Practice Free 300-410 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
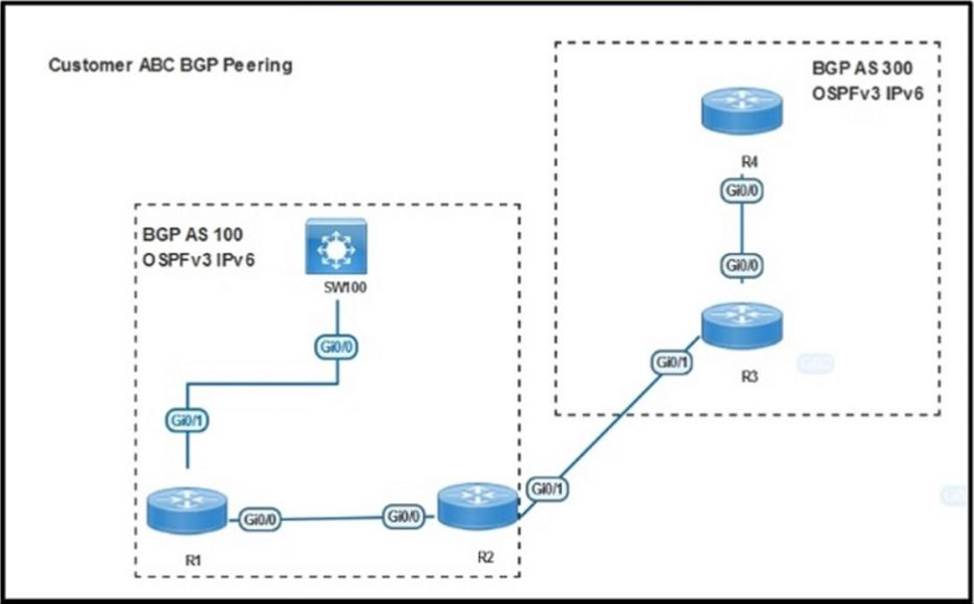
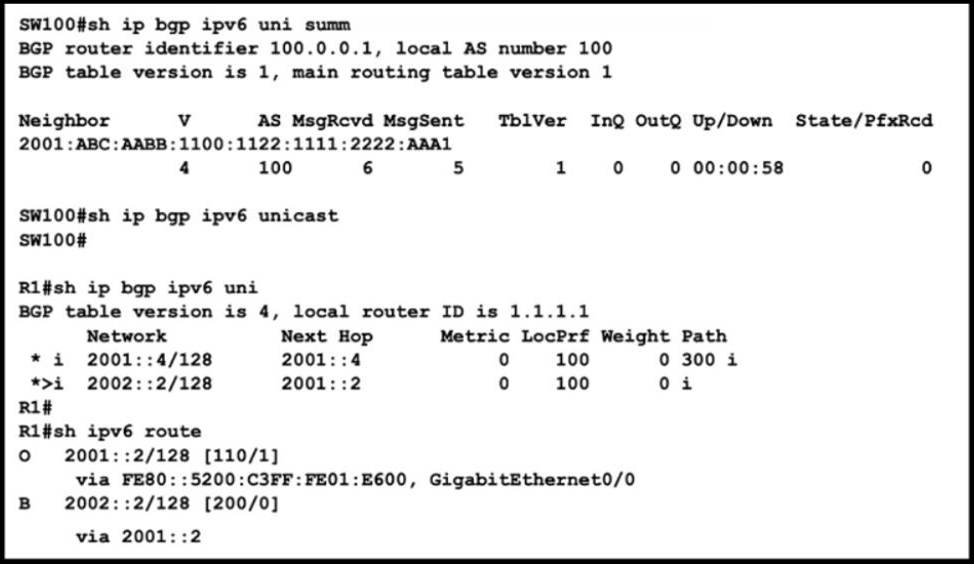
SW100 cannot receive routes from R1.
Which configuration resolves the issue?


- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option C
The summary route is not shown in the RouterB routing table after this below configuration on Router_A.

Which Router_A configuration resolves the issue by advertising the summary route to Router B?
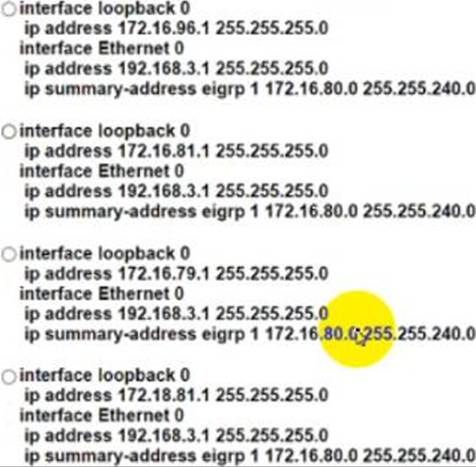
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
Refer to Exhibit.
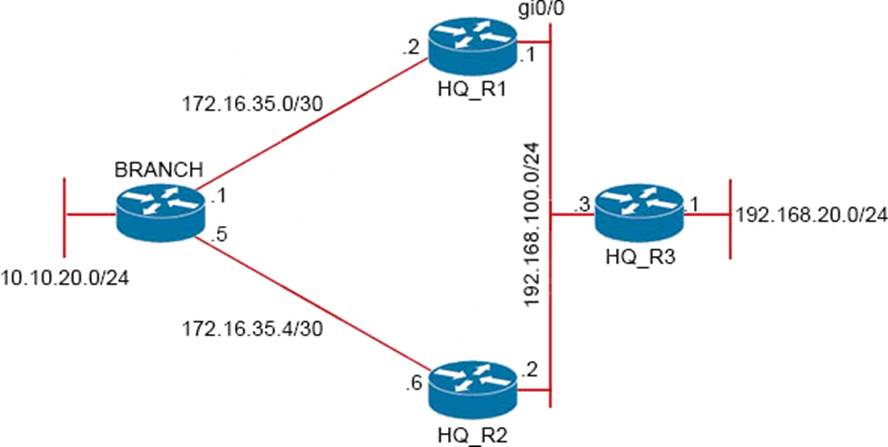
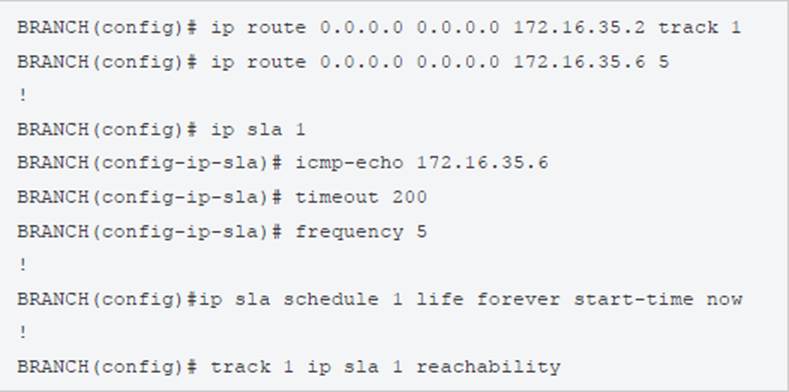
Traffic from the branch network should route through HQ R1 unless the path is unavailable. An engineer tests this functionality by shutting down interface on the BRANCH router toward HQ_R1 router but 192.168.20.0/24 is no longer reachable from the branch router.
Which set of configurations resolves the issue?
- A . HQ_R1(config)# ip sla responder
HQ_R1(config)# ip sla responder icmp-echo 172.16.35.2 - B . BRANCH(config)# ip sla 1
BRANCH(config-ip-sla)# icmp-echo 172.16.35.1 - C . HQ_R2(config)# ip sla responder
HQ_R2(config)# ip sla responder icmp-echo 172.16.35.5 - D . BRANCH(config)# ip sla 1
BRANCH(config-ip-sla)# icmp-echo 172.16.35.2
D
Explanation:
In the configuration above, the engineer has made a mistake as he was tracking 172.16.35.6 (the backup path) instead of tracking the main path (172.16.35.2). Therefore, when he shut down the main path, the track 1 was still up so traffic still went through the main path -> it failed.
To fix this issue, we just need to correct the tracking interface of the main path.
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the descriptions from the left onto the IPv6 first hop security features on the right. Not all options are used.
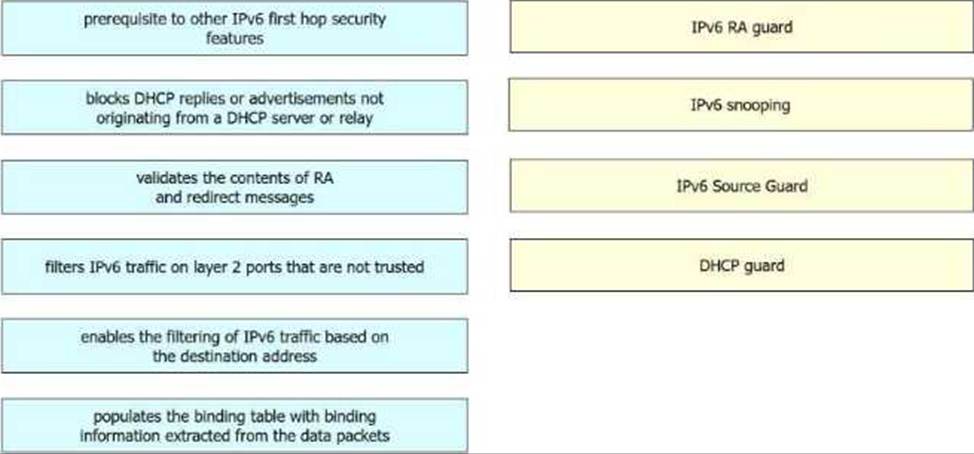
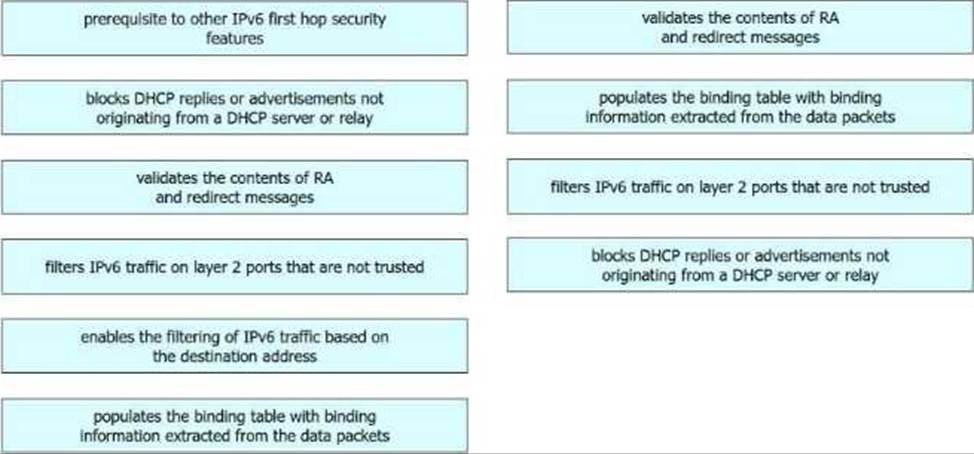
Exhibit:
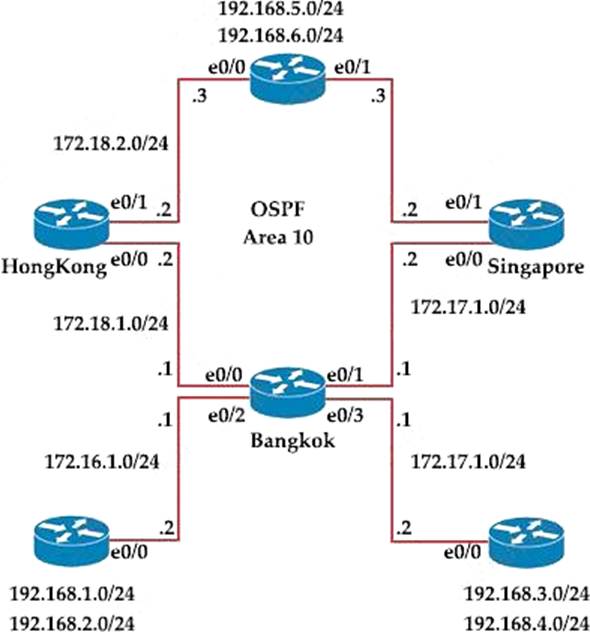
Bangkok is using ECMP to reach to the 192.168.5.0/24 network. The administrator must configure Bangkok in such a way that Telnet traffic from 192.168.3.0/24 and192.168.4.0/24 networks uses the HongKong router as the preferred router.
Which set of configurations accomplishes this task?
- A . access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255
!
route-map PBR1 permit 10
match ip address 101
set ip next-hop 172.18.1.2
interface Ethernet0/3
ip policy route-map PBR1 - B . access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
!
route-map PBR1 permit 10
match ip address 101
set ip next-hop 172.18.1.2
interface Ethernet0/1
ip policy route-map PBR1 - C . access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
!
route-map PBR1 permit 10
match ip address 101
set ip next-hop 172.18.1.2
!
interface Ethernet0/3
ip policy route-map PBR1 - D . access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255
!
route-map PBR1 permit 10
match ip address 101
set ip next-hop 172.18.1.2
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip policy route-map PBR1
C
Explanation:
We need to use Policy Based Routing (PBR) here on Bangkok router to match the traffic from 192.168.3.0/24 & 192.168.4.0/24 and “set ip next-hop” to HongKong router (172.18.1.2 in this case).
Note: Please notice that we have to apply the PBR on incoming interface e0/3 to receive traffic from 192.168.3.0/24 and 192.168.4.0/24.
How does an MPLS Layer 3 VPN function?
- A . set of sites use multiprotocol BGP at the customer site for aggregation
- B . multiple customer sites interconnect through service provider network to create secure tunnels between customer edge devices
- C . set of sites interconnect privately over the Internet for security
- D . multiple customer sites interconnect through a service provider network using customer edge to provider edge connectivity
D
Explanation:
A Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (VPN) consists of a set of sites that are interconnected by means of an MPLS provider core network. At each customer site, one or more customer edge (CE) routers attach to one or more provider edge (PE) routers.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/asr9000/software/asr9k-r6-5/lxvpn/configuration/guide/b-l3vpn-cg-asr9000-65x/b-l3vpn-cg-asr9000-65x_chapter_010.pdf
Refer to the exhibit.

Which action resolves the failed authentication attempt to the router?
- A . Configure aaa authorization login command on line vty 0 4
- B . Configure aaa authorization login command on line console 0
- C . Configure aaa authorization console global command
- D . Configure aaa authorization console command on line vty 0 4
C
Explanation:
In the debug output, we see that the Authorization (not Authentication) failed so we need to correct the authorization. In order to enable authorization, we must use the global command “aaa authorization console” first.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/security/a1/sec-a1-cr-book/sec-cr-a1.html
Refer to the exhibit.
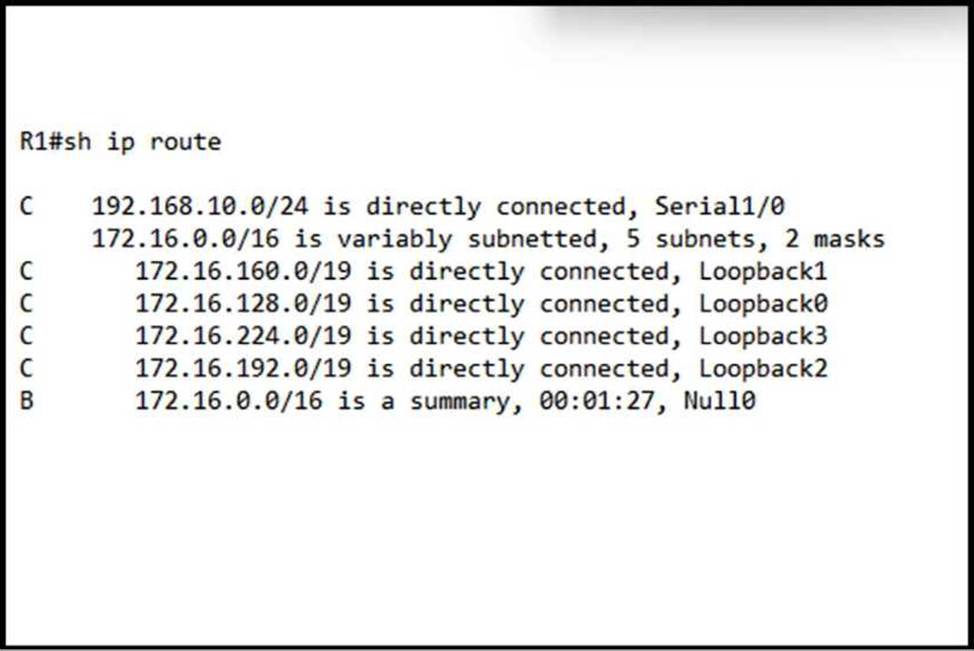
Which configuration advertises more specific routes to R1 without sending a BGP summary route?
- A . R1#configure terminal
R1 (config)#rouler BGP 100
R1 (config-router)#no auto-summary - B . R1#configure terminal
R1 (config)#router BGP 100
R1 (config-router)#auto-summary - C . R2#configure terminal
R2 (config)#router BGP 100
R2 (config-router)#no auto-summary - D . R2#configure terminal
R2 (config)#router BGP 100
R2 (config-router)#auto-summary
Refer to the exhibit.
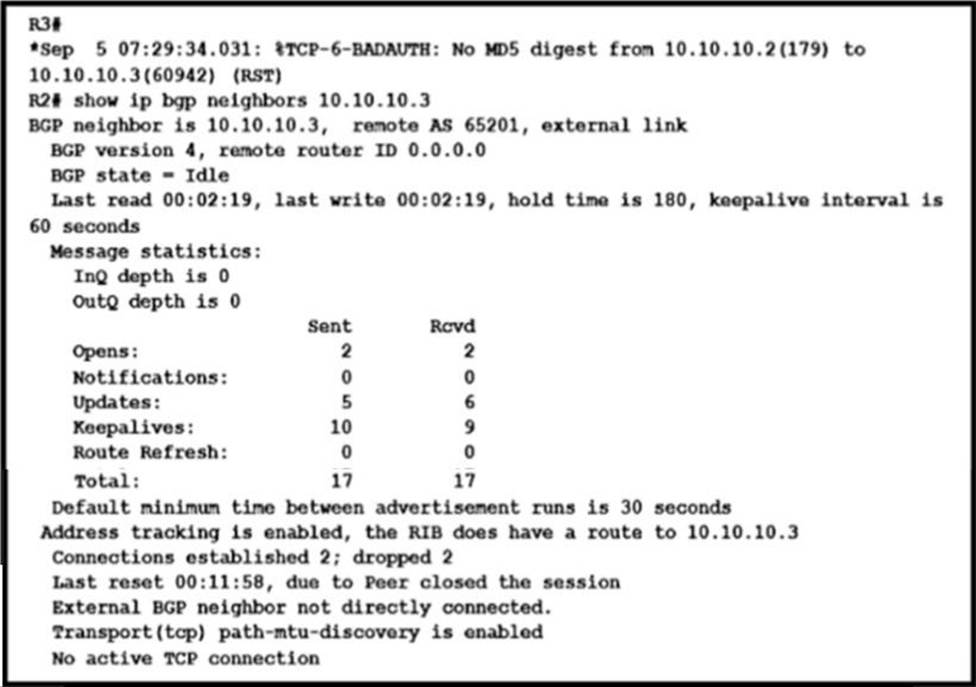
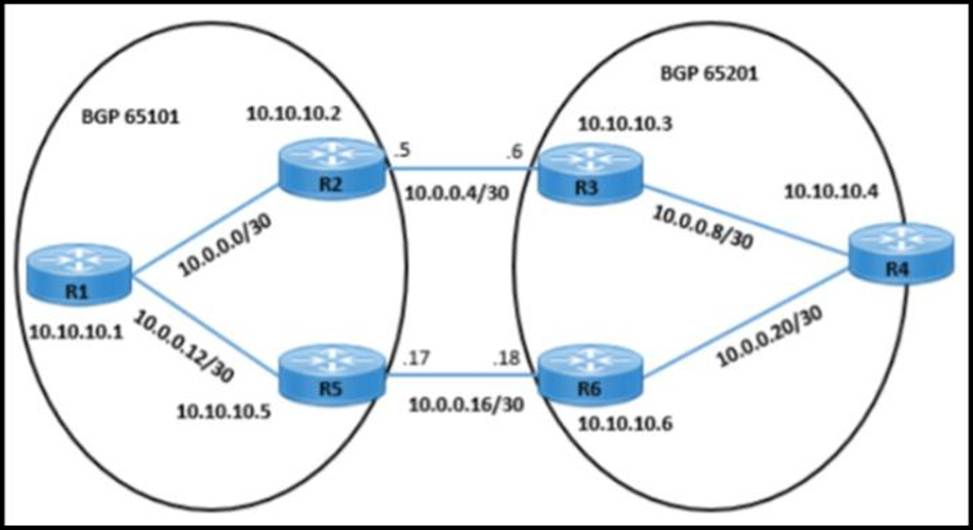
The network operation team observes a traffic forwarding issue between R2 and R3:
✑ Ping and traceroute of loopback IP address from R2 to R3 is successful.
✑ iBGP peering in AS 65101 and AS 65201 is up.
Which configuration resolves the issue?
- A . Configure MD5 password authentication on R2.
- B . Advertise R2 and R3 loopback IPs in AS 65101 and AS 65201.
- C . Remove MD5 password authentication on R3.
- D . Set up eBGP multihop on R2 and R3 routers.
Refer to the exhibit.
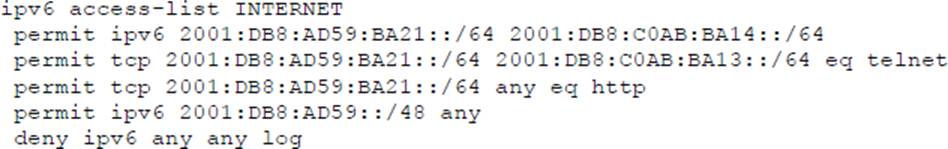
While monitoring VTY access to a router, an engineer notices that the router does not have any filter and anyone can access the router with username and password even though an ACL is configured.
Which command resolves this issue?
- A . access-class INTERNET in
- B . ip access-group INTERNET in
- C . ipv6 traffic-filter INTERNET in
- D . ipv6 access-class INTERNET in
