Practice Free 300-410 Exam Online Questions
What is an advantage of using BFD?
- A . It detects local link failure at layer 1 and updates routing table.
- B . It detects local link failure at layer 2 and updates routing protocols.
- C . It has sub-second failure detection for layer 1 and layer 3 problems.
- D . It has sub-second failure detection for layer 1 and layer 2 problems.
Refer to the exhibit.
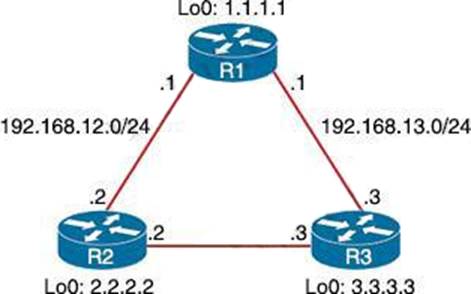

R2 has two paths to reach 192.168.13.0/24. but traffic is sent only through R3.
Which action allows traffic to use both paths?
- A . Configure the bandwidth 2000 command under interface FastEthernet0/0 on R2.
- B . Configure the variance 4 command under the EIGRP process on R2.
- C . Configure the delay 1 command under interface FastEthernet0/0 on R2.
- D . Configure the variance 2 command under the EIGRP process on R2
B
Explanation:
From the output of the “show ip eigrp topology …” command, we notice network 192.168.13.0/24 was learned via two routes:
+ From 192.168.23.3 (R3) with FD = 1075200 and AD = 281600
+ From 192.168.12.1 (R1) with FD = 2611200 and AD = 281600
From the output of the “show ip route …” command, we learned that the best (and chosen) path is via 192.168.23.3 (R3).
To use both paths (called unequal cost load balancing) with EIGRP, the second path via R1 must satisfy the feasibility condition. The feasibility condition states that, the Advertised Distance (AD) of a route must be lower than the feasible distance of the current successor route.
In this case, the second path satisfies the feasible condition as its AD (281600) is smaller than the FD (1075200) of the best path. Therefore we can configure loadbalancing with “variance” command.
In other words, EIGRP will install all paths with metric < variance * best_metric into the local routing table, provided that it meets the feasibility condition to preventrouting loop. Therefore we can calculate the variance > metric / best_metric = 2611200 / 1075200 =2.4.
So with a variance greater than 2 (and must be an integer), we can load balance traffic to network 192.168.13.0/24.
Refer to the exhibit.
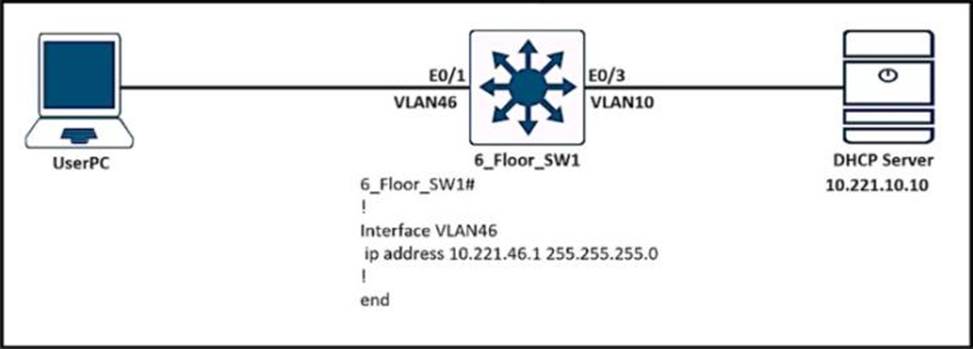
Users in VLAN46 cannot get the IP from the DHCP server. Assume that all the parameters are configured properly in VLAN 10 and on the DHCP server.
Which command on interlace VLAN46 allows users to receive IP from the DHCP server?
- A . ip dhcp-addreos 10.221.10.10
- B . ip dhcp server 10.221.10.10
- C . ip helper-addrets 10.221.10.10
- D . ip dhcp relay information trust-all
Refer to the exhibit.
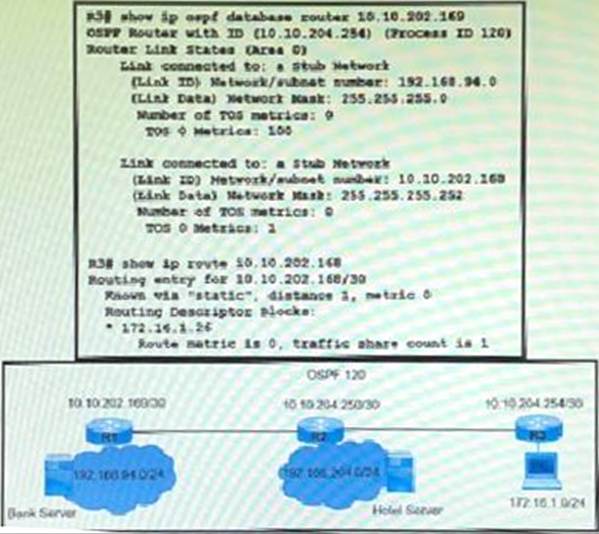
A network engineer finds that PC1 is accessing the hotel website to do the booking but fails to make payment.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Allow stub network 10.10.202.168/30 on router R3 OSPF.
- B . Decrease the AD to 5 OSPF route 192.168.94.0 on R1.
- C . Increase the AD to 200 of static route 192.168.94.0 on R3.
- D . Configure a reverse route on R1 for PC1 172.16.1.0/24.
Refer to the exhibit.
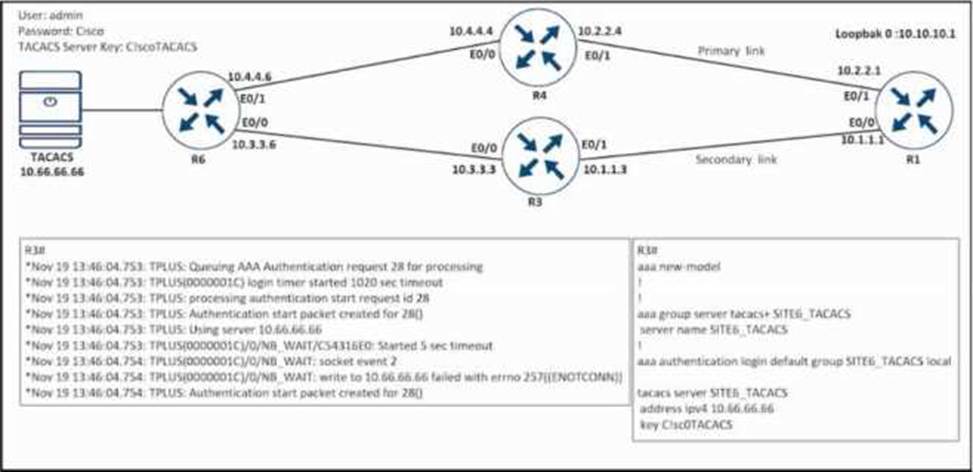
R3 cannot authenticate via TACACS.
Which configuration resolves the issue?
- A . tacacs server SITE6_TACACS key C!scOTACACS
address ipv4 10.60.66.66 - B . tacacs server SITE6_TACACS key C!scoTACACS
address ipv4 10.60.66.66 - C . tacacs server SITE6_TACACS key CiscoTACACS
address ipv4 10.66.66.66 - D . tacacs server SITE6_TACACS key CIscoTACACS
Refer to the exhibit.
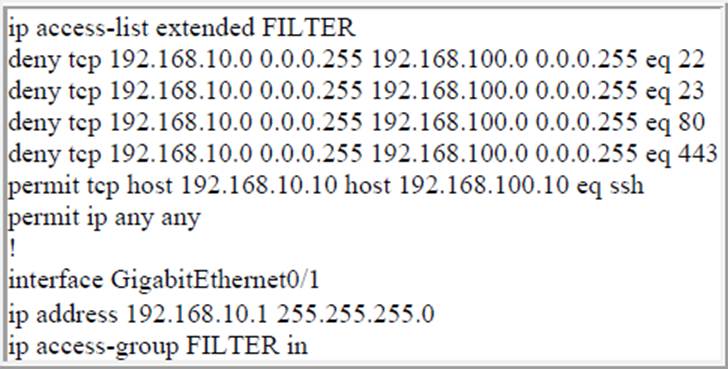
The ACL is placed on the inbound Gigabit 0/1 interface of the router. Host 192.168.10.10cannot SSH to host 192.168.100.10 even though the flow is permitted.
Which action resolves the issue without opening full access to this router?
- A . Move the SSH entry to the beginning of the ACL
- B . Temporarily move the permit ip any any line to the beginning of the ACL to see if the flow works
- C . Temporarily remove the ACL from the interface to see if the flow works
- D . Run the show access-list FILTER command to view if the SSH entry has any hit statistic associated with it
What is a characteristic of Layer 3 MPLS VPNs?
- A . LSP signaling requires the use of unnumbered IP links for traffic engineering.
- B . Traffic engineering supports multiple IGP instances
- C . Traffic engineering capabilities provide QoS and SLAs.
- D . Authentication is performed by using digital certificates or preshared keys.
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/mp_te_diffserv/configuration/15-mt/mp-te-diffserv-15-mt-book/mp-te-diffserv-aw.html
MPLS traffic engineering supports only a single IGP process/instance
The MPLS traffic engineering feature does not support routing and signaling of LSPs over unnumbered IP links.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/mp_te_path_setup/configuration/xe-3s/mp-te-path-setup-xe-3s-book/mp-te-enhance-xe.html
Refer to the exhibit.

The R2 OSPF route 10 2 2 0/24 shows in the R1 EIGRP routing table without route redistribution performed between OSPF and EIGRP routing protocols.
Which configuration is required on router R2 to resolve the issue?
- A . passive-interface FastEthernet 0/0 command in OSPF1.
- B . Add the no auto-summary command in EIGRP 100.
- C . Replace the network 10.0.0.0 command with FastEthernet0/0 network in EIGRP 100.
- D . Add the passive-interface FastEthernet 1/0 command in EIGRP 100
Refer to the exhibit.
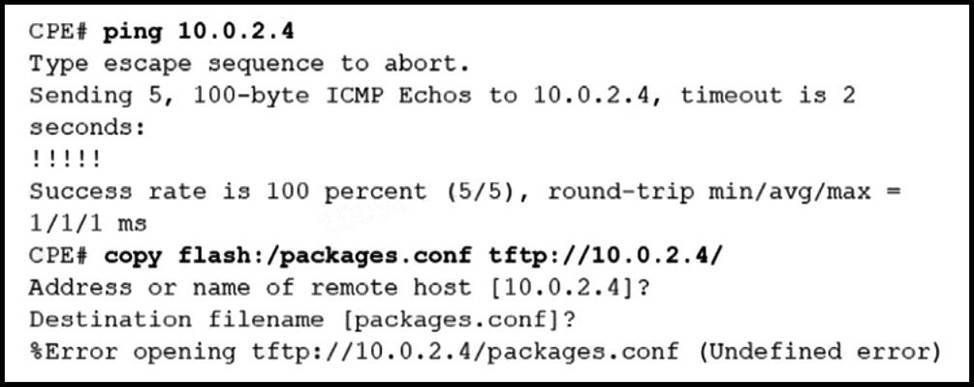
The administrator is trying to overwrite an existing file on the TFTP server that was previously uploaded by another router. However, the attempt to update the file fails.
Which action resolves this issue?
- A . Make the packages.conf file executable by all on the TFTP server
- B . Make the packages.conf file writable by all on the TFTP server
- C . Make sure to run the TFTP service on the TFTP server
- D . Make the TFTP folder writable by all on the TFTP server
Refer to the exhibit.

The server for the finance department is not reachable consistently on the 200.30.40.0/24 network and after every second month it gets a new IP address.
Which two actions must be taken to resolve this Issue? (Choose two.)
- A . Configure the server to use DHCP on the network with default gateway 200 30.40.100.
- B . Configure the server with a static IP address and default gateway.
- C . Configure the router to exclude a server IP address.
- D . Configure the server to use DHCP on the network with default gateway 200 30.30.100.
- E . Configure the router to exclude a server IP address and default gateway.
