Practice Free 300-410 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.

Which two commands provide the administrator with the information needed to resolve the issue? (Choose two.)
- A . snmp user
- B . debug snmp engine-id
- C . debug snmpv3 engine-id
- D . debug snmp packet
- E . showsnmpv3 user
Refer to the exhibit.
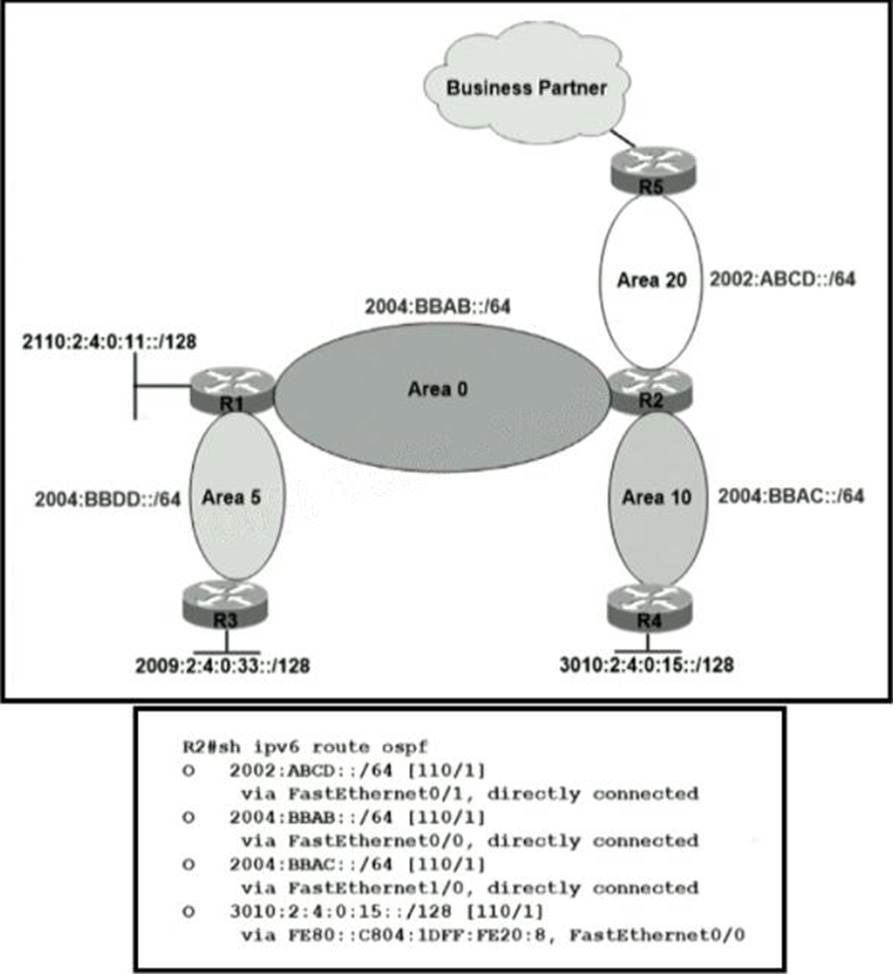
A network engineer applied a filter for LSA traffic on OSPFv3 interarea routes on the area 5 ABR to protect advertising the internal routes of area 5 to the business partner network. All other areas should receive the area 5 internal routes. After the respective route filtering configuration is applied on the ABR, area 5 routes are not visible on any of the areas.
How must the filter list be applied on the ABR to resolve this issue?
- A . in the “in” direction for area 5 on router R1
- B . in the “out” direction for area 5 on router R1
- C . in the “in” direction for area 20 on router R2
- D . in the “out” direction for area 20 on router R2
Refer to the exhibit.
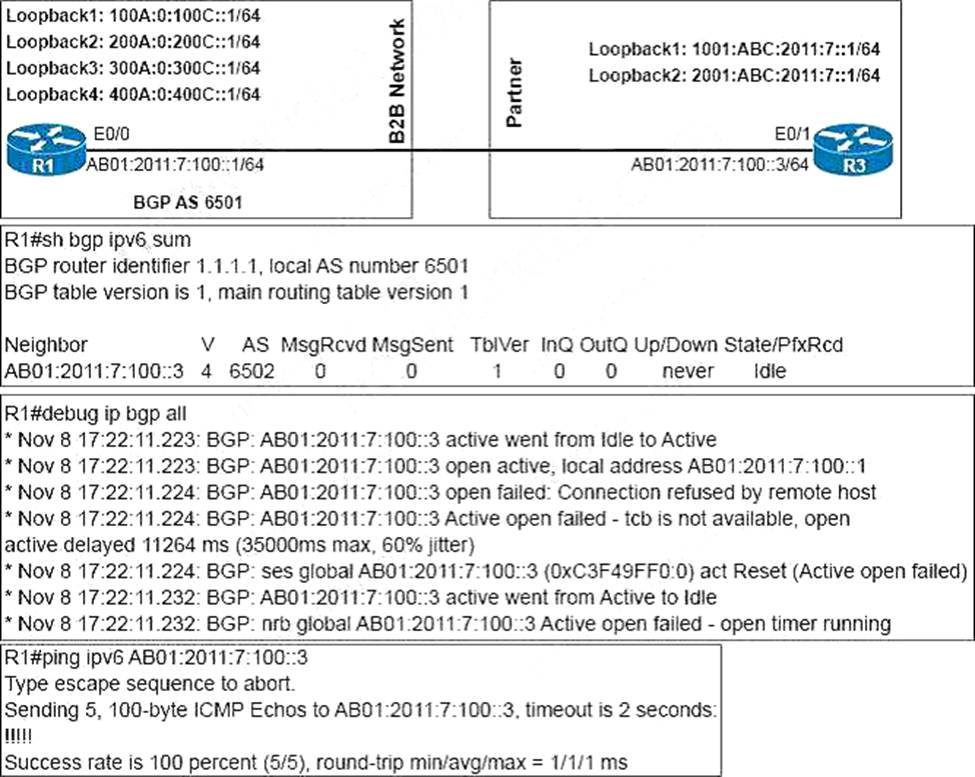
An engineer configured BGP between routers R1 and R3 The BOP peers cannot establish neighbor adjacency to be able to exchange routes.
Which configuration resolves this issue?
- A . R3router bgp 6502address-family ipv6neighbor AB01:2011:7:100::1 activate
- B . R1router bgp 6501address-family ipv6neighbor AB01:2011:7:100;:3 activate
- C . R3router bgp 6502neighbor AB01:2011:7:100::1 ebgp-muttlhop 255
- D . R1router bgp 6501 neighborAB01:2011:7:100::3ebgp-multihop255
A
Explanation:
From the output, we learned that R1 was trying to establish BGP neighbor relationship with R3 but failed. Both of them were using physical interface to establish neighbor relationship so we don’t need the “… ebgp-multihop” command here. The only reasonable answer is R3 has not been configured to activate BGP neighbor relationship with R1.
Which control plane process allows the MPLS forwarding state to recover when a secondary RP takes over from a failed primary RP?
- A . MP-BGP uses control plane services for label prefix bindings in the MPLS forwarding table
- B . LSP uses NSF to recover from disruption *i control plane service
- C . FEC uses a control plane service to distribute information between primary and secondary processors
- D . LDP uses SSO to recover from disruption in control plane service
Refer to the exhibit.

Reachability between servers in a network deployed with DHCPv6 is unstable.
Which command must be removed from the configuration to make DHCPv6 function?
- A . ipv6 dhcp server DHCPPOOL
- B . ipv6 address 2001:0:1:4::/64
- C . ipv6 nd ra suppress
- D . address prefix 2001:0:1:4::/64 lifetime infinite infinite
What is the purpose of the DHCPv6 Guard?
- A . It messages between a DHCPv6 server and a DHCPv6 client ( or relay agent).
- B . It shows that clients of a DHCPv5 server are affected.
- C . It block DHCPv6 messages from relay agents to a DHCPv6 server.
- D . It allows DHCPv6 replay and advertisements from (rouge) DHCPv6 servers.
A
Explanation:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipv6_fhsec/configuration/xe-16/ip6fxe-16-book/ip6-dhcpv6-guard.html
Refer to the exhibit.
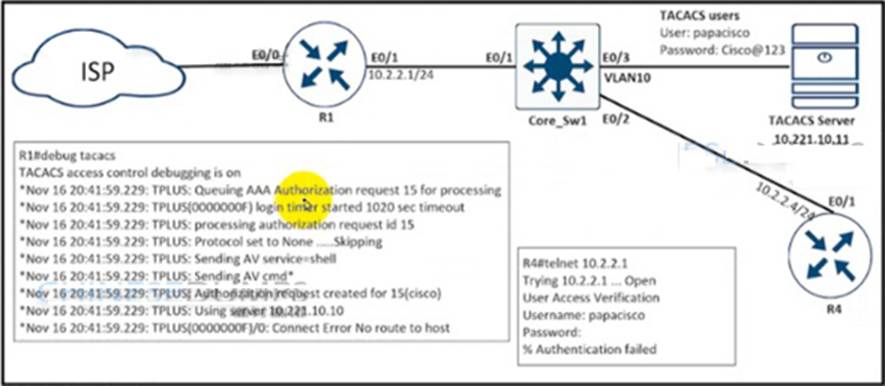
An engineer is trying to connect to R1 via Telnet with no success.
Which configuration resolves the issue?
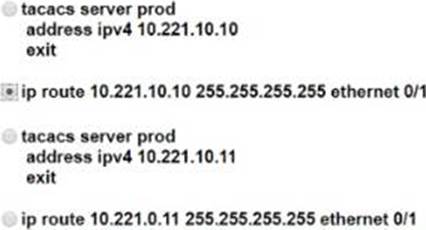
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
Refer to Exhibit.
A network administrator has successfully configured DMVPN topology between a hub and two spoke routers.
Which two configuration commands should establish direct communications between spoke 1 and spoke 2 without going through the hub? (Choose two).
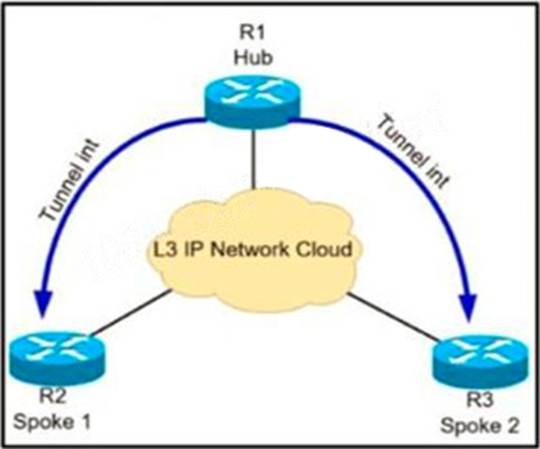
- A . At the hub router, configure the ip nhrp shortcut command.
- B . At the spoke routers, configure the ip nhrp spoke-tunnel command.
- C . At the hub router, configure ip nhrp redirect the command
- D . At the spoke routers, configure the ip nhrp shortcut command.
- E . At the hub router, configure tne Ip nhrp spoke-tunnel command
C,D
Explanation:
To configure Spoke to Spoke communication we can configure DMVPN Phase II or Phase III. But in Phase II, the first few packets would go through Hub. In order tototally ignore the hub, we have to use DMVPN Phase III:
DMVPN Phase III is same as Phase 2 but removes some restrictions and complexities of Phase 2.
Also allows greater variety of DMVPN network designs we use:
+ ip nhrp redirect in hub: tells the initiator spoke to look for a better path to the destination spoke than through the Hub. Upon receiving the NHRP redirect message the spokes communicate with each other over the hub and they have their NHRP replies for the NHRP Resolution Requests that they sent out.
+ ip nhrp shortcut in spokes: overwrite the CEF table on the spoke. It basically overrides the next-hop value for a remote spoke network from the default initial hub tunnel IP address to the NHRP resolved remote spoke tunnel IP address)
A company is expanding business by opening 35 branches over the Internet. A network engineer must configure DMVPN at the branch routers to connect with the hub router and allow NHRP to add spoke routers securely to the multicast NHRP mappings automatically.
Which configuration meets this requirement at the hub router?
- A . interface Tunnel0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
ip nhrp authentication KEY1
ip nhrp nhs dynamic
ip nhrp network-id 10
tunnel mode mgre auto - B . interface Tunne10
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
ip nhrp authentication KEY1
ip nhrp registration no-unique
ip nhrp network-id 10
tunnel mode gre nmba - C . interface Tunnel0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
ip nhrp authentication KEY1
ip nhrp map multicast dynamic
ip nhrp network-id 10
tunnel mode gre multi pointe - D . interface Tunnel0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
ip nhrp authentication KEY 1
ip nhrp map multicast 224.0.0.0
ip nhrp network-id 10
tunnel mode gre ipv4
C
Explanation:
The command “ip nhrp map multicast dynamic” allows NHRP to automatically add spoke routers to the multicast NHRP mappings.
Refer to the exhibit.
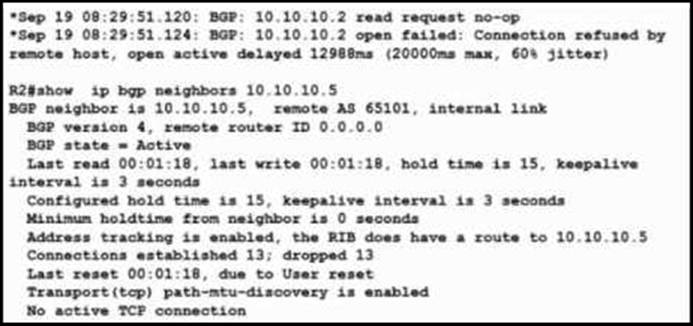
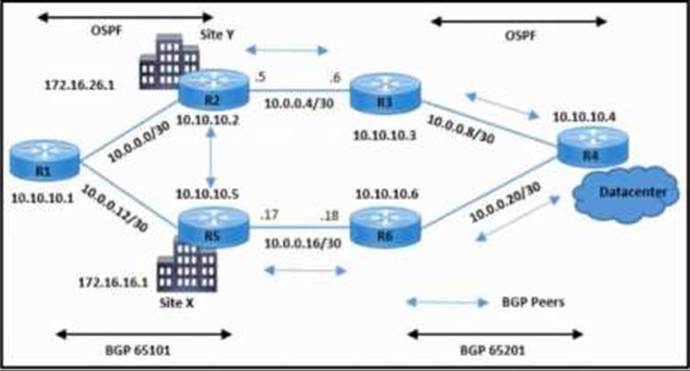
A customer reports a failure and intermittent disconnection between two office buildings, site X and site Y. The network team determines that both sites are exchanging email application traffic with the data center network.
Which configuration resolves the issue between site X and site Y?
- A . R5(config-router)#neighbor 10.10.10.2 next-hop-self
R5(config)#router bgp 65101 - B . R2(config-router)#no timers bgp 3 15
R2(config)#router bgp 65101 - C . R2(config-router)#neighbor 10.10.10.5 update-source loopback 0
R2(config)#router bgp 65101 - D . R2(config-router)#neighbor 10.10.10.5 next-hop-self
R2(config)#router bgp 65101
