Practice Free 300-410 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer is trying to redistribute OSPF to BGP, but not all of the routes are redistributed.
What is the reason for this issue?
- A . By default, only internal routes and external type 1 routes are redistributed into BGP
- B . Only classful networks are redistributed from OSPF to BGP
- C . BGP convergence is slow, so the route will eventually be present in the BGP table
- D . By default, only internal OSPF routes are redistributed into BGP
D
Explanation:
If you configure the redistribution of OSPF into BGP without keywords, only OSPF intra-area and inter-area routes are redistributed into BGP, by default.
You can redistribute both internal and external (type-1 & type-2) OSPF routes via this command:
DRouter(config-router)#redistribute ospf 1 match internal external 1 external 2‖
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/border-gateway-protocol-bgp/5242-bgp-ospf-redis.html
Refer to the exhibit.
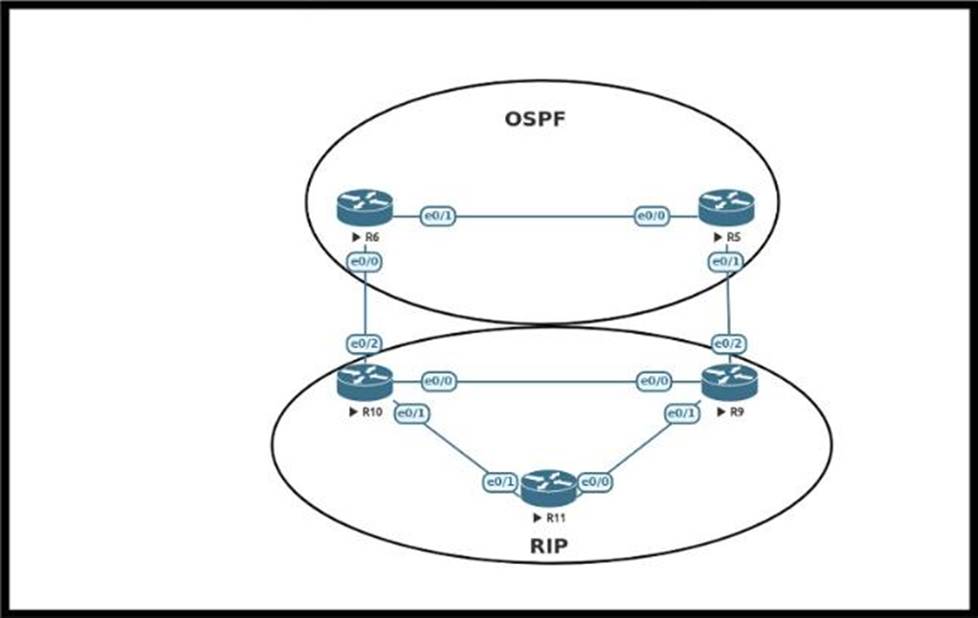
An engineer must configure OSPF with R9 and R10 and configure redistribution between OSPF and RIP causing a routing loop.
Which configuration on R9 and R10 meets this objective?
A)

B)

C)

D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer must block access to the console ports for all corporate remote Cisco devices based on the recent corporate security policy but the security team stilt can connect through the console port.
Which configuration on the console port resolves the issue?
- A . transport input telnet
- B . login and password
- C . no exec
- D . exec 0.0
C
Explanation:
“no exec” will disable access to a line. It is used if we want to allow only outgoing session (and disable incoming session) so this command will block all console port access.
There is no “exec 0 0” command. We can only find the “exec prompt” command in IOS Version 15.4(2)T4.
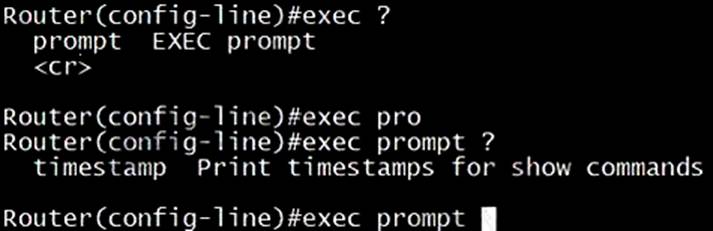
The most similar command is “exec-timeout 0 0” command, which is used to prevent Telnet/SSH sessions from timing out.
The network administrator must implement IPv6 in the network to allow only devices that not only have registered IP addresses but are also connecting from assigned locations.
Which security feature must be implemented?
- A . IPv6 Snooping
- B . IPv6 Destination Guard
- C . IPv6 Prefix Guard
- D . IPv6 Router Advertisement Guard
Refer to the exhibit.
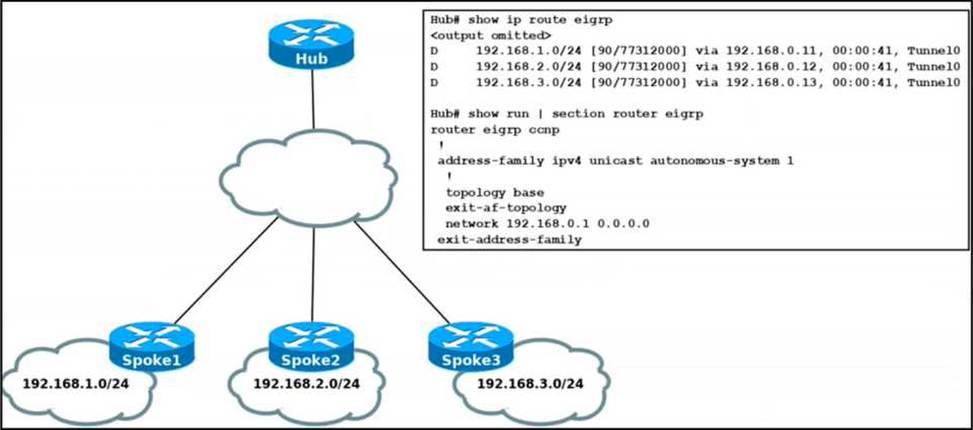
Spoke routers do not learn about each other’s routes in the DMVPN Phase2 network.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Remove default route from spoke routers to establish a spoke-to-spoke tunnel.
- B . Configure a static route in each spoke to establish a spoke-to-spoke tunnel.
- C . Rectify incorrect wildcard mask configured on the hub router network command.
- D . Disable EIGRP split horizon on the TunnelO interface of the hub router.
In a DMVPN network, the Spoke1 user observed that the voice traffic is coming to Spoke2 users via the hub router.
Which command is required on both spoke routers to communicate directly to one another?
- A . ip nhrp map dynamic
- B . ip nhrp shortcut
- C . ip nhrp nhs multicast
- D . ip nhrp redirect
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the MPLS concepts from the left onto the descriptions on the right.
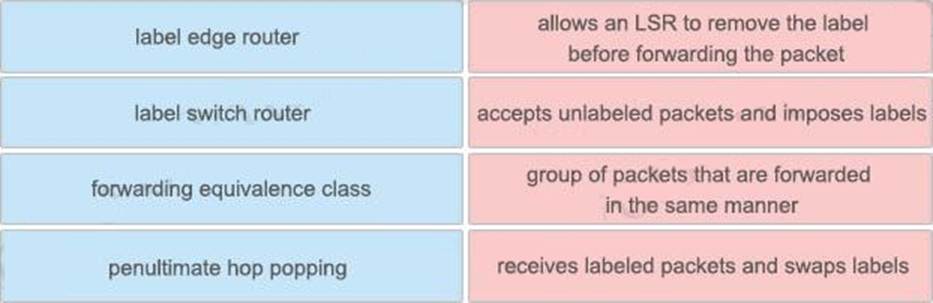
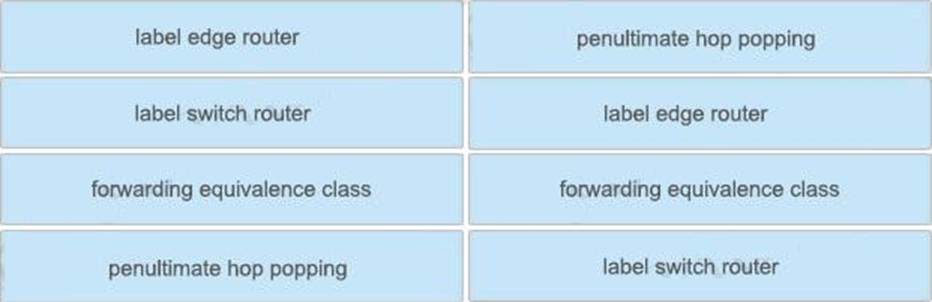
Explanation:
+ allows an LSR to remove the label before forwarding the packet: penultimate hop popping
+ accepts unlabeled packets and imposes labels: label edge router
+ group of packets that are forwarded in the same manner: forwarding equivalence class
+ receives labeled packets and swaps labels: label switch router
Explanation
A label edge router (LER, also known as edge LSR) is a router that operates at the edge of an MPLS network and acts as the entry and exit points for the network. LERs push an MPLS label onto an incoming packet and pop it off an outgoing packet.
A forwarding equivalence class (FEC) is a term
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer configured summarization for the R1 loopback addresses and failed.
Which action permits the successful advertisement of the R1 loopback addresses?
- A . Configure EIGRP 100 with a network statement for loopback 0 and configure and redistribute the static route for loopback 50.
- B . Configure EIGRP 100 with a network statement for loopback 0 and redistribute the connected route for loopback 50.
- C . Configure EIGRP 100 with a network statement for loopback 0 and remove the leak map for loopback 50.
- D . Configure 100.1.1.1 permit statement in the prefix list LOPPBACK50 and redistribute the connected route for loopback 50.
Refer to the exhibit.

A bank ATM site has difficulty connecting with the bank server. A network engineer troubleshoots the issue and finds that R4 has no active route to the bank ATM site.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Advertise 10.10.30.0/24 subnet in R1 EIGRP AS.
- B . EIGRP peering between R3 and R4 to be fixed.
- C . EIGRP peering between R1 and R2 to be fixed.
- D . Advertise 10.10.30.0/24 subnet in R3 EIGRP AS.
Refer to the exhibit.
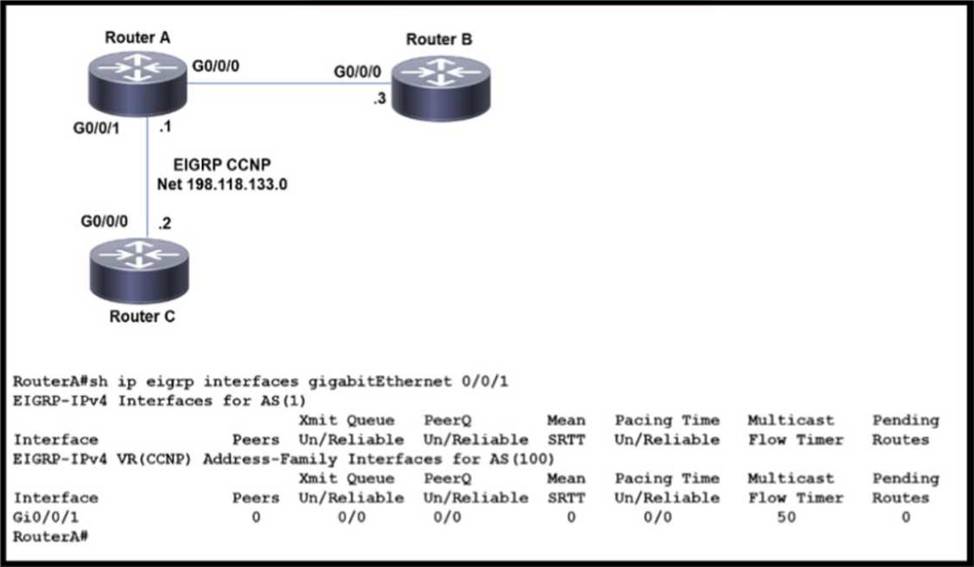
EIGRP adjacency between router A and router C is not working as expected.
Which two configurations resolve the issue? (Choose two)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
- E . Option E
