Practice Free 300-410 Exam Online Questions
An engineer configured access list NON-CISCO in a policy to influence routes
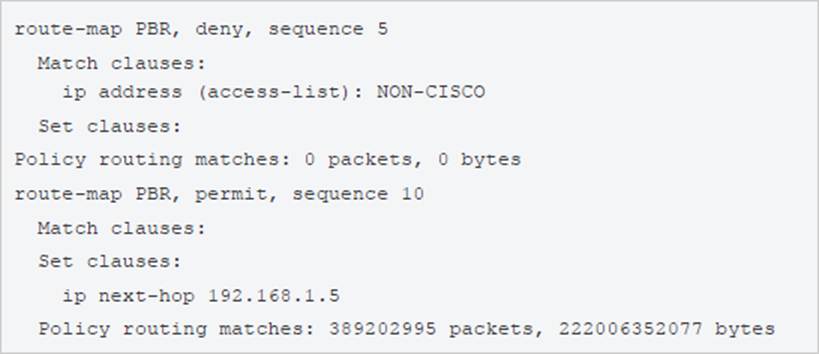
What are the two effects of this route map configuration? (Choose two.)
- A . Packets are not evaluated by sequence 10.
- B . Packets are evaluated by sequence 10.
- C . Packets are forwarded to the default gateway.
- D . Packets are forwarded using normal route lookup.
- E . Packets are dropped by the access list.
B,C
Explanation:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/ip-routed-protocols/47121-pbr-cmds-ce.html
Refer to the exhibit.
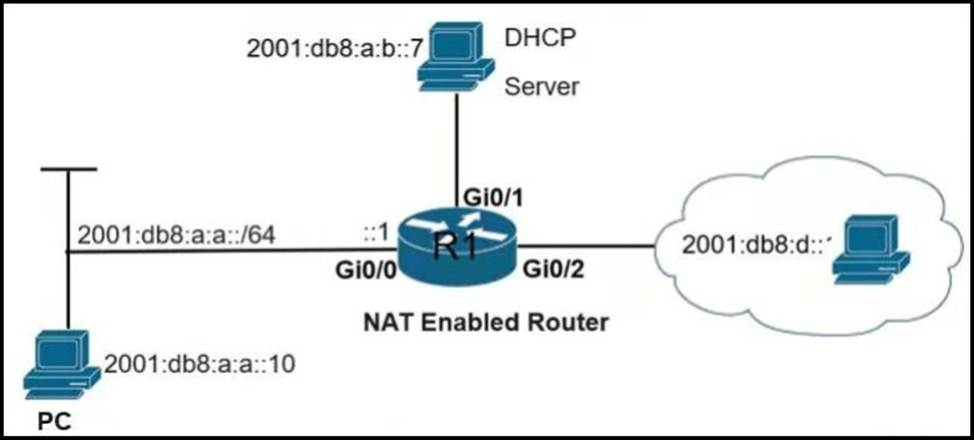

An engineer is troubleshooting a failed Telnet session from PC to the DHCP server.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Remove sequence 30 and add it back to the IPv6 traffic filter as sequence 5.
- B . Remove sequence 20 and add it back to the IPv6 traffic filter as sequence 5.
- C . Remove sequence 10 to add the PC source IP address and add it back as sequence 10.
- D . Remove sequence 20 for sequence 40 in the access list to allow Telnet.
Refer to the exhibit.


An engineer is troubleshooting a failed Telnet session from PC to the DHCP server.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Remove sequence 30 and add it back to the IPv6 traffic filter as sequence 5.
- B . Remove sequence 20 and add it back to the IPv6 traffic filter as sequence 5.
- C . Remove sequence 10 to add the PC source IP address and add it back as sequence 10.
- D . Remove sequence 20 for sequence 40 in the access list to allow Telnet.
Refer to the exhibit.
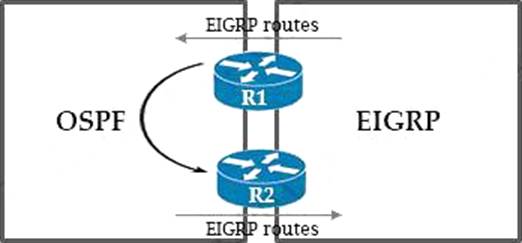
A network administrator configured mutual redistribution on R1 and R2 routers, which caused instability in the network.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Set a tag in the route map when redistributing EIGRP into OSPF on R1. and match the same tag on R2 to allow when redistributing OSPF into EIGRP.
- B . Apply a prefix list of EIGRP network routes in OSPF domain on R1 to propagate back into the EIGRP routing domain.
- C . Set a tag in the route map when redistributing EIGRP into OSPF on R1, and match the same tag on R2 to deny when redistributing OSPF into EIGRP.
- D . Advertise summary routes of EIGRP to OSPF and deny specific EIGRP routes when redistributing into OSPF.
C
Explanation:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/enhanced-interior-gateway-routing-protocol-eigrp/8606-redist.html
168.5.32/28 subnet to the 172.16.3.16/28 segment using the slowest links.
Which configuration resolves the suboptimal routing issue?
- A . R1(config-router)#router elgrp 100
R1(config-router)#redistribute ospf 1 metric 1000000 1111 - B . R2(config-router)#router ospf 1
R2(config-roiiter)#default-metric 1
R1(config-router)#router ospf 1
R1(config-router)#default-metric 10 - C . R2(config-router)#ro liter eigrp 100
R2(config-router)#redistribute ospf 1 metric 1000000 1111 - D . R2(config-router)#ro uter ospf 1
R2(config-router)#default-metric 10
R1(config-router)#router ospf 1
R1(config-router)#default-metric 1
Refer to the exhibit.
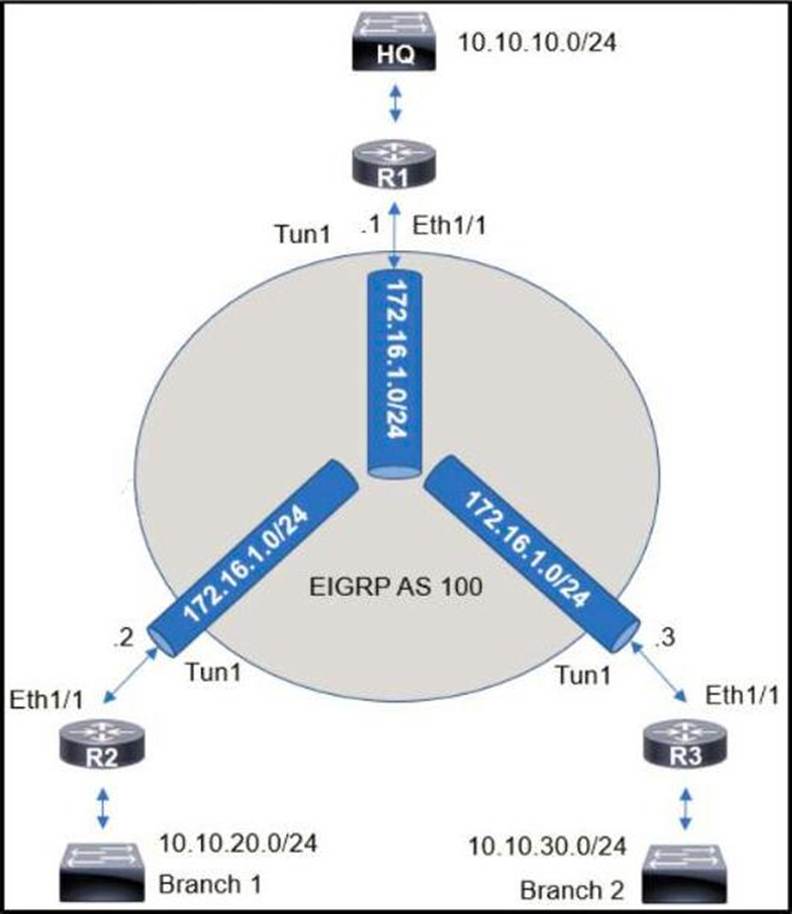
An engineer sets up a DMVPN connection to connect branch 1 and branch 2 to HQ branch 1 and branch 2 cannot communicate with each other.
Which change must be made to resolve this issue?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
D
Explanation:
R1(config)#int tunnel 1
R1(config-if) no ip split-horizon eigrp 100
Refer to the exhibit.
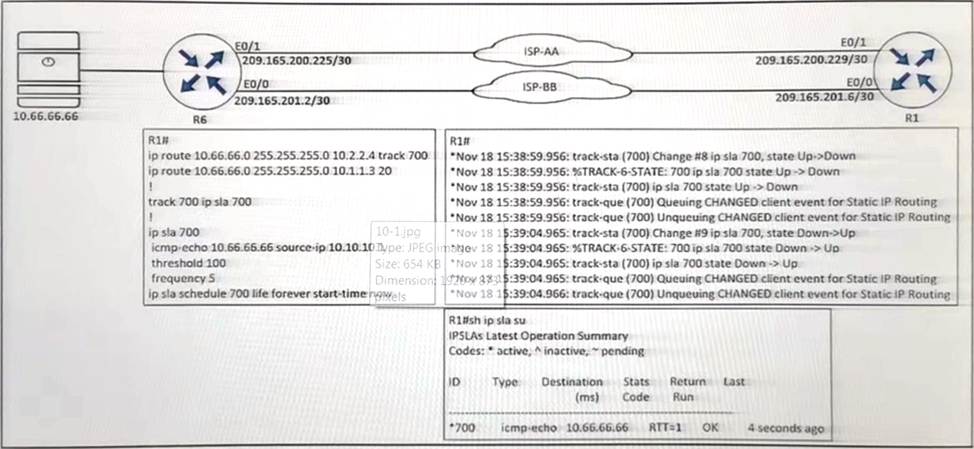
An engineer configured IP SLA on R1 to avoid the ISP link flapping problem. but it is not working as designed IP SLA should wait 30 seconds before switching traffic to a secondary connection and then revert to the primary link after waning 20 seconds, when the primary link is available and stabilized.
Which configuration resolves the issue?
- A . R1(config)#ip sla 700
R1(config-ip-sla)#delay down 30 up 20 - B . R1(config)#ip sla 700
R1(config-ip-sla)#delay down 20 up 30 - C . R1(config)#track 700 ip sla 700
R1(config-track)#delay down 30 up 20 - D . R1(config)#track 700 ip sla 700
R1(config-track)#delay down 20 up 30
C
Explanation:
“wait 30 seconds before switching traffic to a secondary connection” -> delay down 30 “then revert to the primary link after waiting 20 seconds” -> up 20
Under the track object, you can specify delays so we have to configure delay under “track 700 ip sla 700” (not under “ip sla 700”).
Refer to the exhibit.
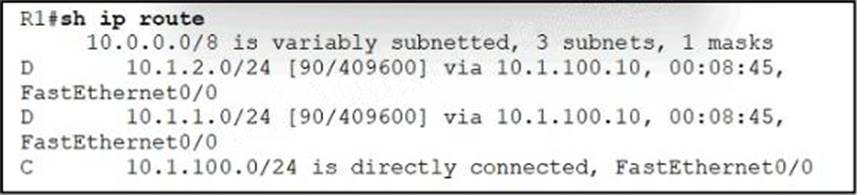
Although summarization is configured for R1 to receive 10.0.0.0/8. more specific routes are received by R1.
How should the 10.0.0.0/8 summary route be received from the neighbor, attached to R1 via Fast Ethernet0/0 interface?
- A . R1 should configure the ip summary-address eigrp <AS number> 10.0.0.0.255.0.0.0 command under the Fast Ethernet 0/0 interface.
- B . The summarization condition is not met Router 10 1 100.10 requires a route for 10 0.0.0/8 that points to null 0
- C . The summarization condition is not met. The network 10.1.100.0/24 should be changed to 172.16.0.0/24.
- D . R1 should configure the ip summary-address eigrp <AS number> 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 command under the Fast Ethernet 0/0 interface.
Refer to the exhibit.
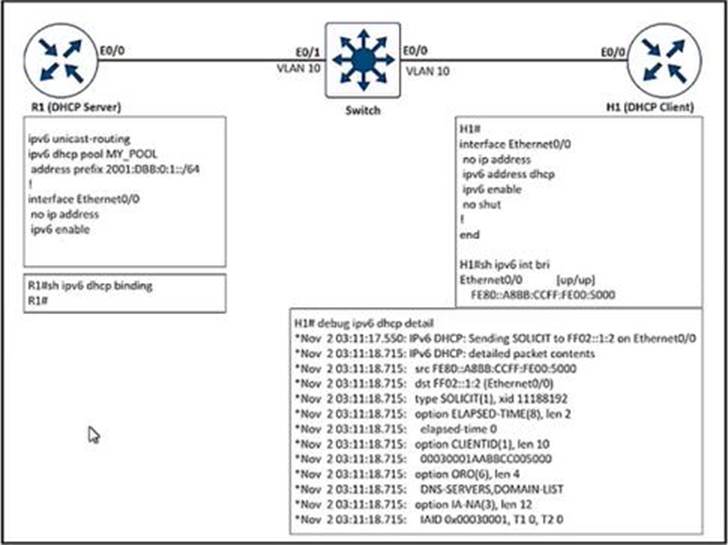
After the network administrator rebuilds the IPv6 DHCP server, clients are not getting the IPv6 address lease.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Remove FE80 A8BB CCFF FEOO 5000 assigned by the IPV6 DHCP server.
- B . Add Ipv6 dhcp sarver MY_POOL under the interface ethernet 0/0 on H1.
- C . Add Ipv6 dhcp server MY_POOL under the interface ethernet 0/0 on R1.
- D . Configure FF02::1:2 to discover al IPv6 OHCP cfcents
Refer to the exhibit.
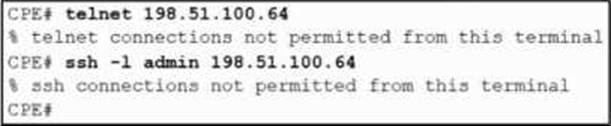
After a security hardening was performed on a router, the administrator cannot access the command line of any remote device.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Remove the transport output none command from the line con 0 section.
- B . Remove the egress ACL blocking Telnet and SSH on the router interfaces.
- C . Move Telnet and SSH commands to a nonzero privilege level.
- D . Modify the AAA policy to allow the user to run the Telnet and SSH commands.
