Practice Free 300-410 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
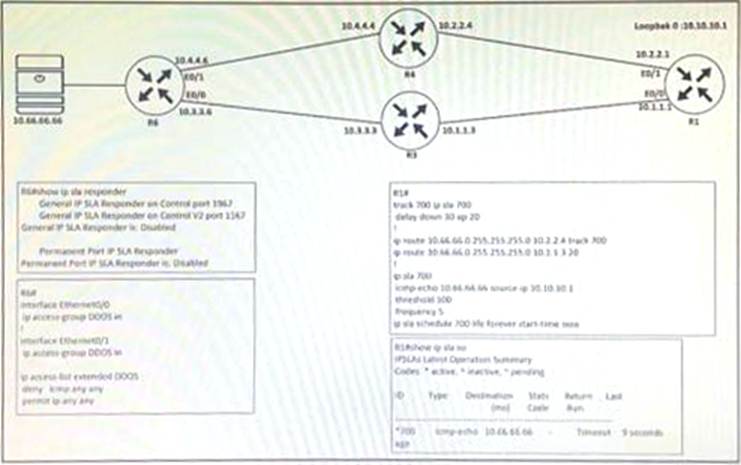
A network administrator is trying to switch to the privileged EXEC level on R1 but failed.
Which configuration resolves the issue?
- A . Enable password Cisco@123
- B . tacass server enable-password Cisco@123
- C . tacacs-server enable-password Cisco@123
- D . enable-password Cisco@123
Which mechanism must be chosen to optimize the reconvergence time for OSPF at company location 407173257 that is less CPU-intensive than reducing the hello and dead timers?
- A . BFD
- B . Dead Peer Detection keepalives
- C . SSO
- D . OSPF demand circuit
Refer to the exhibit.
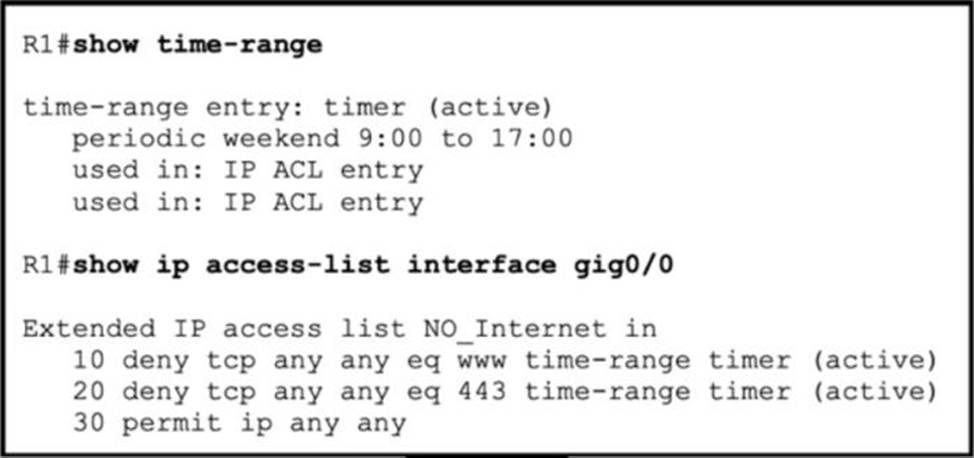
Users on a call center report that they cannot browse the internet on Saturdays during the afternoon.
Which configuration resolves the issue?
A)

B)

C)
![]()
D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
How are CE advertised routes segmented from other CE routers on an MPLS PE router?
- A . with a combination of VRF-Lite and MP-BGP
- B . by pushing MPLS labels advertised by LDP on customer routes
- C . by enabling multiple instances of BGP. one for each CE router
- D . by assigning CE-facing interfaces to different VRFs
D
Explanation:
In an MPLS PE router, CE advertised routes are segmented from other CE routers by assigning CE-facing interfaces to different Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instances12. A VRF is a technology that allows multiple instances of a routing table to co-exist within the same router at the same time. By associating a network interface with a VRF, the network layer (Layer 3) has a different view of the network topology. This allows the segmentation of routing paths for traffic from different customers or different types of traffic. In the context of MPLS, VRFs are used to create separate routing instances for each customer on a PE router3.
Reference: Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) training videos CCNP Enterprise Advanced Routing ENARSI 300-410 Official Cert Guide Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services source documents or study guide MPLS routes to advertise from CE to PE – Cisco Community Configuring Route Exchange Between PE and CE Devices – CloudEngine 12800 and 12800E V200R005C10 Configuration Guide – VPN C Huawei Customer edge router – Wikipedia
Refer to the exhibit.
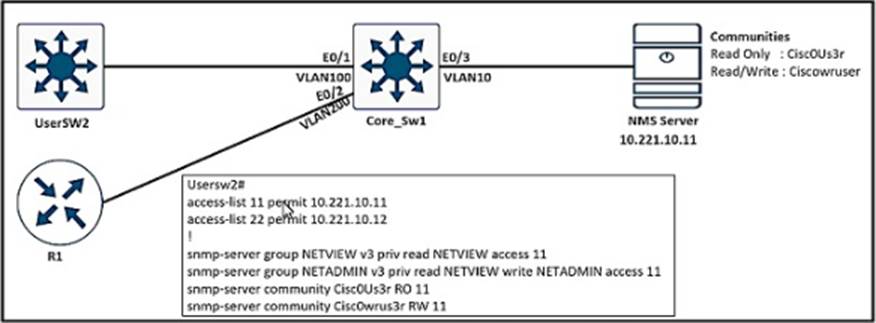
An engineer configured SNMP Commimes on UserSW2 switch, but the SNMP server cannot upload modified configurations to the switch.
Which configuration resolves this issue?
- A . snmp-server community Ciscowruser RW 11
- B . snmp-server group NETADMIN v3 priv read NETVIEW write NETADMIN access 22
- C . snmp-server community CiscOUs3r RW 11
- D . snmp-server group NETVIEW v2c priv read NETVIEW access 11
Refer to the exhibit.
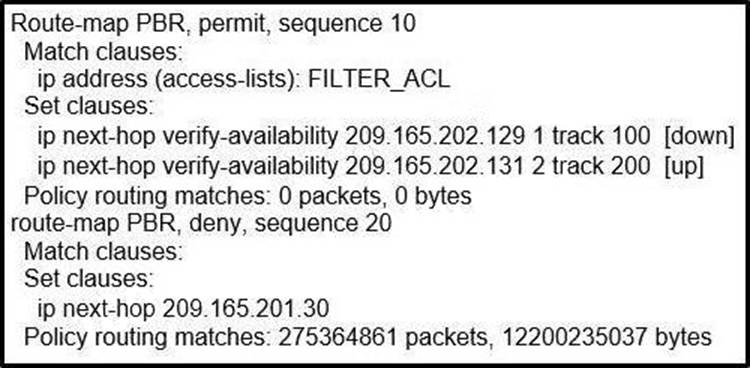
Which two commands provide the administrator with the information needed to resolve the issue? (Choose two.)
- A . Show snmp user
- B . debug snmp engine-id
- C . debug snmpv3 engine-id
- D . debug snmp packet
- E . showsnmpv3 user
A,D
Explanation:
There are 3 values in the SNMPv3 header that must match for the communication to take place: snmpEngineID, snmpEngineTime, snmpEngineBoots. The error received indicates a problem with the EngineID value: “authentication failure, Unknown Engine ID”
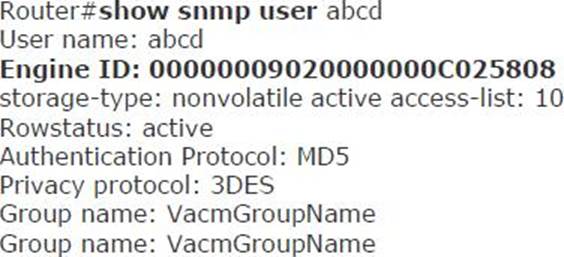
To specify the Engine ID, we can use the command “show snmp user”. The following example specifies the username as abcd with Engine ID: 00000009020000000C025808:
The “debug snmp packet” command displays all SNMP packets that are arriving and being replied to.
R2 has a locally originated prefix 192.168.130.0/24 and has these configurations:

What is the result when the route-map OUT command is applied toward an eBGP neighbor R1 (1.1.1.1) by using the neighbor 1.1.1.1 route-map OUT out command?
- A . R1 sees 192.168.130.0/24 as two AS hops away instead of one AS hop away.
- B . R1 does not accept any routes other than 192.168.130.0/24
- C . R1 does not forward traffic that is destined for 192.168.30.0/24
- D . Network 192.168.130.0/24 is not allowed in the R1 table
Which rouler takes an active role between two LDP neighbors when initiating LDP session negotiation and LDP TCP connection establishment?
- A . with the higher IP address
- B . with the larger number of LDP TCP neighbors
- C . with the lowest IP address
- D . with one interface in the MPLS backbone
What are the two goals of micro BFD sessions? (Choose two.)
- A . The high bandwidth member link of a link aggregation group must run BFD
- B . Run the BFD session with 3×3 ms hello timer
- C . Continuity for each member link of a link aggregation group must be verified
- D . Eny member link on a link aggregation group must run BFD
- E . Each member link of a link aggregation group must run BFD.
C,E
Explanation:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_bfd/configuration/xe-16-8/irb-xe-16-8-book/irb-micro-bfd.html
Which two protocols are used by a P router to transfer VPN traffic between PE routers in an MPLS network? (Choose two.)
- A . BGP
- B . OSPF
- C . MP-BGP
- D . LDP
- E . RSVP
