Practice Free N10-009 Exam Online Questions
Which of the following VPN types provides secure remote access to the network resources through a web portal?
- A . Proxy
- B . Clientless
- C . Site-to-site
- D . Direct connect
B
Explanation:
Clientless VPNs allow users to access network resources through a secure web portal using a browser, with no VPN software needed. This is ideal for occasional access to internal resources via HTTPS.
Which of the following is a cost-effective advantage of a split-tunnel VPN?
- A . Web traffic is filtered through a web filter.
- B . More bandwidth is required on the company’s internet connection.
- C . Monitoring detects insecure machines on the company’s network.
- D . Cloud-based traffic flows outside of the company’s network.
D
Explanation:
A split-tunnel VPN allows certain traffic (e.g., cloud-based services) to bypass the VPN and go directly to the Internet. This reduces the amount of traffic that needs to traverse the company’s VPN and Internet connection, conserving bandwidth and reducing costs. It also means that not all traffic is subject to the same level of inspection or filtering, which can improve performance for cloud-based services.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ study materials.
SIMULATION
A network technician replaced an access layer switch and needs to reconfigure it to allow the connected devices to connect to the correct networks.
INSTRUCTIONS
Click on the appropriate port(s) on Switch 1 and Switch 3 to verify or reconfigure the correct settings:
・ Ensure each device accesses only its correctly associated network.
・ Disable all unused switchports.
. Require fault-tolerant connections between the switches.
. Only make necessary changes to complete the above requirements.
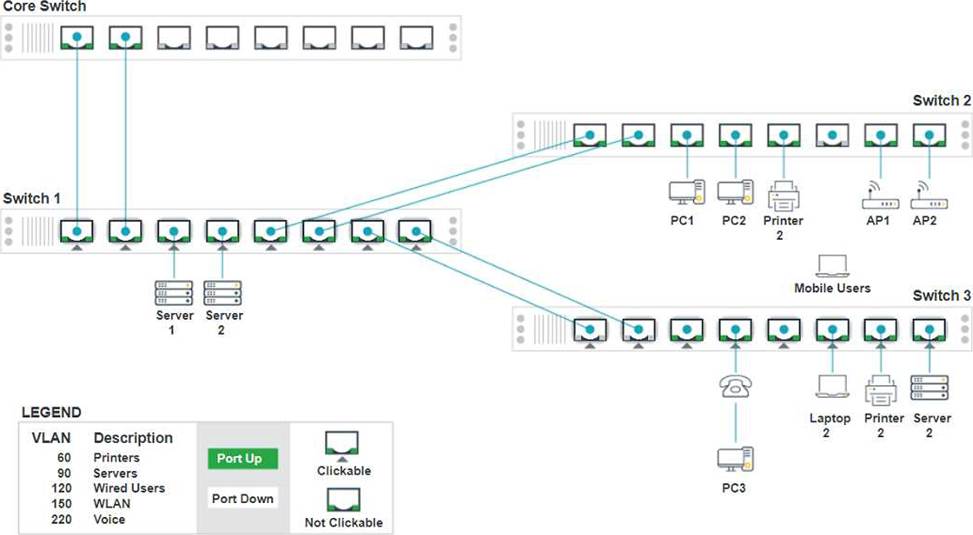
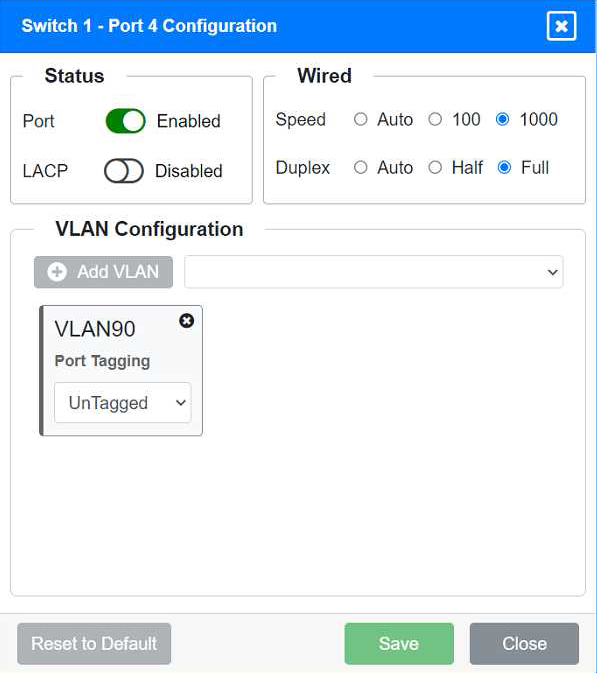
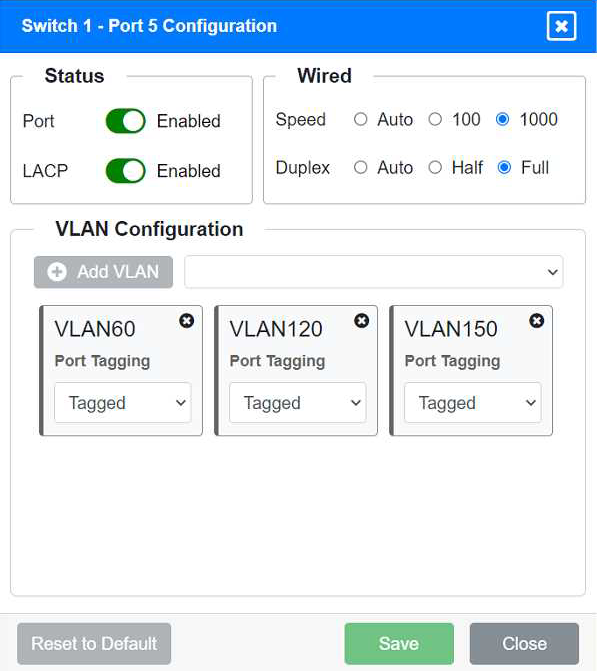
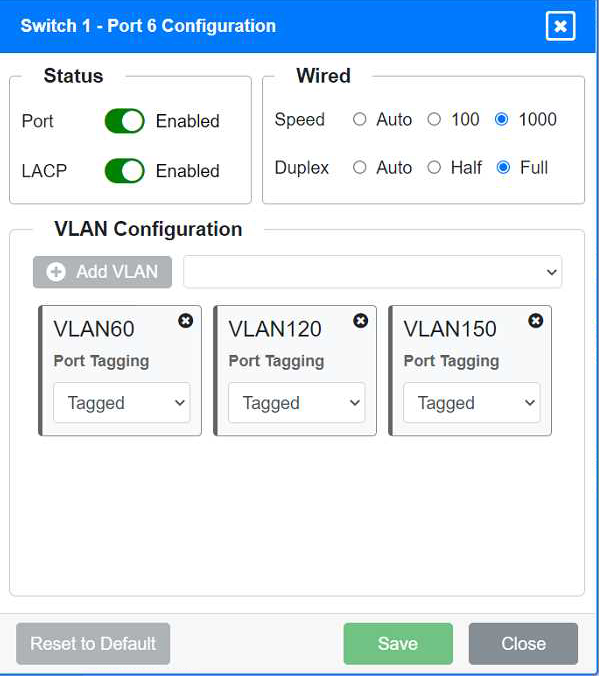
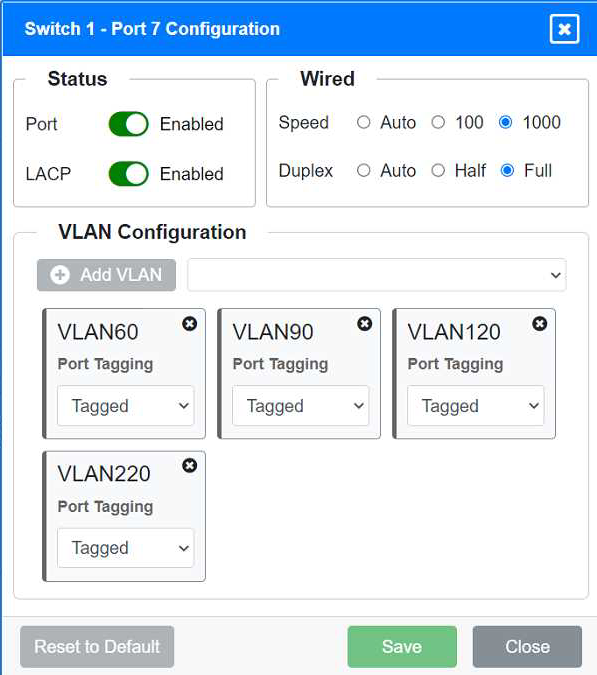
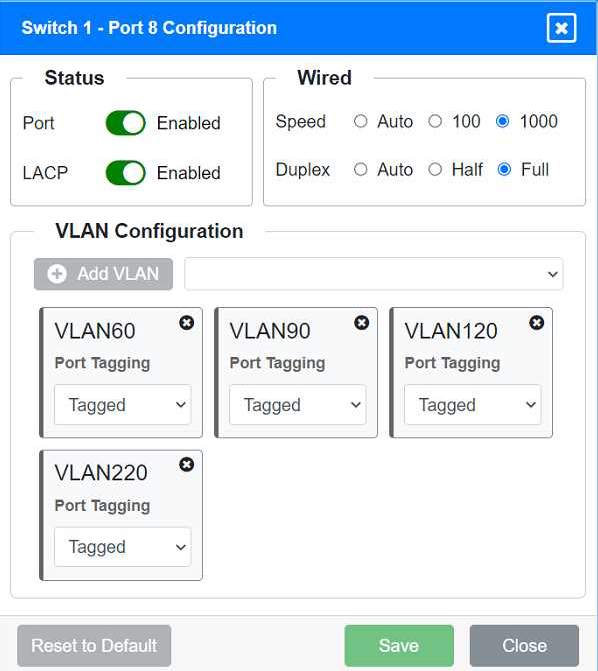
Identify the correct VLANs for each device and port.
Enable necessary ports and disable unused ports.
Configure fault-tolerant connections between the switches.
Configuration Details
Switch 1
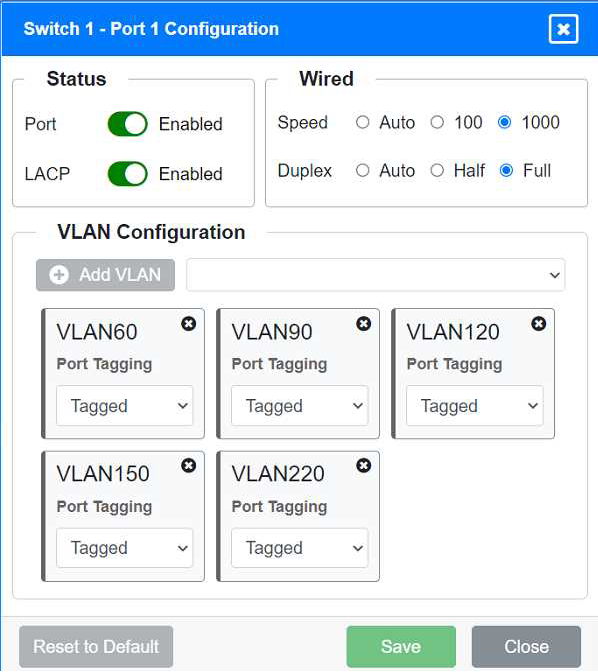
Port 1 Configuration (Uplink to Core Switch)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
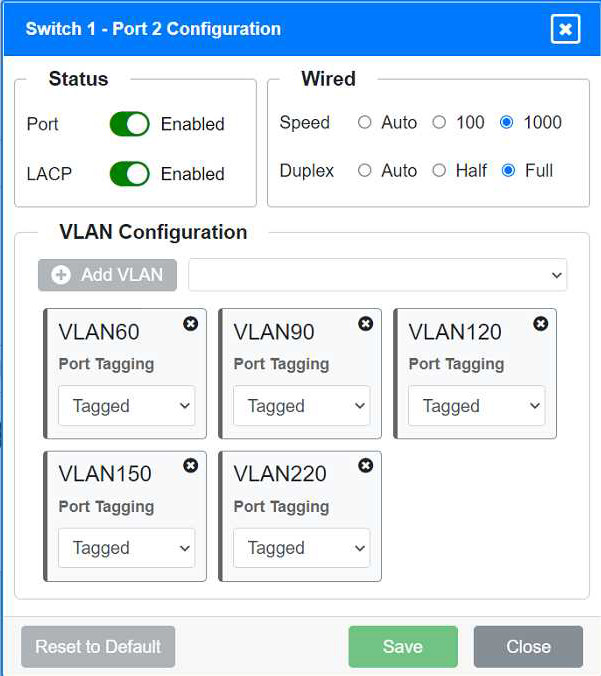
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN90, VLAN120, VLAN150, VLAN220 Port 2 Configuration (Uplink to Core Switch) Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
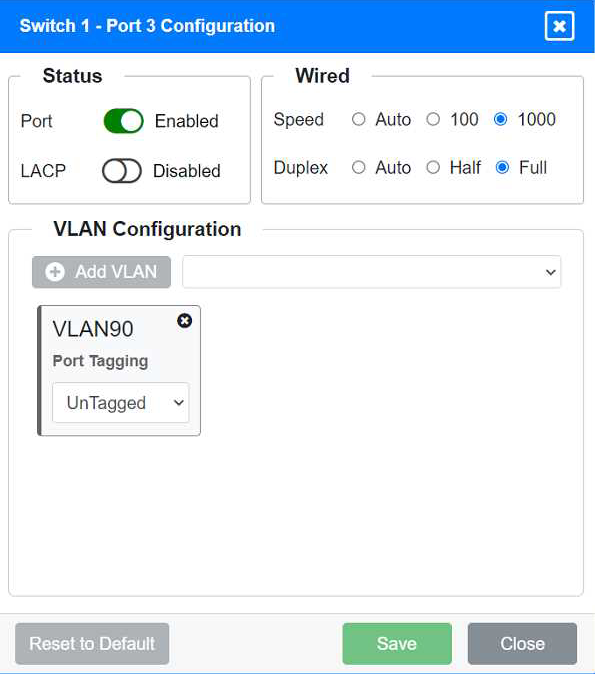
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN90, VLAN120, VLAN150, VLAN220 Port 3 Configuration (Server Connection) Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN90 (Servers)
Port 4 Configuration (Server Connection)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN90 (Servers)
Port 5 Configuration (Wired Users and WLAN)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN120, VLAN150 Port 6 Configuration (Wired Users and WLAN) Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN120, VLAN150 Port 7 Configuration (Voice and Wired Users) Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN90, VLAN120, VLAN220 Port 8 Configuration (Voice, Printers, and Wired Users) Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN90, VLAN120, VLAN220 Switch 3
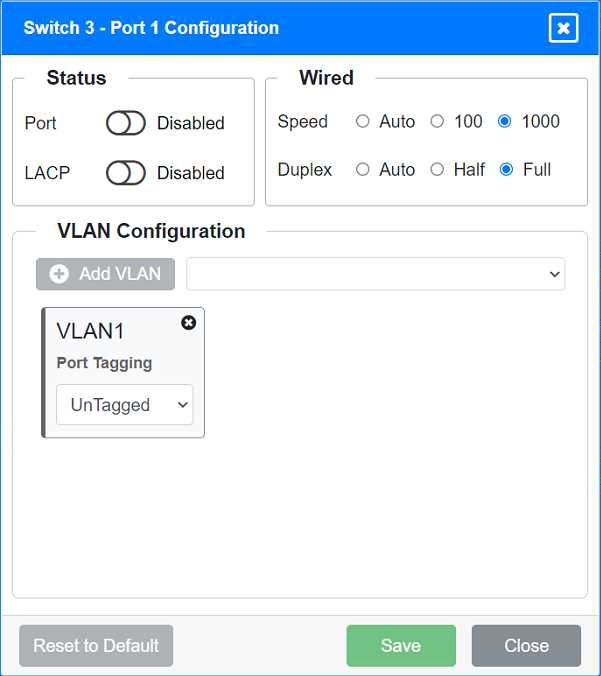
Port 1 Configuration (Unused)
Status: Disabled
LACP: Disabled
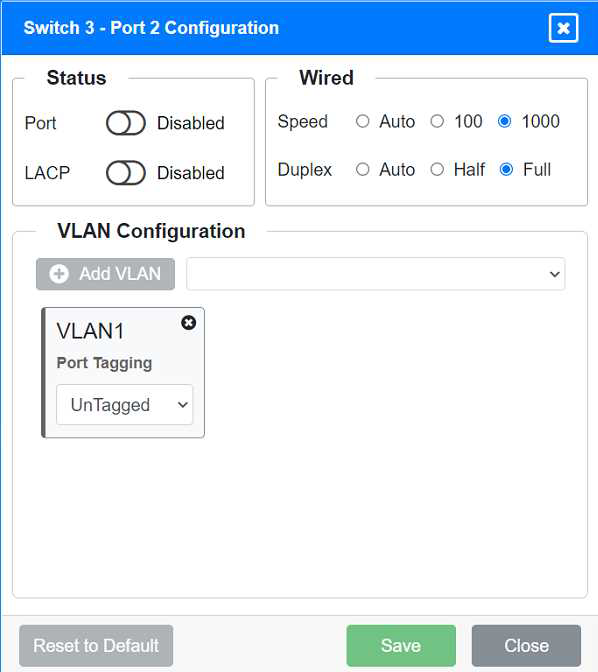
Port 2 Configuration (Unused)
Status: Disabled
LACP: Disabled
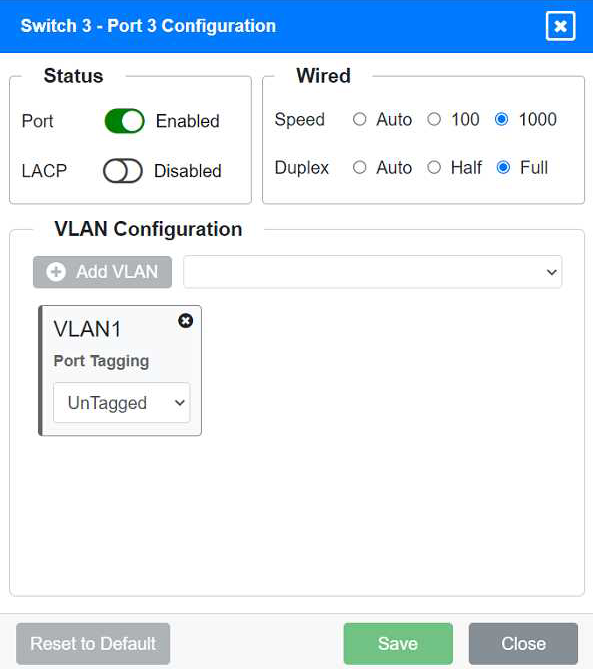
Port 3 Configuration (Connection to Device)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN1 (Default)
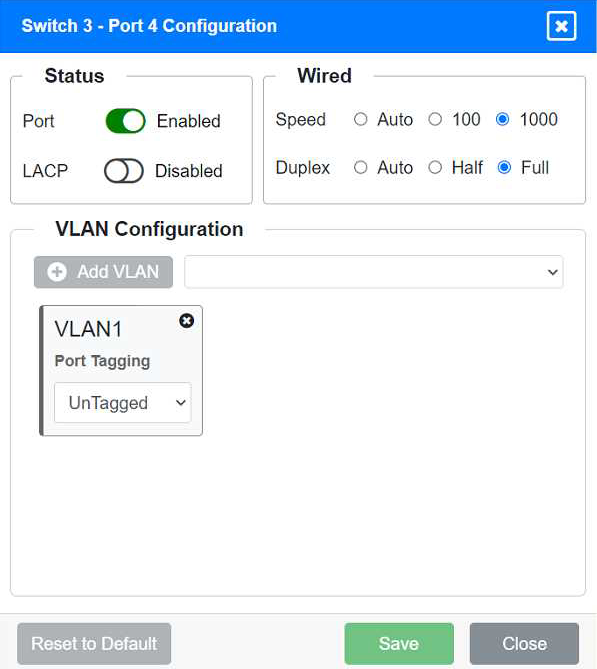
Port 4 Configuration (Connection to Device)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN1 (Default)
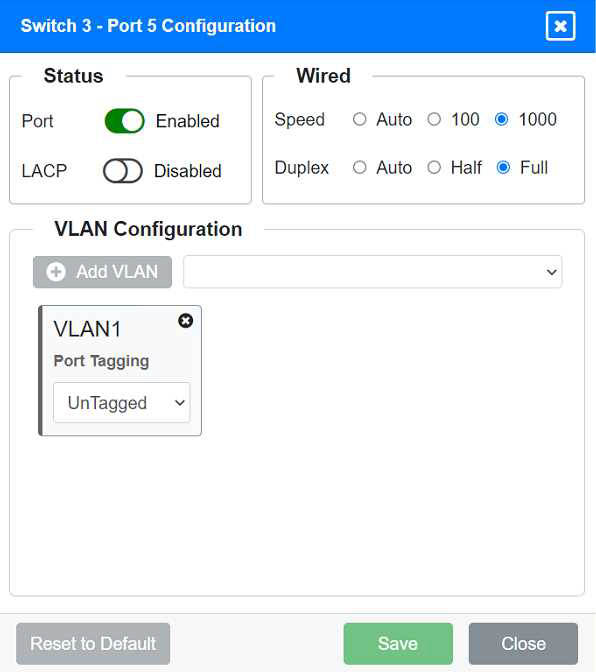
Port 5 Configuration (Connection to Device)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN1 (Default)
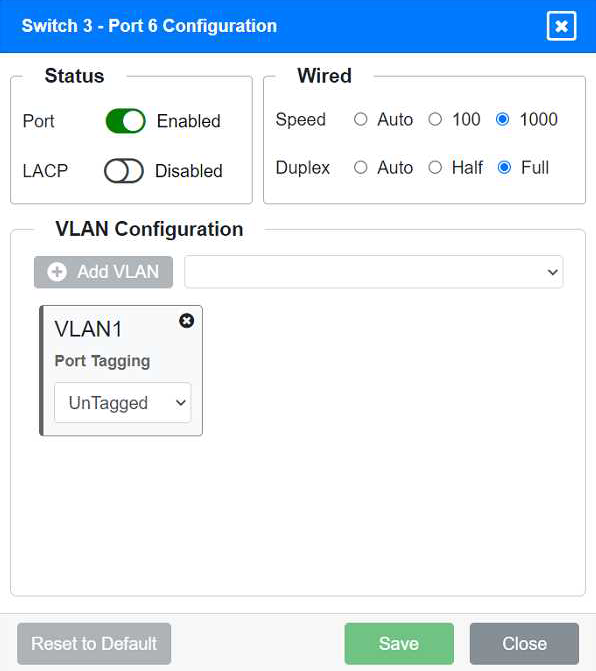
Port 6 Configuration (Connection to Device)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN1 (Default)
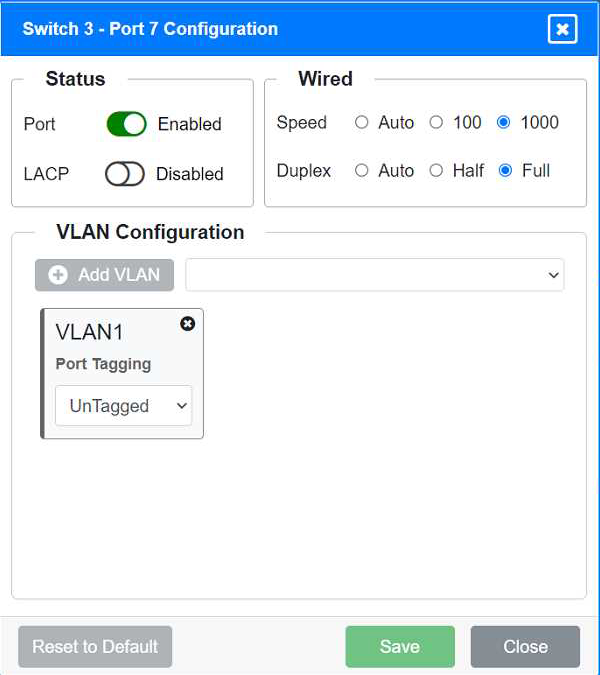
Port 7 Configuration (Connection to Device)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN1 (Default)
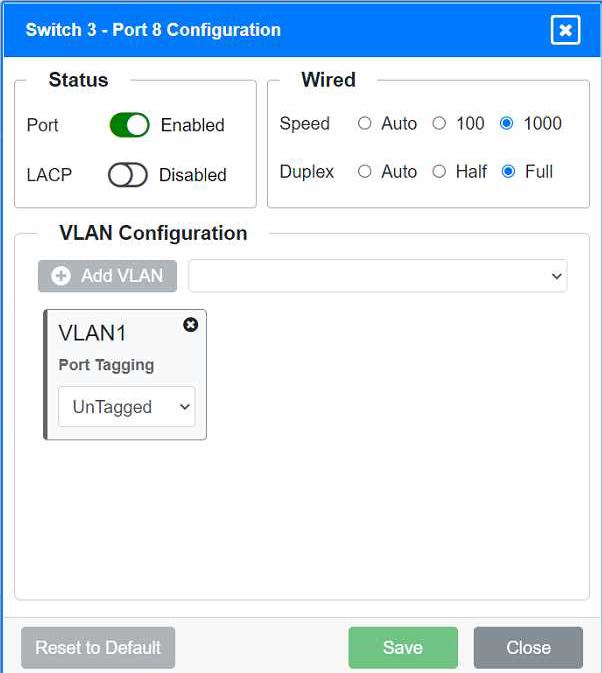
Summary of Configurations
Ports 1 and 2 on Switch 1 are configured as trunk ports with VLAN tagging enabled for all necessary VLANs.
Ports 3 and 4 on Switch 1 are configured for server connections with VLAN 90 untagged.
Ports 5, 6, 7, and 8 on Switch 1 are configured for devices needing access to multiple VLANs.
Unused ports on Switch 3 are disabled.
Ports 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 on Switch 3 are enabled for default VLAN1. Ensure All Switches and Ports are Configured as per the Requirements: Core Switch Ports should be configured as needed for uplinks to Switch 1. Ensure LACP is enabled for redundancy on trunk ports between switches.
By following these configurations, each device will access only its correctly associated network, unused switch ports will be disabled, and fault-tolerant connections will be established between the switches.
Which of the following connection methods allows a network engineer to automate the configuration deployment for network devices across the environment?
- A . RDP
- B . Telnet
- C . GUI
- D . API
D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation (aligned to N10-009):
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) allow automation tools and scripts to push configurations to network devices programmatically. Modern network automation platforms rely on APIs to ensure consistency and scalability.
Which of the following is an example of a split-tunnel VPN?
- A . Only public resources are accessed through the user’s internet connection.
- B . Encrypted resources are accessed through separate tunnels.
- C . All corporate and public resources are accessed through routing to on-site servers.
- D . ACLs are used to balance network traffic through different connections.
A
Explanation:
In a split-tunnel VPN, only corporate traffic is sent through the VPN tunnel, while public internet traffic goes directly through the user’s local ISP. This reduces bandwidth use on the corporate VPN concentrator and improves performance for non-work traffic.
B. Separate tunnels for encrypted traffic describes multi-tunnel VPNs, not split tunneling.
C. All traffic routed through on-site servers is a full-tunnel VPN, not split-tunnel.
D. ACLs balancing traffic relates to routing or load balancing, not VPN split tunneling.
Reference (CompTIA Network+ N10-009):
Domain: Networking Concepts ― VPN types, split vs. full tunnel, remote access.
A network administrator recently updated configurations on a Layer 3 switch. Following the updates, users report being unable to reach a specific file server.
Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- A . Incorrect ACLs
- B . Switching loop
- C . Duplicate IP addresses
- D . Wrong default route
A
Explanation:
• Since this issue occurred after a configuration change on a Layer 3 switch, the most likely cause is misconfigured ACLs (Access Control Lists).
• ACLs control which traffic is allowed or denied, so an incorrect ACL may be blocking access to the file server.
• Why not the other options?
• Switching loop (B): A switching loop occurs at Layer 2 (not Layer 3) and causes network-wide broadcast storms, not just loss of access to a file server.
• Duplicate IP addresses (C): This would cause connectivity issues for the devices with the conflict, but not necessarily prevent all users from accessing the file server.
• Wrong default route (D): The default route is used for traffic leaving the local network. If users are unable to access an internal file server, this is unlikely to be the issue.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ (N10-009) Official Guide C Chapter 8: Network Access Control and ACLs
An attacker gained access to the hosts file on an endpoint and modified it. Now, a user is redirected from the company’s home page to a fraudulent website.
Which of the following most likely happened?
- A . DNS spoofing
- B . Phishing
- C . VLAN hopping
- D . ARP poisoning
A
Explanation:
When the hosts file is altered, local name resolution is compromised, and domain queries are redirected to malicious IP addresses. This is a form of DNS spoofing/poisoning, where false mappings trick users into visiting fraudulent websites.
B. Phishing typically uses emails or messages to trick users, not local file modification.
C. VLAN hopping is a Layer 2 attack to gain unauthorized network access, unrelated to DNS.
D. ARP poisoning manipulates ARP tables on a LAN to reroute traffic, not name resolution.
Reference (CompTIA Network+ N10-009):
Domain: Network Security ― DNS poisoning/spoofing, host file manipulation, endpoint attacks.
SIMULATION
A network technician needs to resolve some issues with a customer’s SOHO network. The customer reports that some of the PCs are not connecting to the network, while others appear to be working as intended.
INSTRUCTIONS
Troubleshoot all the network components.
Review the cable test results first, then diagnose by clicking on the appropriate PC, server, and Layer 2 switch.
Identify any components with a problem and recommend a solution to correct each problem.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.
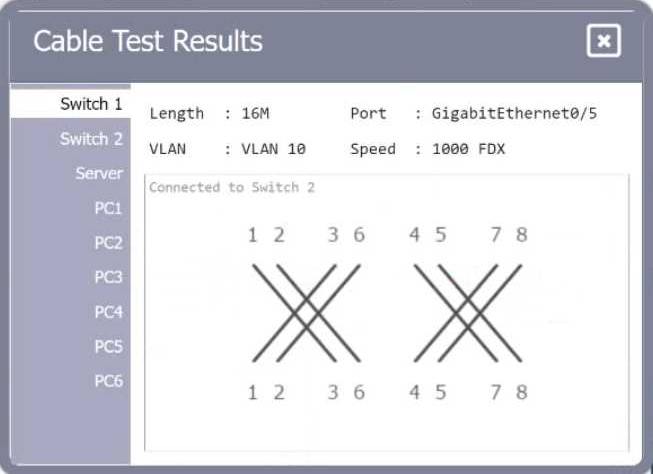
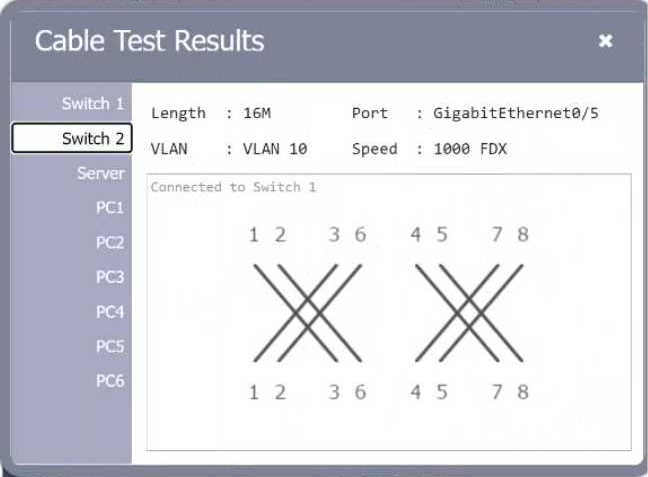
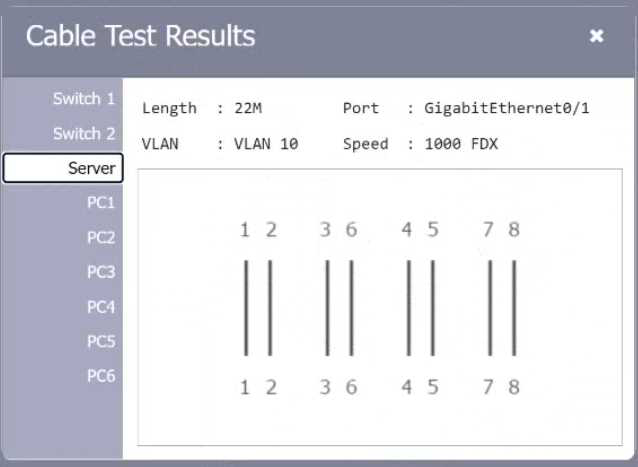
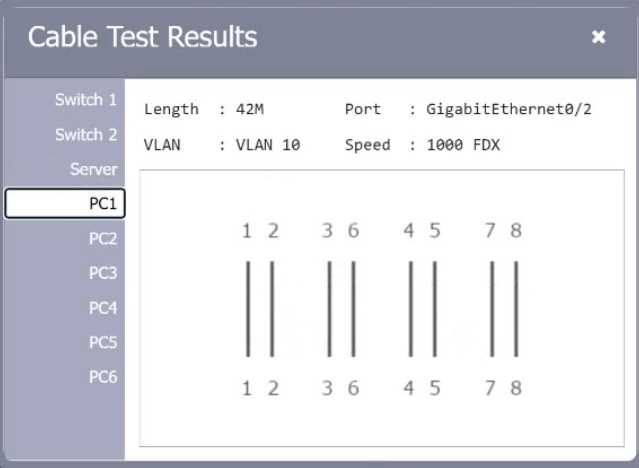
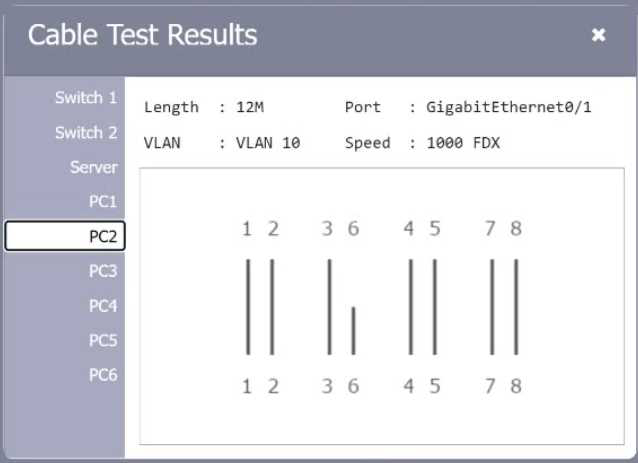
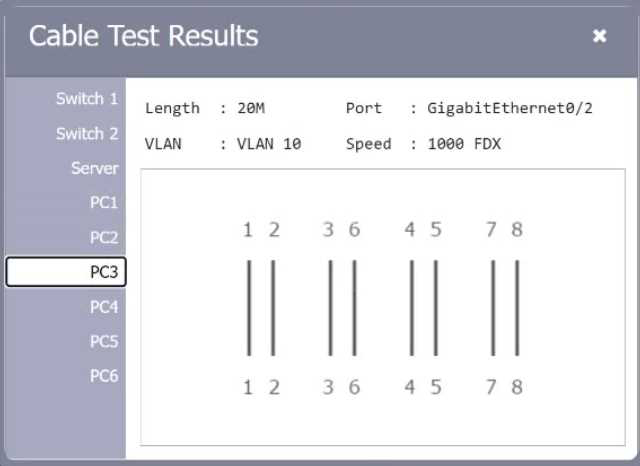
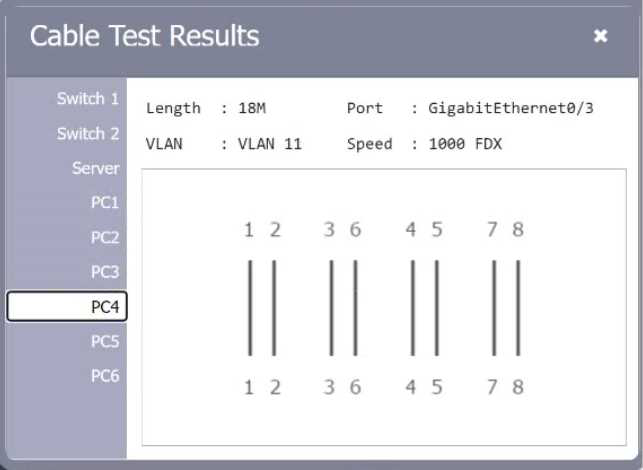
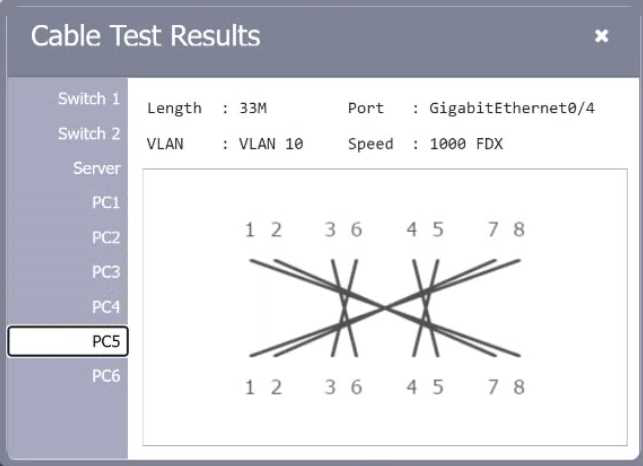
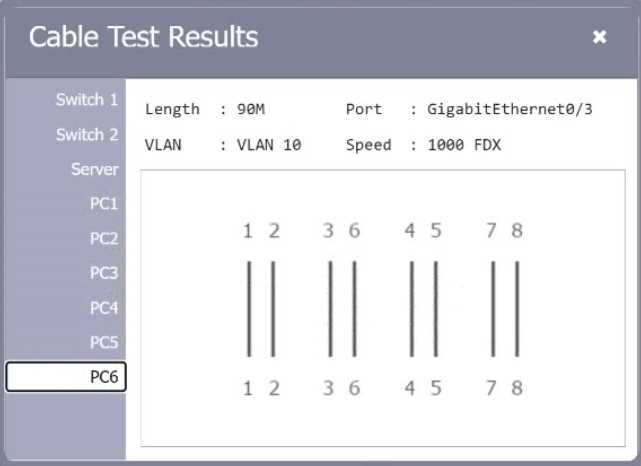
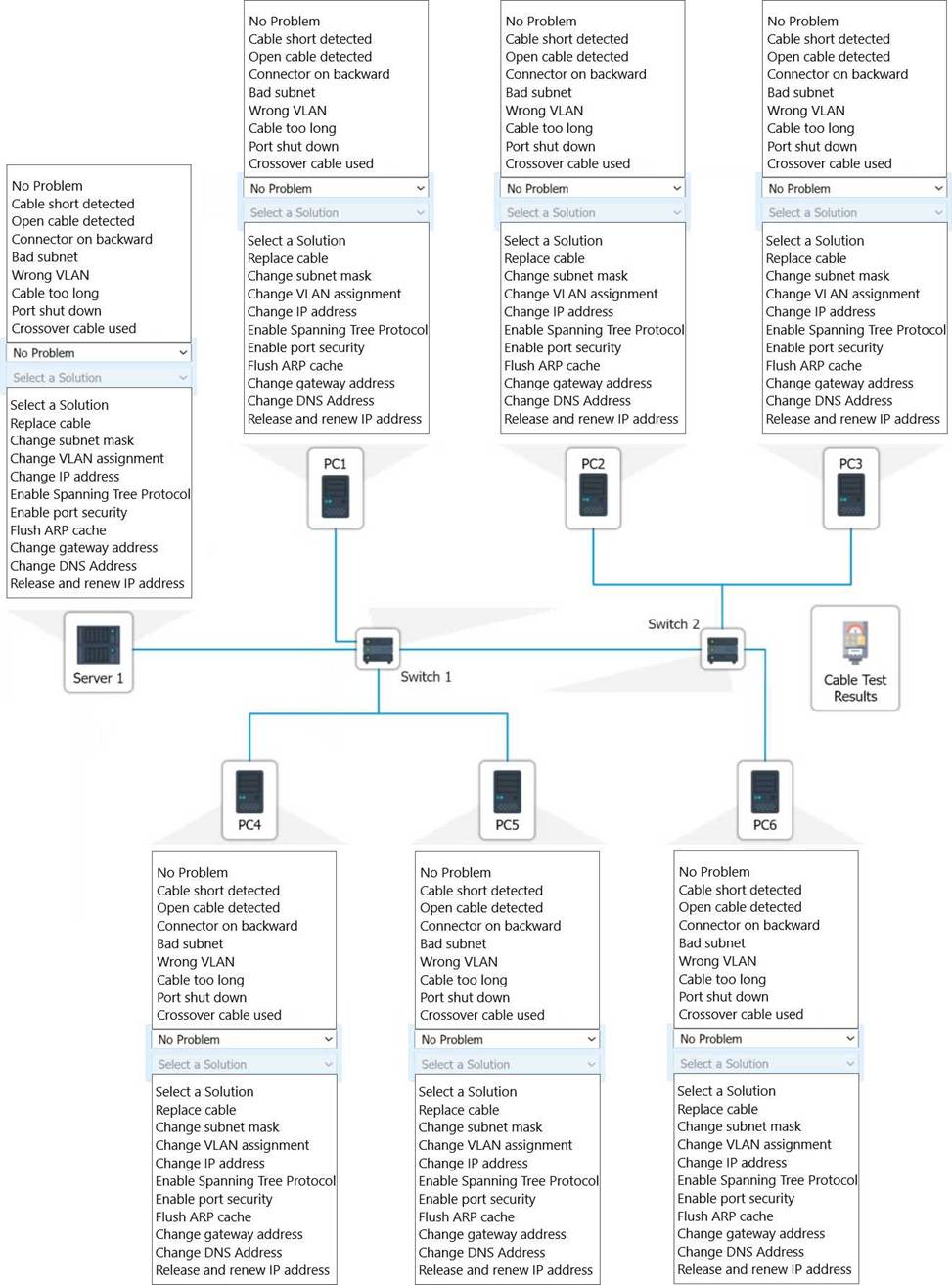
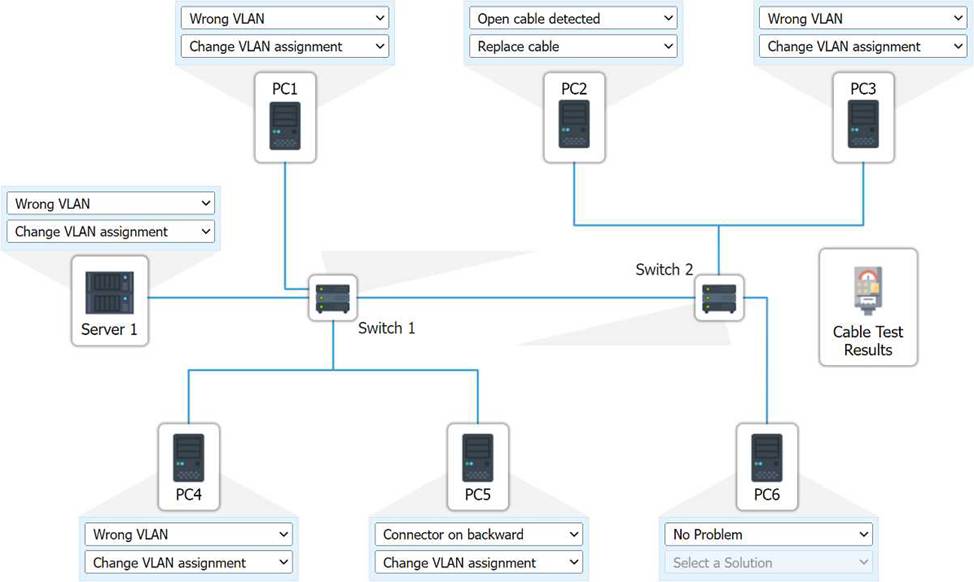
Explanation:
A computer network diagram with many boxes and text AI-generated content may be incorrect.
An organization moved its DNS servers to new IP addresses. After this move, customers are no longer able to access the organization’s website.
Which of the following DNS entries should be updated?
- A . AAAA
- B . CNAME
- C . MX
- D . NS
D
Explanation:
When an organization moves its DNS servers to new IP addresses, the NS (Name Server) records must be updated. The NS record defines which DNS servers are authoritative for a domain. If these records still point to the old IP addresses, clients will continue to query the outdated servers, leading to connectivity issues.
Breakdown of Options:
A network administrator is creating a subnet that will include 45 separate hosts on a small private network within a large network architecture.
Which of the following options is the most efficient use of network addresses when assigning this network?
- A . 10.0.50.128/25
- B . 10.7.142.128/27
- C . 10.152.4.192/26
- D . 10.192.1.64/28
C
Explanation:
For 45 hosts, the minimum subnet size must allow at least 46 usable addresses (1 each for network and broadcast addresses).
A /26 subnet provides 64 addresses, 62 usable ― suitable.
A /27 subnet gives only 30 usable ― insufficient.
A /25 offers 126 usable ― more than needed.
A /28 provides just 14 ― too small.
So, the most efficient subnet with minimal wastage is /26.
From Andrew Ramdayal’s guide:
“When designing subnets, always choose the smallest subnet mask that still accommodates all hosts. A /26 provides 62 usable host addresses, suitable for networks with about 50 hosts.”
