Practice Free 300-410 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
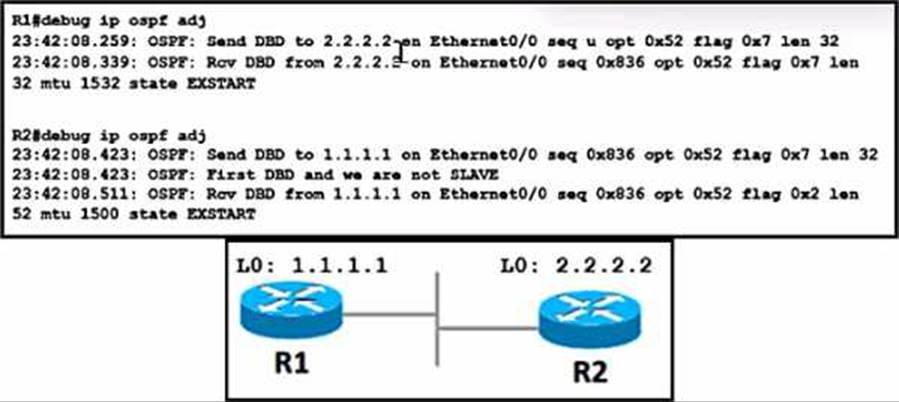
R1 cannot establish a neighbor relationship with R2.
Which action resolves the issue"?
- A . Configure the mtu Ignore command on the Interfaces of R1 and R2
- B . Configure the ip ospf network point-to-point command on the interfaces of R1 and R2
- C . Configure the ip ospf network broadcast command on the interfaces of R1 and R2
- D . Configure the neighbor 2.2.2.2 command on R1 under the OSPF process
A
Explanation:
In OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) size must match on both sides of a link for OSPF neighbors to form an adjacency12. If the MTU sizes do not match, the OSPF adjacency will not form, and the routers will not become neighbors12.
In this case, R1 cannot establish a neighbor relationship with R2. One possible reason for this could be a mismatch in the MTU size on the interfaces of R1 and R212.
To resolve this issue, you can configure the mtu ignore command on the interfaces of R1 and R2 (Option A). This command allows OSPF to ignore the MTU size when determining if it can form an adjacency with a neighbor12. This means that even if the MTU sizes do not match, OSPF will still form an adjacency, and R1 and R2 will become neighbors12.
Reference: OSPF MTU Mismatch – NetworkLessons.com
Understanding OSPF MTU Mismatch Conditions and Solutions – Cisco
Refer to the exhibit.
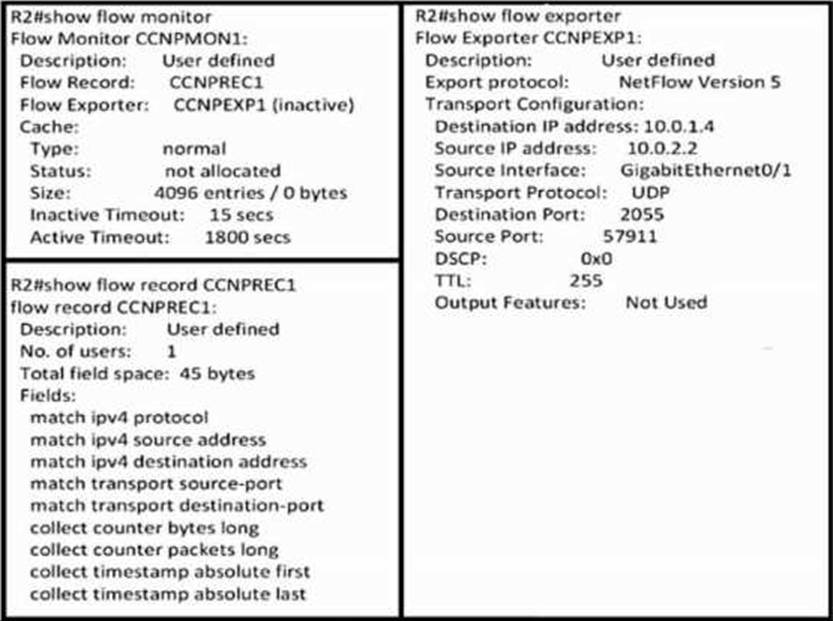
An engineer uses NetFlow to troubleshoot a voice quality issue from the branch office and notices that the traffic is not arriving in the correct format to the collector.
Which configuration resolves the issue?
- A . R2(config-flow-exporter)#export-protocol netflow-v5
R2(config)#flow exporter CCNPEXP1 - B . R2(config-flow-exporter)#export-protocol netflow-v9
R2(config)#flow exporter CCNPEXP1 - C . R2(config-flow-exporter)#export-protocol netflow-v9
R2(config-flow-monitor)#flow exporter CCNPEXP1
R2(config-flow-monitor)#no exporter CCNPEXP1
R2(config)#flow monitor CCNPMON1 - D . R2(config-flow-exporter)#export-protocol ipfix
R2(config-flow-monitor)#flow exporter CCNPEXP1
R2(config-flow-monitor)#no exporter CCNPEXP1
R2(config)#flow monitor CCNPMON1
Refer to the exhibit.
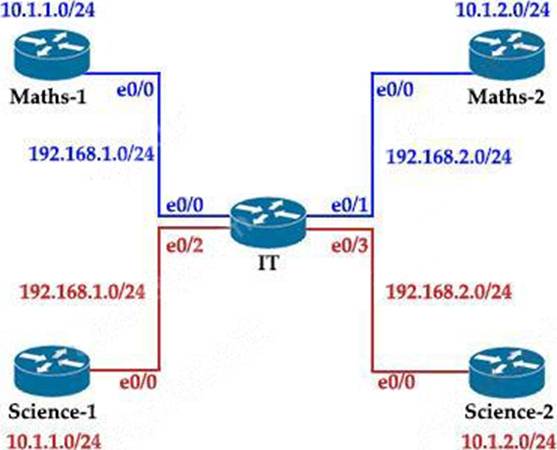
The Math and Science departments connect through the corporate. IT router but users in the Math department must not be able to reach the Science department and vice versa.
Which configuration accomplishes this task?
- A . vrf definition Science
!
interface E 0/2
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
!
interface E 0/3
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
no shut - B . vrf definition Science
address-family ipv4
!
interface E 0/2
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
vrf forwarding Science
no shut
!
interface E 0/3
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
vrf forwarding Science
no shut - C . vrf definition Science
address-family ipv4
!
interface E 0/2
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
!
interface E 0/3
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
no shut - D . vrf definition Science
address-family ipv4
!
interface E 0/2
vrf forwarding Science
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no shut
!
interface E 0/3
vrf forwarding Science
ip address 192.168.2.1
Refer to the exhibit.
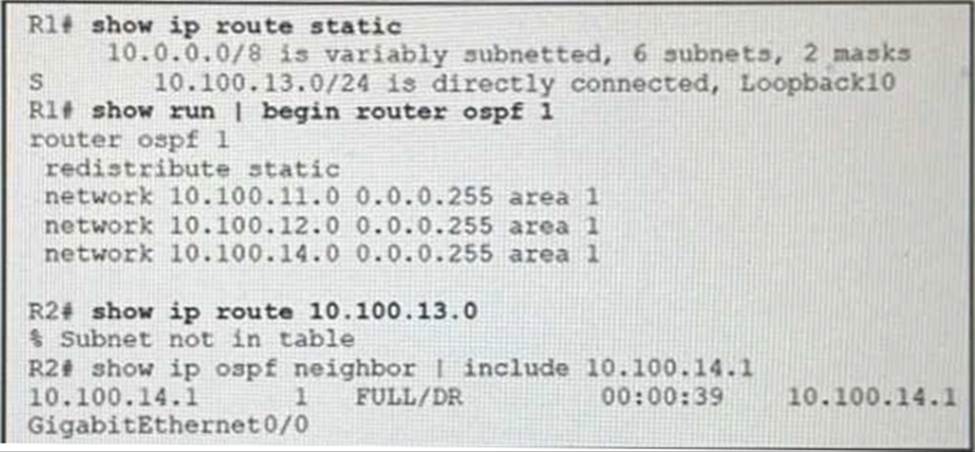
R1 is directly connected to R2 over network 10.100.14.0/24. An engineer configures R1 to advertise a static route that is connected to a local loopback for network 10.100.13.0/24. The network is not in the routing table of R2.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . The redistribution command is incorrect on R1 The default metric metric 200 should be inducted
with the redistribution command. - B . The Loopback interface on R1 is administratively down The interface should be enabled with the no shutdown command
- C . R2 must use a different OSPF process number and should be changed lo ospf 1 to match R1
- D . The redistribution command is incorrect on R1 The keyword subnets should be included with the redistribution command
What are two characteristics of IPv6 Source Guard? (Choose two.)
- A . requires IPv6 snooping on Layer 2 access or trunk ports
- B . used in service provider deployments to protect DDoS attacks
- C . requires the user to configure a static binding
- D . requires that validate prefix be enabled
- E . recovers missing binding table entries
D,E
Explanation:
IPv6 Source Guard uses the IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table to drop traffic from unknown sources or bogus IPv6 addresses not in the binding table. The switch also tries to recover from lost address information, querying DHCPv6 server or using IPv6 neighbor discovery to verify the source IPv6 address after dropping the offending packet(s).
Reference: https://blog.ipspace.net/2013/07/first-hop-ipv6-security-features-in.html
What are two characteristics of IPv6 Source Guard? (Choose two.)
- A . requires IPv6 snooping on Layer 2 access or trunk ports
- B . used in service provider deployments to protect DDoS attacks
- C . requires the user to configure a static binding
- D . requires that validate prefix be enabled
- E . recovers missing binding table entries
D,E
Explanation:
IPv6 Source Guard uses the IPv6 First-Hop Security Binding Table to drop traffic from unknown sources or bogus IPv6 addresses not in the binding table. The switch also tries to recover from lost address information, querying DHCPv6 server or using IPv6 neighbor discovery to verify the source IPv6 address after dropping the offending packet(s).
Reference: https://blog.ipspace.net/2013/07/first-hop-ipv6-security-features-in.html
What are two functions of MPLS Layer 3 VPNs? (Choose two.)
- A . LDP and BGP can be used for Pseudowire signaling.
- B . It is used for transparent point-to-multipoint connectivity between Ethernet links/sites.
- C . BGP is used for signaling customer VPNv4 routes between PE nodes.
- D . A packet with node segment ID is forwarded along with shortest path to destination.
- E . Customer traffic is encapsulated in a VPN label when it is forwarded in MPLS network.
C,E
Explanation:
MPLS Layer-3 VPNs provide IP connectivity among CE sites* MPLS VPNs enable full-mesh, hub-andspoke, and hybrid IP connectivity* CE sites connect to the MPLS network via IP peering across PE-CE links* MPLS Layer-3 VPNs are implemented via VRFs on PE edge nodes* VRFs providing customer routing and forwarding segmentation* BGP used for signaling customer VPN (VPNv4) routes between PE nodes* To ensure traffic separation, customer traffic is encapsulated in an additional VPN label when forwarded in MPLS network* Key applications are layer-3 business VPN services, enterprise network segmentation, and segmented layer-3 Data Center access
Reference: https://www.ciscolive.com/c/dam/r/ciscolive/us/docs/2018/pdf/BRKMPL-1100.pdf
Refer to the exhibit.
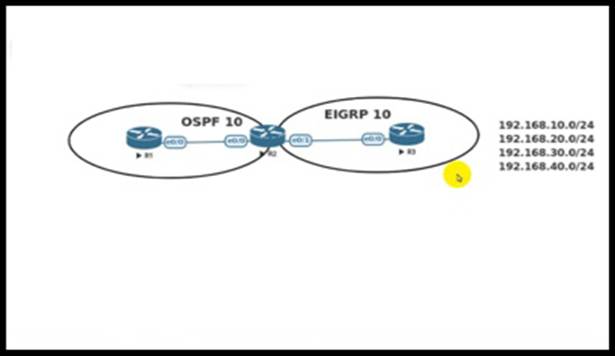
An engineer must redistribute networks 192.168.10.0/24 and 192.168.20.0/24 into OSPF from EIGRP. where the metric must be added when traversing through multiple hops to start an external route of 20 The engineer notices that the external metric is fixed and does not add at each hop.
Which configuration resolves the issue?
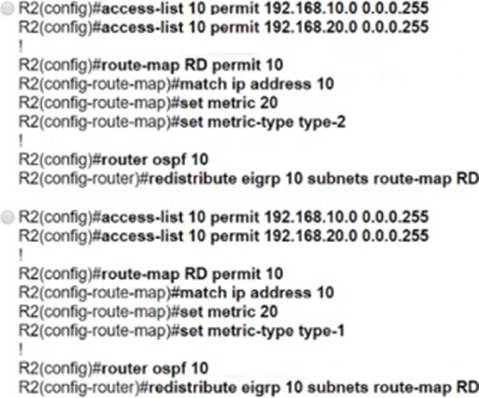
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
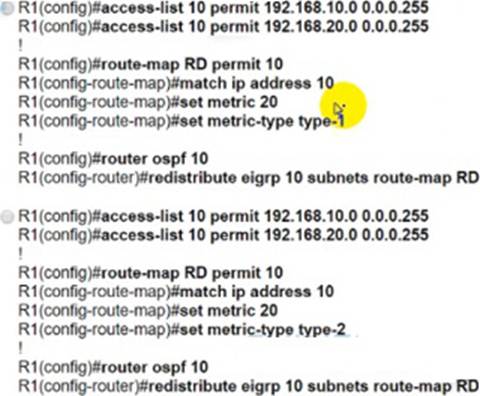
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
Refer to the exhibit.

An administrator is configuring a GRE tunnel to establish an EIGRP neighbor to a remote router. The other tunnel endpoint is already configured. After applying the configuration as shown, the tunnel started flapping.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Modify the network command to use the Tunnel0 interface netmask
- B . Advertise the Loopback0 interface from R2 across the tunnel
- C . Stop sending a route matching the tunnel destination across the tunnel
- D . Readdress the IP network on the Tunnel0 on both routers using the /31 netmask
C
Explanation:
In this question we are advertising the tunnel IP address 192.168.12.2 to the other side. When other end receives the EIGRP advertisement, it realizes it can reach the other side of the tunnel via EIGRP. In other words, it reaches the tunnel destination through the tunnel itself -> This causes “recursive routing” error.
Note: In order to avoid this error, do not advertise the tunnel destination IP address on the tunnel interface to other side.
Good recursive routing reference: https://networklessons.com/cisco/ccie-routing-switching/gretunnel-recursive-routing-error
Refer to the exhibit.
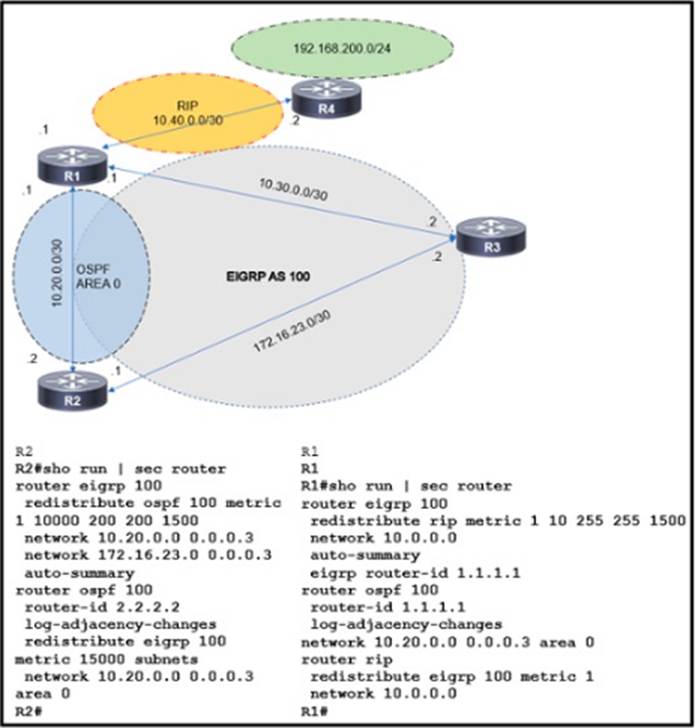
The route to 192 168 200 0 is flapping between R1 and R2.
Which set of configuration changes resolves the flapping route?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
