Practice Free N10-009 Exam Online Questions
Which of the following attacks forces a switch to send all traffic out of all ports?
- A . ARP poisoning
- B . Evil twin
- C . MAC flooding
- D . DNS spoofing
C
Explanation:
MAC flooding overwhelms a switch’s CAM (Content Addressable Memory) table by sending a flood of frames with spoofed MAC addresses. Once the CAM table overflows, the switch cannot learn legitimate MAC addresses and defaults to flooding all frames out all ports, effectively turning it into a hub. This allows an attacker to capture traffic not originally destined for their port.
Which of the following is the most secure way to provide site-to-site connectivity?
- A . VXLAN
- B . IKE
- C . GRE
- D . IPsec
D
Explanation:
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) is the most secure way to provide site-to-site connectivity. It provides robust security services, such as data integrity, authentication, and encryption, ensuring that data sent across the network is protected from interception and tampering. Unlike other options, IPsec operates at the network layer and can secure all traffic that crosses the IP network, making it the most comprehensive and secure choice for site-to-site VPNs.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ study materials and NIST Special Publication 800-77.
SIMULATION
A network technician needs to resolve some issues with a customer’s SOHO network.
The customer reports that some of the devices are not connecting to the network, while others appear to work as intended.
INSTRUCTIONS
Troubleshoot all the network components and review the cable test results by Clicking on each device and cable.
Diagnose the appropriate component(s) by identifying any components with a problem and recommend a solution to correct each problem.
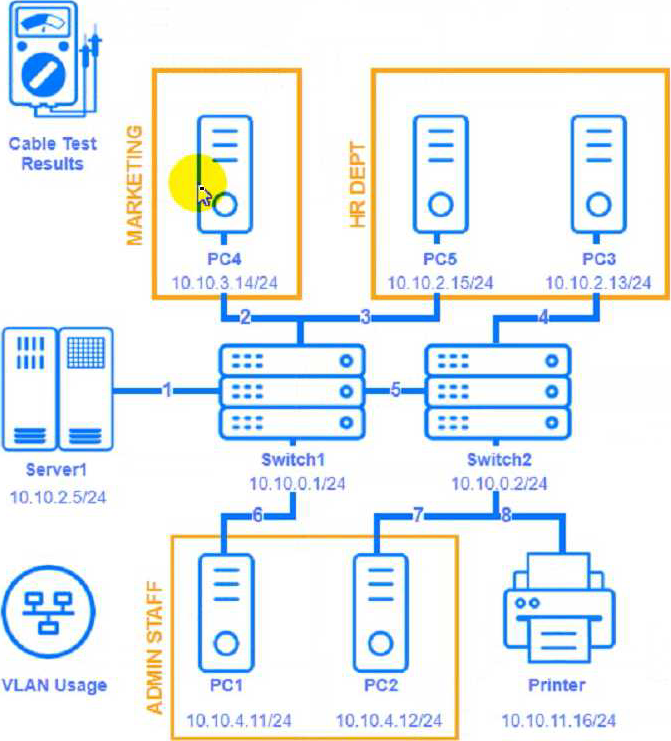



Cable Test Results:
Cable 1:
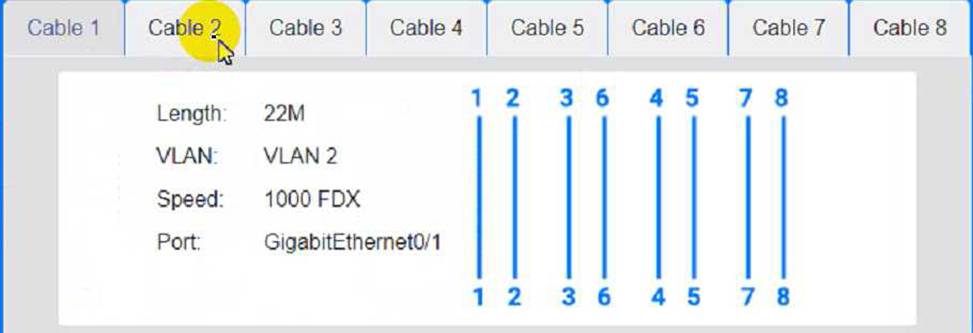
Cable 2:
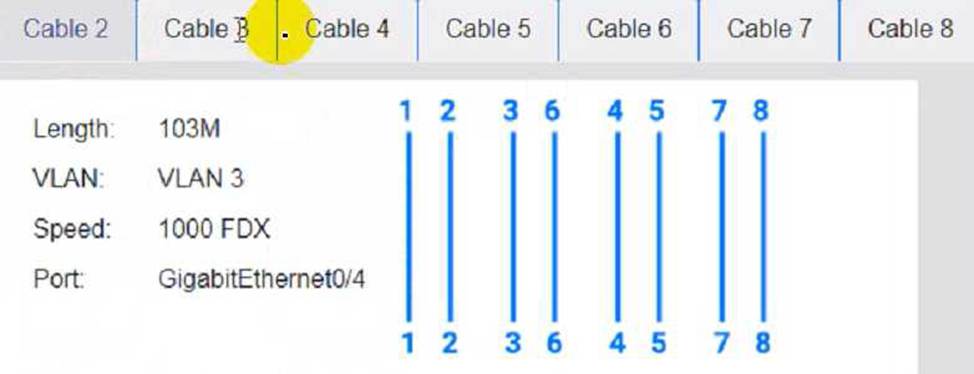
Cable 3:
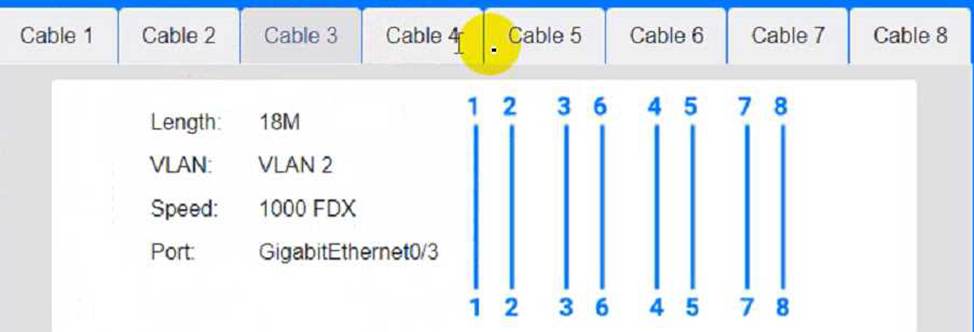
Cable 4:
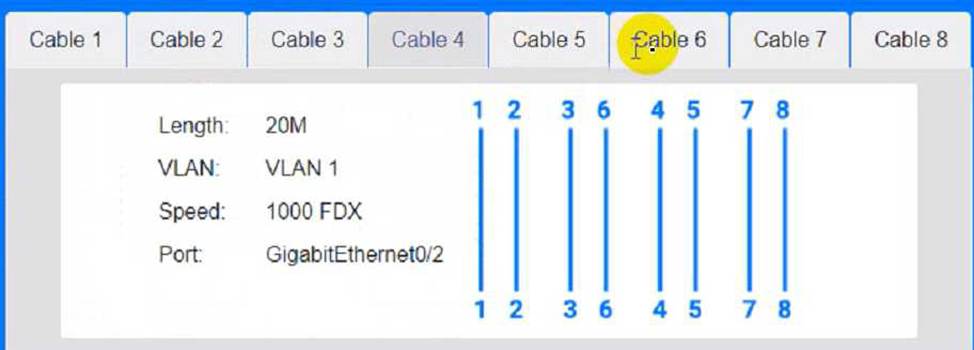
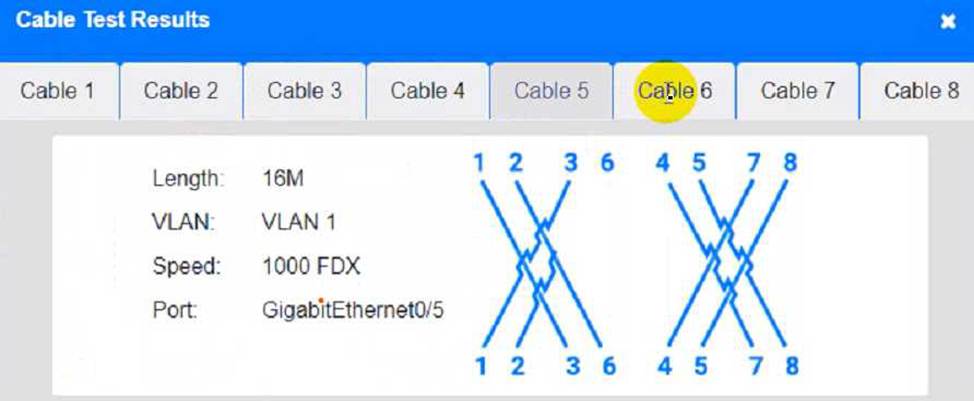
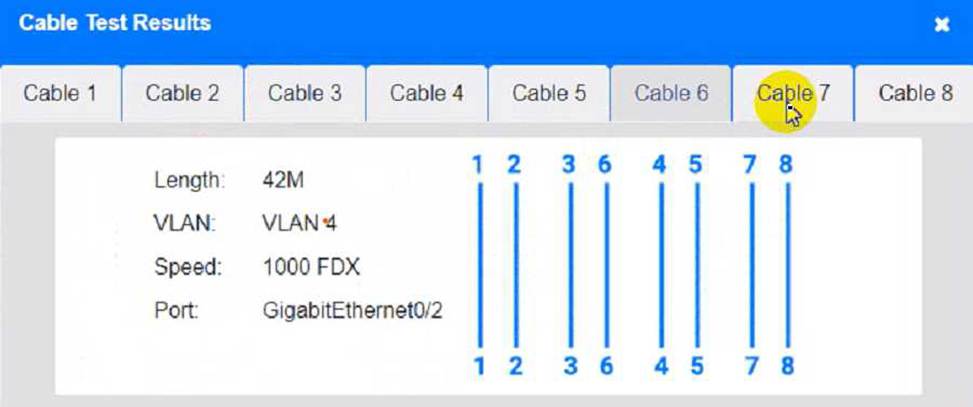
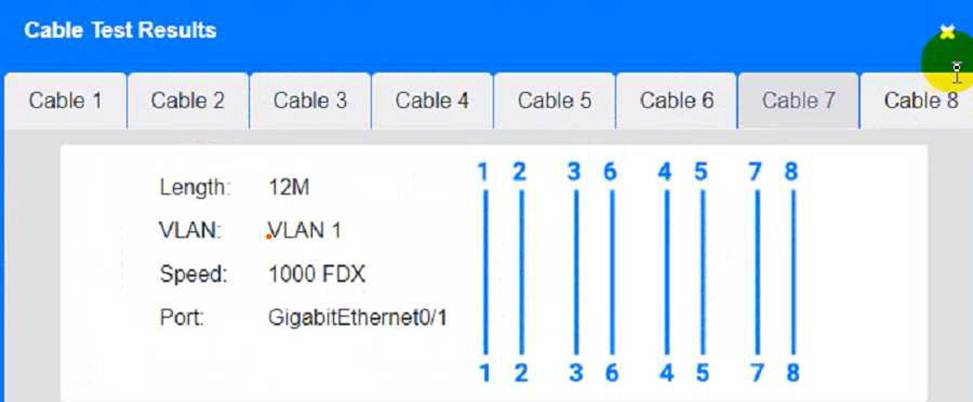
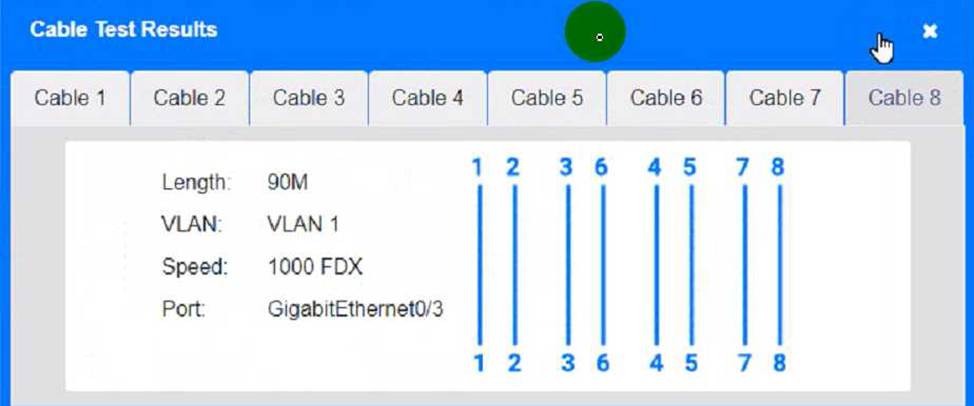
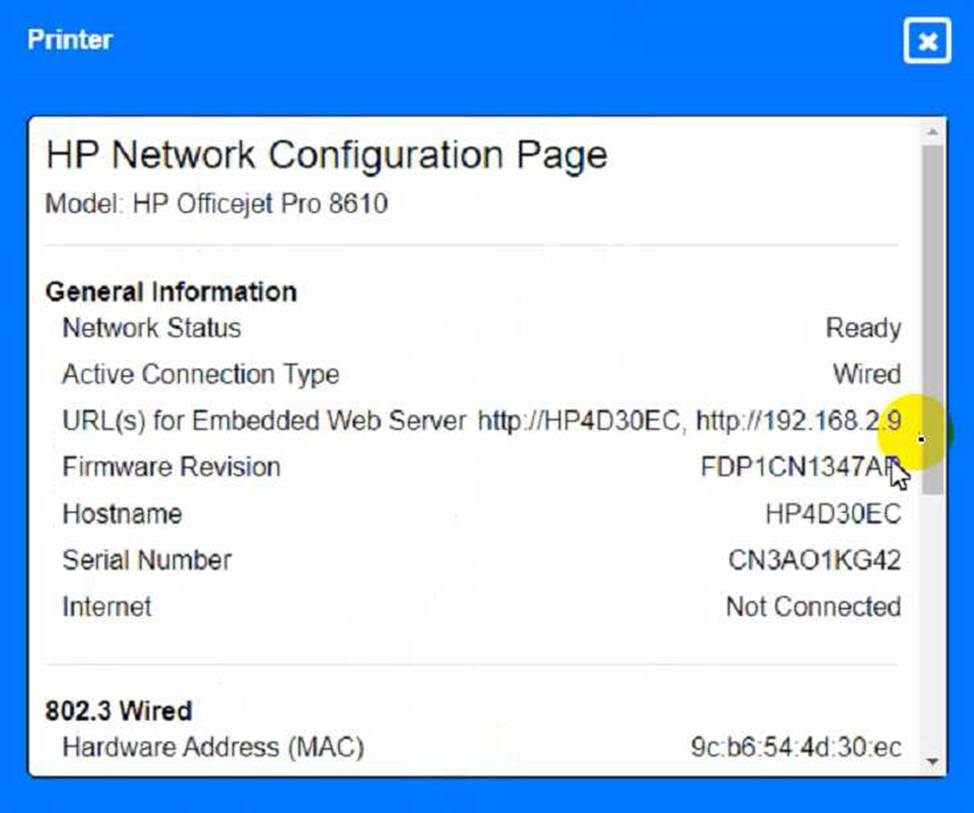
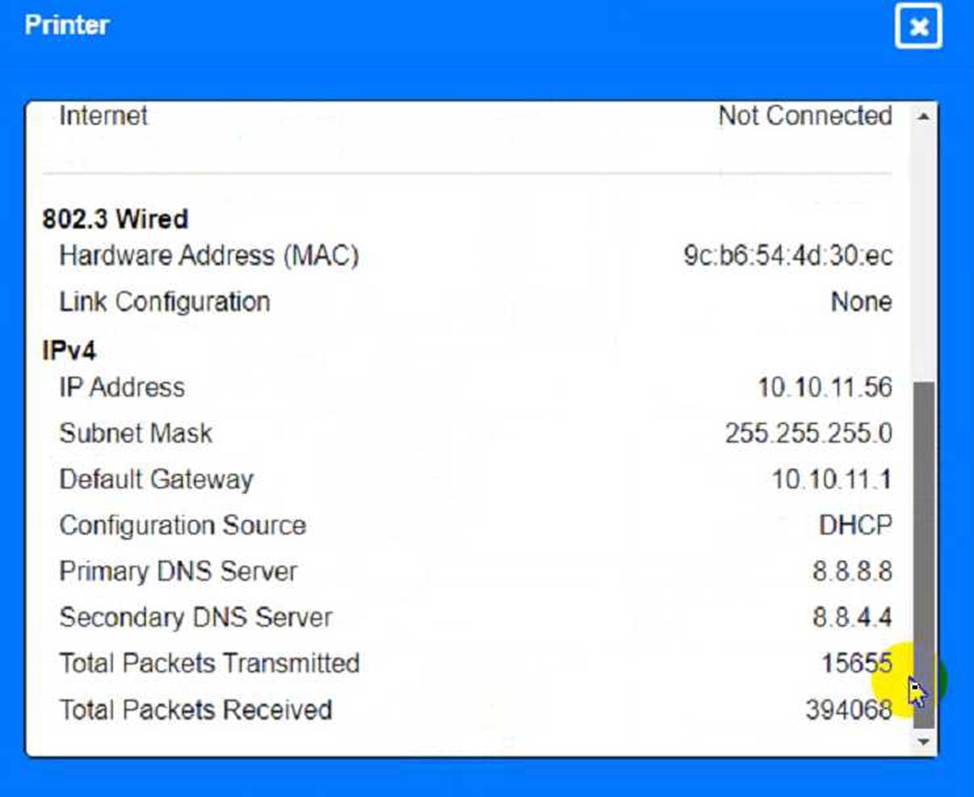
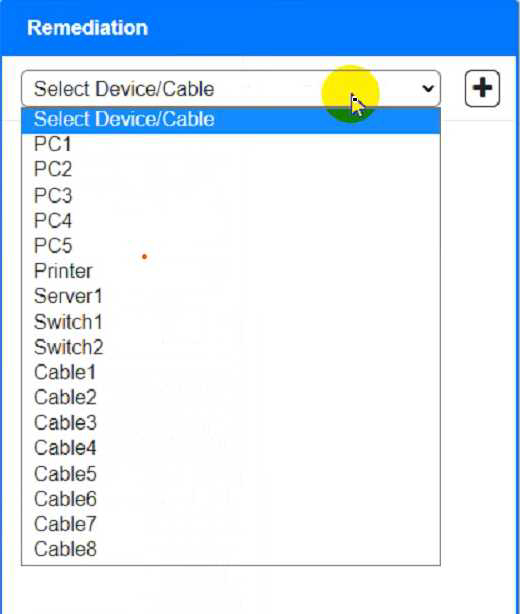
To troubleshoot all the network components and review the cable test results, you can use the following steps:
Click on each device and cable to open its information window.
Review the information and identify any problems or errors that may affect the network connectivity or performance.
Diagnose the appropriate component(s) by identifying any components with a problem and recommend a solution to correct each problem.
Fill in the remediation form using the drop-down menus provided. Here is an example of how to fill in the remediation form for PC1: The component with a problem is PC1. The problem is Incorrect IP address.
The solution is Change the IP address to 192.168.1.10.
You can use the same steps to fill in the remediation form for other components.
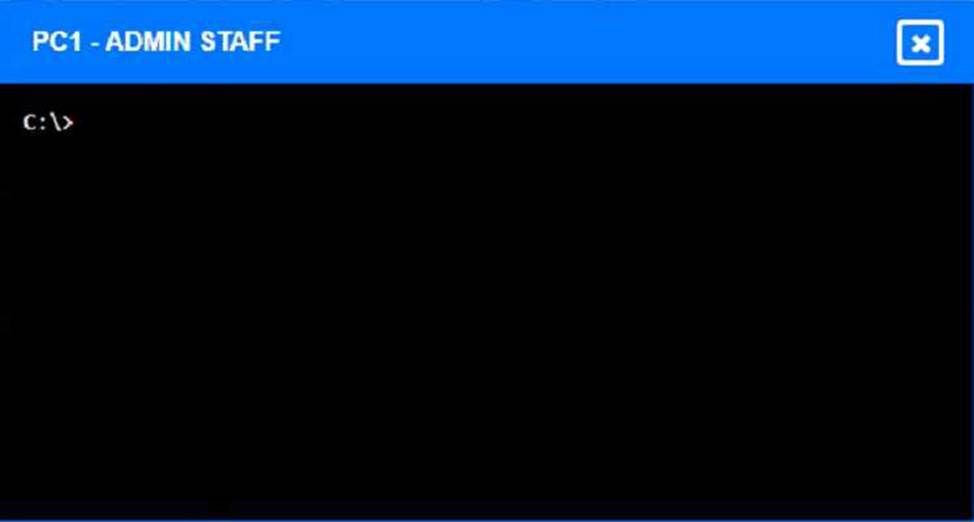
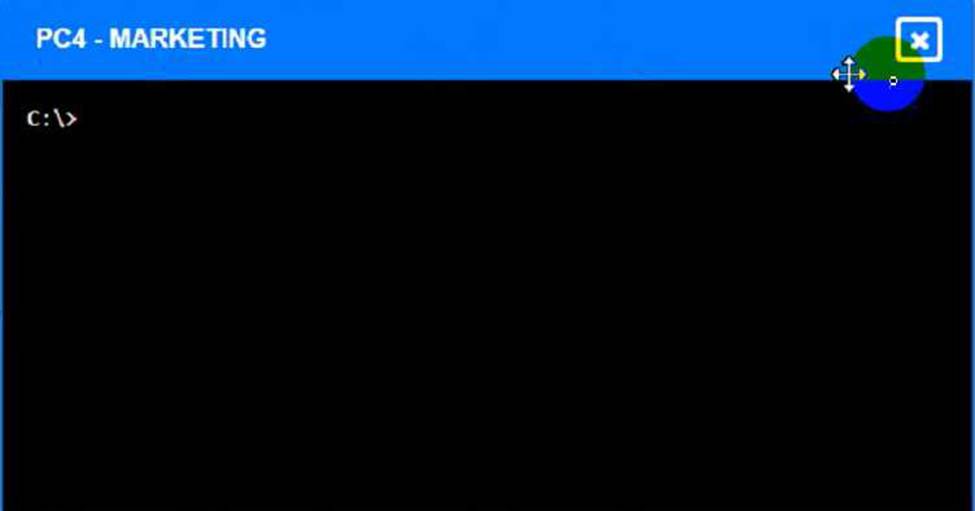
To enter commands in each device, you can use the following steps:
Click on the device to open its terminal window.
Enter the command ipconfig /all to display the IP configuration of the device, including its IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers.
Enter the command ping <IP address> to test the connectivity and reachability to another device on the network by sending and receiving echo packets. Replace <IP address> with the IP address of the destination device, such as 192.168.1.1 for Core Switch 1.
Enter the command tracert <IP address> to trace the route and measure the latency of packets from the device to another device on the network by sending and receiving packets with increasing TTL values. Replace <IP address> with the IP address of the destination device, such as 192.168.1.1 for Core Switch 1.
Here is an example of how to enter commands in PC1:
Click on PC1 to open its terminal window.
Enter the command ipconfig /all to display the IP configuration of PC1. You should see that PC1 has an incorrect IP address of 192.168.2.10, which belongs to VLAN 2 instead of VLAN 1.
Enter the command ping 192.168.1.1 to test the connectivity to Core Switch 1. You should see that PC1 is unable to ping Core Switch 1 because they are on different subnets.
Enter the command tracert 192.168.1.1 to trace the route to Core Switch 1. You should see that PC1 is unable to reach Core Switch 1 because there is no route between them.
You can use the same steps to enter commands in other devices, such as PC3, PC4, PC5, and Server 1.
A technician is planning an equipment installation into a rack in a data center that practices hot aisle/cold aisle ventilation.
Which of the following directions should the equipment exhaust face when installed in the rack?
- A . Sides
- B . Top
- C . Front
- D . Rear
C
Explanation:
In a data center that practices hot aisle/cold aisle ventilation, equipment should be installed so that the exhaust faces the rear of the rack. This setup ensures that hot air is expelled into the hot aisle, maintaining proper airflow and cooling efficiency.
Hot Aisle/Cold Aisle Configuration: Equipment intake should face the cold aisle where cool air is supplied, and exhaust should face the hot aisle where hot air is expelled.
Cooling Efficiency: Proper orientation of equipment helps maintain an efficient cooling environment by segregating hot and cold air, preventing overheating and improving energy efficiency. Network
Reference: CompTIA Network+ N10-007 Official Certification Guide: Discusses data center design principles, including hot aisle/cold aisle configurations.
Cisco Data Center Design Guide: Provides best practices for data center layout and equipment installation.
Network+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide: Covers data center environmental controls and ventilation strategies.
A network administrator deploys several new desk phones and workstation cubicles. Each cubicle has one assigned switchport.
The administrator runs the following commands:
nginx
CopyEdit
switchport mode access
switchport voice vlan 69
With which of the following VLANs will the workstation traffic be tagged?
- A . Private VLAN
- B . Voice VLAN
- C . Native VLAN
- D . Data VLAN
D
Explanation:
When the command switchport voice vlan 69 is used, it tags the voice traffic with VLAN 69, while the workstation traffic continues untagged on the access VLAN, which is typically considered the data VLAN. This configuration enables both voice and data traffic over the same port while keeping them in separate VLANs for QoS and traffic management.
Reference: Section 2.2 C Switching Technologies and Features C “Switchport Voice VLAN Configuration”
Users at an organization report that the wireless network is not working in some areas of the building. Users report that other wireless network SSIDs are visible when searching for the network, but the organization’s network is not displayed.
Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- A . Interference or channel overlap
- B . Insufficient wireless coverage
- C . Roaming misconfiguration
- D . Client disassociation issues
B
Explanation:
If the company’s SSID is not visible in some areas while other networks are still visible, the most likely cause is insufficient wireless coverage. The wireless signal does not reach those areas, meaning additional access points or signal boosters may be required.
Breakdown of Options:
A network administrator is deploying a new switch and wants to make sure that the default priority value was set for a spanning tree.
Which of the following values would the network administrator expect to see?
- A . 4096
- B . 8192
- C . 32768
- D . 36684
C
Explanation:
Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol (STP):
STP is used to prevent network loops in Ethernet networks by creating a spanning tree that selectively blocks some redundant paths.
Default Priority Value:
Bridge Priority: STP uses bridge priority to determine which switch becomes the root bridge. The default bridge priority value for most switches is 32768.
Priority Range: The bridge priority can be set in increments of 4096, ranging from 0 to 61440.
Configuration and Verification:
When deploying a new switch, the network administrator can verify the bridge priority using commands such as show spanning-tree to ensure it is set to the default value of 32768.
Comparison with Other Values:
4096 and 8192: Lower than the default priority, indicating these would be manually configured for higher preference.
36684: A non-standard value, likely a result of specific configuration changes.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ study materials on Spanning Tree Protocol and network configuration.
Which of the following ports should a network administrator enable for encrypted login to a network switch?
- A . 22
- B . 23
- C . 80
- D . 123
A
Explanation:
Port 22 is used for Secure Shell (SSH), which enables encrypted remote login and command execution on network devices.
Port 23 = Telnet (unencrypted)
Port 80 = HTTP
Port 123 = NTP
From Andrew Ramdayal’s guide:
“SSH uses port 22 to provide secure command-line access to devices such as switches and routers. Unlike Telnet (port 23), SSH encrypts session traffic, making it the preferred method for remote administration.”
A company’s marketing team created a new application and would like to create a DNS record for newapplication.comptia.org that always resolves to the same address as www.comptia.org.
Which of the following records should the administrator use?
- A . SOA
- B . MX
- C . CNAME
- D . NS
C
Explanation:
A CNAME (Canonical Name) record is used in DNS to alias one domain name to another. This means that newapplication.comptia.org can be made to resolve to the same IP address as www.comptia.org by creating a CNAME record pointing newapplication.comptia.org to www.comptia.org. SOA (Start of Authority) is used for DNS zone information, MX (Mail Exchange) is for mail server records, and NS (Name Server) is for specifying authoritative DNS servers.
Reference: The DNS section of the CompTIA Network+ materials describes the use of CNAME records for creating domain aliases.
After a company installed a new IPS, the network is experiencing speed degradation. A network
administrator is troubleshooting the issue and runs a speed test.
The results from the different network locations are as follows:
Location Speed Down Speed Up
Wireless laptop4.8 Mbps47.1 Mbps
Wired desktop5.2 Mbps49.3 Mbps
Firewall48.8 Mbps49.5 Mbps
Which of the following is the most likely issue?
- A . Packet loss
- B . Bottlenecking
- C . Channel overlap
- D . Network congestion
B
Explanation:
Bottlenecking occurs when a device in the network (such as an IPS) cannot process traffic efficiently, resulting in a dramatic drop in throughput. The significant difference between the firewall’s speed (48.8 Mbps down) and the end-user devices’ speeds (4.8 – 5.2 Mbps down) indicates a bottleneck caused by the IPS.
• Why not the other options?
• Packet loss (A) C Would typically cause connection timeouts, not just slow speeds.
• Channel overlap (C) C Affects only wireless networks, but the wired desktop is also experiencing slow speeds.
• Network congestion (D) C Would show fluctuations in both upload and download speeds, but upload speeds remain unaffected.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ (N10-009) Official Guide C Chapter 13: Network Performance Optimization
