Practice Free 300-410 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.

The network administrator configured VRF lite for customer A. The technician at the remote site misconfigured VRF on the router.
Which configuration will resolve connectivity for both sites of customer_a?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
D
Explanation:
From the exhibit, we learned:
+ VRF customer_a was exported with Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site it must be imported with the same RT 1:1.
+ VRF customer_a was imported with Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site it must be exported with the same RT 1:1.
Therefore at the remote site we must configure the command “route-target both 1:1” (which is equivalent to two commands “route-target import 1:1” & “route-target export 1:1”.
Refer to the exhibit.

The network administrator configured VRF lite for customer A. The technician at the remote site misconfigured VRF on the router.
Which configuration will resolve connectivity for both sites of customer_a?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
D
Explanation:
From the exhibit, we learned:
+ VRF customer_a was exported with Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site it must be imported with the same RT 1:1.
+ VRF customer_a was imported with Route target (RT) of 1:1 so at the remote site it must be exported with the same RT 1:1.
Therefore at the remote site we must configure the command “route-target both 1:1” (which is equivalent to two commands “route-target import 1:1” & “route-target export 1:1”.
Refer to the exhibit.

A company is evaluating multiple network management system tools. Trending graphs generated by SNMP data are returned by the NMS and appear to have multiple gaps. While troubleshooting the issue, an engineer noticed the relevant output.
What solves the gaps in the graphs?
- A . Remove the exceed-rate command in the class map.
- B . Remove the class map NMS from being part of control plane policing.
- C . Configure the CIR rate to a lower value that accommodates all the NMS tools
- D . Separate the NMS class map in multiple class maps based on the specific protocols with appropriate CoPP actions
D
Explanation:
Reference: https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/resources/copp_best_practices
The class-map NMS in the exhibit did not classify traffic into specific protocols so many packets were dropped. We should create some class-map to classify the receiving traffic. It is also a recommendation of CoPP/CPP policy:
“Developing a CPP policy starts with the classification of the control plane traffic. To that end, the control plane traffic needs to be first identified and separated into different class maps.”
Refer to the exhibit.
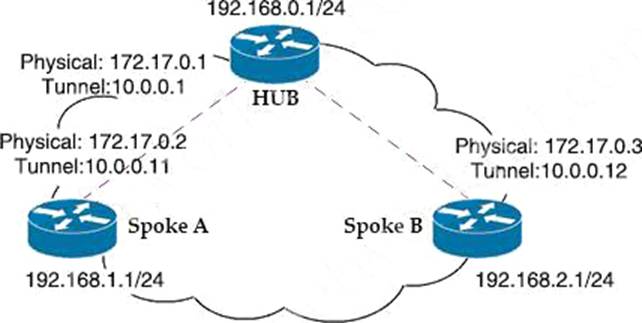
Which interface configuration must be configured on the spoke A router to enable a dynamic DMVPN tunnel with the spoke B router?


- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
Refer to the exhibit.
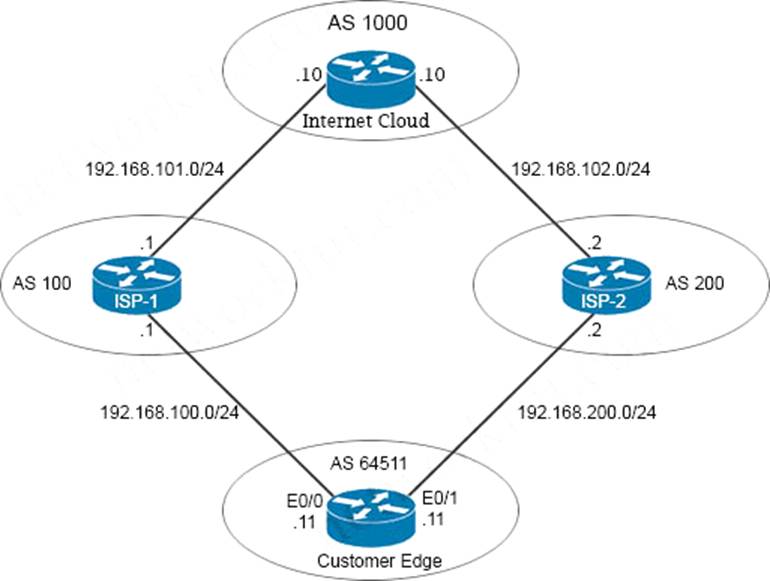
The network administrator has configured the Customer Edge router (AS 64511) to send only summarized routes toward ISP-1 (AS 100) and ISP-2 (AS 200).
router bgp 64511
network 172.16.20.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.21.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.22.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
aggregate-address 172.16.20.0 255.255.252.0
After this configuration. ISP-1 and ISP-2 continue to receive the specific routes and the summary route.
Which configuration resolves the issue?
- A . router bgp 64511
aggregate-address 172.16.20.0 255.255.252.0 summary-only - B . router bgp 64511
neighbor 192.168.100.1 summary-only
neighbor 192.168.200.2 summary-only - C . interface E 0/0
ip bgp suppress-map BLOCK_SPECIFIC
!
interface E 0/1
ip bgp suppress-map BLOCK_SPECIFIC
!
ip prefix-list PL_BLOCK_SPECIFIC
permit 172.16.20.0/22 ge 24
!
route-map BLOCK_SPECIFIC permit 10
match ip address prefix-list PL_BLOCK_SPECIFIC - D . ip prefix-list PL_BLOCK_SPECIFIC
deny 172.16.20.0/22 ge 22
ip prefix-list PL BLOCK SPECIFIC
permit 172.16.20.0/22
!
route-map BLOCK_SPECIFIC permit 10
match ip address prefix-list PL_BLOCK_SPECIFIC
!
router bgp 64511
aggregate-address 172.16.20.0 255 255.252.0 suppress-map BLOCKSPECIFIC
A
Explanation:
When the aggregate-address command is used within BGP routing, the aggregated address is advertised, along with the more specific routes. The exception to this rule is through the use of the summary-only command. The “summary-only” keyword suppresses the more specific routes and announces only the summarized route.
Refer to the exhibit.
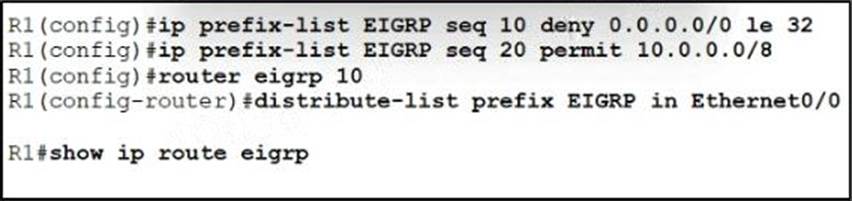
A prefix list is created to filter routes inbound to an EIGRP process except for network 10 prefixes After the prefix list is applied no network 10 prefixes are visible in the routing table from EIGRP.
Which configuration resolves the issue?
- A . ip prefix-list EIGRP seq 20 permit 10.0.0.0/8 ge 9.
- B . ip prefix-list EIGRP seq 10 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
- C . ip prefix-list EIGRP seq 5 permit 10.0.0.0/8 ge 9 no
ip prefix-list EIGRP seq 20 permit 10.0.0.0/8 - D . ip prefix-list EIGRP seq 20 permit 10.0.0.0/8 ge 9
ip prefix-list EIGRP seq 10 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
Refer to the exhibit.
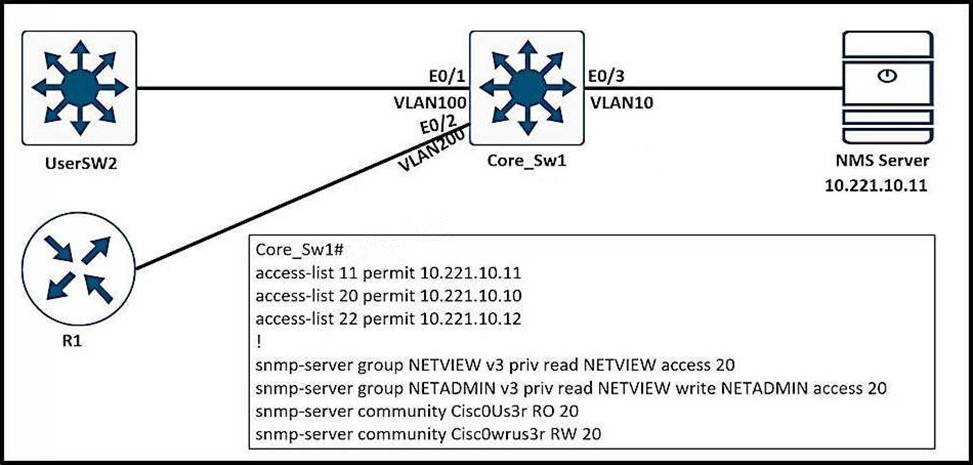
An engineer configured SNMP communities on the Core_SW1, but the SNMP server cannot obtain information from Core_SW1.
Which configuration resolves this issue?
- A . snmp-server group NETVIEW v2c priv read NETVIEW access 20
- B . access-list 20 permit 10.221.10.11
- C . access-list 20 permit 10.221.10.12
- D . snmp-server group NETADMIN v3 priv read NETVIEW write NETADMIN access 22
Refer to the exhibit.
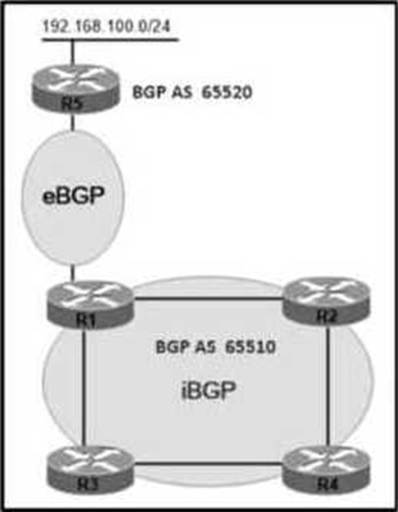
AS65510 iBGP is configured for directly connected neighbors. R4 cannot ping or traceroute network 192 168.100.0/24.
Which action resolves this issue?
- A . Configure R4 as a route reflector server and configure R1 as a route reflector client
- B . Configure R1 as a route reflector server and configure R2 and R3 as route reflector clients
- C . Configure R4 as a route reflector server and configure R2 and R3 as route reflector clients.
- D . Configure R1 as a route reflector server and configure R4 as a route reflector client
D
Explanation:
A route received from one iBGP peer will NOT be advertised to another iBGP peer. Therefore R4 could not receive advertisement for network 192.168.100.0/24. We can overcome this BGP limitation by configuring R1 as a route reflector server and R4 as a route reflector client so that R1 sends advertisements for R4.
An engineer configured VRF-Lite on a router for VRF blue and VRF red. OSPF must be enabled on each VRF to peer to a directly connected router in each VRF.
Which configuration forms OSPF neighbors over the network 10.10.10.0/28 for VRF blue and 192.168.0.0/30 for VRF red?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
Which protocol is used in a DMVPN network to map physical IP addresses to logical IP addresses?
- A . BGP
- B . LLDP
- C . EIGRP
- D . NHRP
