Practice Free SY0-701 Exam Online Questions
A company is adding a clause to its AUP that states employees are not allowed to modify the operating system on mobile devices.
Which of the following vulnerabilities is the organization addressing?
- A . Cross-site scripting
- B . Buffer overflow
- C . Jailbreaking
- D . Side loading
C
Explanation:
Jailbreaking is the process of removing the restrictions imposed by the manufacturer or carrier on a mobile device, such as an iPhone or iPad. Jailbreaking allows users to install unauthorized applications, modify system settings, and access root privileges. However, jailbreaking also exposes the device to potential security risks, such as malware, spyware, unauthorized access, data loss, and voided warranty. Therefore, an organization may prohibit employees from jailbreaking their mobile devices to prevent these vulnerabilities and protect the corporate data and network.: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide: Exam SY0-701, 9th Edition, Chapter 10: Mobile Device Security, page 507 2
Which of the following describes the understanding between a company and a client about what will be provided and the accepted time needed to provide the company with the resources?
- A . SLA
- B . MOU
- C . MOA
- D . BPA
A
Explanation:
A Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a formal document between a service provider and a client that defines the expected level of service, including what resources will be provided and the agreed-upon time frames. It typically includes metrics to evaluate performance, uptime guarantees, and response times.
MOU (Memorandum of Understanding) and MOA (Memorandum of Agreement) are less formal and may not specify the exact level of service.
BPA (Business Partners Agreement) focuses more on the long-term relationship between partners.
Which of the following is a benefit of launching a bug bounty program? (Select two)
- A . Transference of risk to a third party
- B . Reduction in the number of zero-day vulnerabilities
- C . Increased security awareness for the workforce
- D . Reduced cost of managing the program
- E . Quicker discovery of vulnerabilities
- F . Improved patch management process
B,E
Explanation:
Bug bounty programs invite vetted external researchers to report software vulnerabilities in exchange for rewards.
According to Security+ SY0-701, two major benefits are:
(1) Reduction in the number of zero-day vulnerabilities (B) C Ethical hackers can discover unknown vulnerabilities before malicious attackers do. These vulnerabilities are often zero-days because they
are unknown to vendors at the time of discovery. Bug bounty programs surface these issues early, helping organizations mitigate severe risks proactively.
(2) Quicker discovery of vulnerabilities (E) C A distributed network of global security researchers can identify vulnerabilities far faster than an internal team alone. This accelerates detection, increases coverage, and lowers attacker dwell time.
Option A (Transference of risk) is incorrect because bug bounties do not transfer risk―they help identify vulnerabilities.
C (Security awareness) relates to internal training, not bug bounties.
D (Reduced cost) is misleading; bug bounties can be expensive depending on payout structure.
F (Patch management) does not directly improve through bug bounty programs.
Therefore, the correct benefits are B and E.
A recent penetration test identified that an attacker could flood the MAC address table of network switches.
Which of the following would best mitigate this type of attack?
- A . Load balancer
- B . Port security
- C . IPS
- D . NGFW
B
Explanation:
Port security is the best mitigation technique for preventing an attacker from flooding the MAC address table of network switches. Port security can limit the number of MAC addresses learned on a port, preventing an attacker from overwhelming the switch’s MAC table (a form of MAC flooding attack). When the allowed number of MAC addresses is exceeded, port security can block additional devices or trigger alerts.
Load balancer distributes network traffic but does not address MAC flooding attacks.
IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) detects and prevents attacks but isn’t specifically designed for MAC flooding mitigation.
NGFW (Next-Generation Firewall) offers advanced traffic inspection but is not directly involved in MAC table security.
A security analyst finds a rogue device during a monthly audit of current endpoint assets that are connected to the network. The corporate network utilizes 002.1X for access control. To be allowed on the network, a device must have a Known hardware address, and a valid user name and password must be entered in a captive portal.
The following is the audit report:
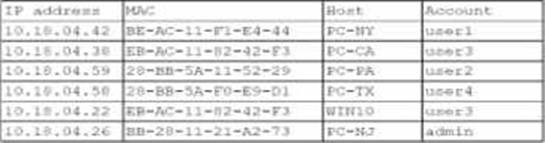
Which of the following is the most likely way a rogue device was allowed to connect?
- A . A user performed a MAC cloning attack with a personal device.
- B . A DMCP failure caused an incorrect IP address to be distributed
- C . An administrator bypassed the security controls for testing.
- D . DNS hijacking let an attacker intercept the captive portal traffic.
A
Explanation:
The most likely way a rogue device was able to connect to the network is through a MAC cloning attack. In this attack, a personal device copies the MAC address of an authorized device, bypassing the 802.1X access control that relies on known hardware addresses for network access. The matching MAC addresses in the audit report suggest that this technique was used to gain unauthorized network access.
CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 Course Content: Domain 03 Security Architecture.
CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 Study Guide: Chapter on Network Security and MAC Address Spoofing.
In order to strengthen a password and prevent a hacker from cracking it, a random string of 36 characters was added to the password.
Which of the following best describes this technique?
- A . Key stretching
- B . Tokenization
- C . Data masking
- D . Salting
D
Explanation:
Adding a random string of characters, known as a "salt," to a password before hashing it is known as salting. This technique strengthens passwords by ensuring that even if two users have the same password, their hashes will be different due to the unique salt, making it much harder for attackers
to crack passwords using precomputed tables.: CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 course content and official CompTIA study resources.
Which of the following describes the reason root cause analysis should be conducted as part of incident response?
- A . To gather loCs for the investigation
- B . To discover which systems have been affected
- C . To eradicate any trace of malware on the network
- D . To prevent future incidents of the same nature
D
Explanation:
Root cause analysis is a process of identifying and resolving the underlying factors that led to an incident. By conducting root cause analysis as part of incident response, security professionals can learn from the incident and implement corrective actions to prevent future incidents of the same nature. For example, if the root cause of a data breach was a weak password policy, the security team can enforce a stronger password policy and educate users on the importance of password security. Root cause analysis can also help to improve security processes, policies, and procedures, and to enhance security awareness and culture within the organization. Root cause analysis is not meant to gather loCs (indicators of compromise) for the investigation, as this is a task performed during the identification and analysis phases of incident response. Root cause analysis is also not meant to discover which systems have been affected or to eradicate any trace of malware on the network, as these are tasks performed during the containment and eradication phases of incident response. = CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 Certification Study Guide, page 424-425; Professor Messer’s CompTIA SY0-701 Security+ Training Course, video 5.1 – Incident Response, 9:55 – 11:18.
Which of the following would best explain why a security analyst is running daily vulnerability scans on all corporate endpoints?
- A . To track the status of patching installations
- B . To find shadow IT cloud deployments
- C . To continuously the monitor hardware inventory
- D . To hunt for active attackers in the network
A
Explanation:
Running daily vulnerability scans on all corporate endpoints is primarily done to track the status of patching installations. These scans help identify any missing security patches or vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Keeping the endpoints up-to-date with the latest patches is critical for maintaining security.
Finding shadow IT cloud deployments and monitoring hardware inventory are better achieved through other tools.
Hunting for active attackers would typically involve more real-time threat detection methods than daily vulnerability scans.
A university uses two different cloud solutions for storing student data.
Which of the following does this scenario represent?
- A . Load balancing
- B . Parallel processing
- C . Platform diversity
- D . Clustering
C
Explanation:
Using two different cloud solutions to store data is an example of platform diversity, which helps reduce dependency on a single cloud provider and enhances resilience against vendor-specific failures or outages.
Load balancing (A) distributes workloads across resources; parallel processing (B) refers to simultaneous processing of tasks; clustering (D) involves grouping servers to act as a single system.
Platform diversity is a recognized architectural strategy to improve availability and fault tolerance, covered in Security Architecture concepts for SY0-701 【 6:Chapter 10†CompTIA Security+ Study Guide 】
A government worker secretly copies classified files that contain defense tactics information to an external drive. The government worker then gives the external drive to a corrupt organization.
Which of the following best describes the motivation of the worker?
- A . Espionage
- B . Data exfiltration
- C . Financial gain
- D . Blackmail
A
Explanation:
The act described is espionage, where classified information is stolen and provided to adversaries or unauthorized parties, usually for political, military, or strategic advantage.
Data exfiltration (B) is the technical act of stealing data but doesn’t specify motivation. Financial gain (C) or blackmail (D) could be motivations but are not clearly indicated here.
Espionage is a classic threat actor motivation outlined in the Threats domain 【 6:Chapter 2†CompTIA Security+ Study Guide 】 .
