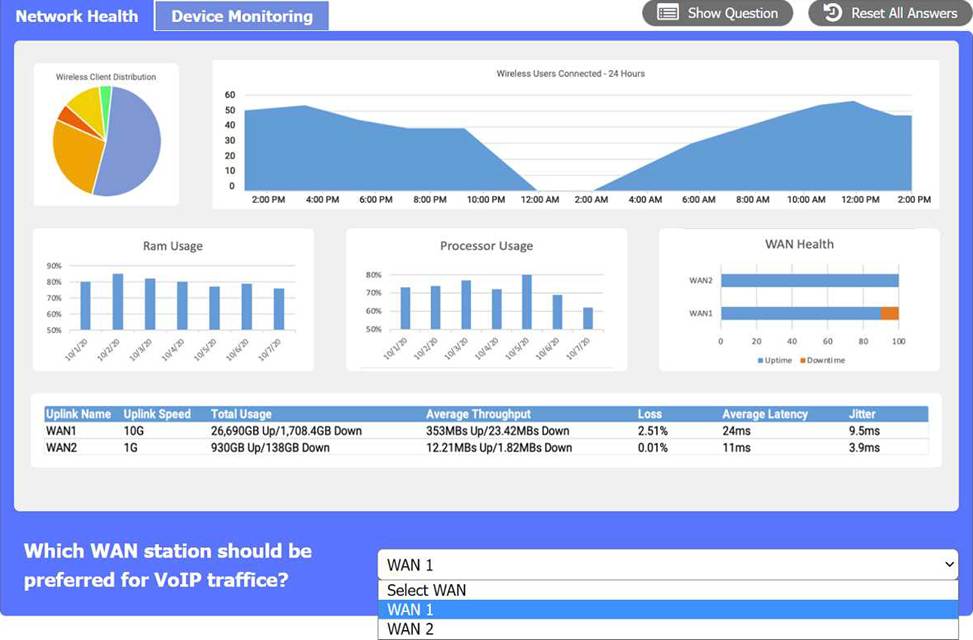
WAN 2 appears to have a lower average latency and loss percentage, which would make it the preferred WAN station for VoIP traffic. VoIP traffic requires low latency and packet loss to ensure good voice quality and reliability. WAN 1 seems to have higher RAM and processor usage, which could also affect the performance of VoIP traffic.
Here’s the summary of the key metrics for WAN 1 and WAN 2 from the image provided:
WAN 1:
Uplink Speed: 10G
Total Usage: 26.969GB Up / 1.748GB Down
Average Throughput: 353MBps Up / 23.42MBps Down
Loss: 2.51%
Average Latency: 24ms
Jitter: 9.5ms
WAN 2:
Uplink Speed: 1G
Total Usage: 930GB Up / 138GB Down
Average Throughput: 12.21MBps Up / 1.82MBps Down
Loss: 0.01%
Average Latency: 11ms
Jitter: 3.9ms
For VoIP traffic, low latency and jitter are particularly important to ensure voice quality. While WAN 1 has higher bandwidth and throughput, it also has higher latency and jitter compared to WAN 2. However, WAN 2 has much lower loss, lower latency, and lower jitter, which are more favorable for VoIP traffic that is sensitive to delays and variation in packet arrival times.
Given this information, WAN 2 would generally be preferred for VoIP traffic due to its lower latency, lower jitter, and significantly lower loss percentage, despite its lower bandwidth compared to WAN
A technician needs to identify a computer on the network that is reportedly downloading unauthorized content.
Which of the following should the technician use?
- A . Anomaly alerts
- B . Port mirroring
- C . Performance monitoring
- D . Packet capture
D
Explanation:
Packet Capture: This method captures and inspects network traffic to identify unauthorized downloads or malicious behavior. It provides detailed insight into the data being transmitted, making it the best tool for this scenario.
Anomaly alerts (A): Alerts may indicate unusual activity but do not provide detailed traffic analysis. Port mirroring (B): Port mirroring can redirect traffic for analysis but requires a packet capture tool for deeper inspection.
Performance monitoring (C): Focuses on system performance metrics, not detailed traffic content.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ Official Study Guide, Domain 4.3 (Network Monitoring Tools).
Which of the following would be violated if an employee accidentally deleted a customer’s data?
- A . Integrity
- B . Confidentiality
- C . Vulnerability
- D . Availability
D
Explanation:
Availability refers to ensuring that data is accessible when needed. If a customer’s data is accidentally deleted, it impacts availability, as the data can no longer be accessed.
A network engineer needs to change, update, and control APs remotely, with real-time visibility over HTTPS.
Which of the following will best allow these actions?
- A . Web interface
- B . Command line
- C . SNMP console
- D . API gateway
D
Explanation:
API gateways offer programmable control and real-time communication, commonly over HTTPS, which allows administrators to update and manage devices like access points remotely and efficiently.
From Andrew Ramdayal’s guide:
“APIs enable automation and real-time interaction with network devices via secure interfaces, often using HTTPS for encrypted communication and control.”
A Chief Information Officer wants a DR solution that runs only after a failure of the primary site and can be brought online quickly once recent backups are imported.
Which of the following DR site solutions meets these requirements?
- A . Cold
- B . Warm
- C . Active
- D . Hot
B
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation (aligned to N10-009):
A warm site is partially configured with necessary infrastructure and systems, but it requires recent backups to be restored before becoming fully operational. This provides a balance between cost and recovery time.
