Practice Free SY0-701 Exam Online Questions
A security engineer at a large company needs to enhance IAM to ensure that employees can only access corporate systems during their shifts.
Which of the following access controls should the security engineer implement?
- A . Role-based
- B . Time-of-day restrictions
- C . Least privilege
- D . Biometric authentication
B
Explanation:
Detailed
Time-of-day restrictions limit access to corporate systems based on predefined schedules. This ensures employees can only access resources during their assigned work hours.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 Study Guide, Domain 3: Security Architecture, Section: "Access Control Models".
Which of the following is used to validate a certificate when it is presented to a user?
- A . OCSP
- B . CSR
- C . CA
- D . CRC
A
Explanation:
OCSP stands for Online Certificate Status Protocol. It is a protocol that allows applications to check the revocation status of a certificate in real-time. It works by sending a query to an OCSP responder, which is a server that maintains a database of revoked certificates. The OCSP responder returns a response that indicates whether the certificate is valid, revoked, or unknown. OCSP is faster and more efficient than downloading and parsing Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs), which are large files that contain the serial numbers of all revoked certificates issued by a Certificate Authority (CA).: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide: Exam SY0-701, 9th Edition, page 337 1
A security analyst finds a rogue device during a monthly audit of current endpoint assets that are connected to the network. The corporate network utilizes 002.1X for access control. To be allowed on the network, a device must have a Known hardware address, and a valid user name and password must be entered in a captive portal.
The following is the audit report:
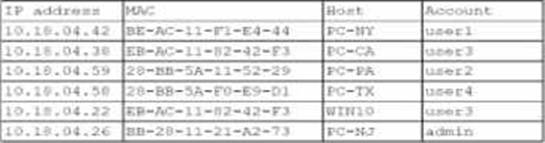
Which of the following is the most likely way a rogue device was allowed to connect?
- A . A user performed a MAC cloning attack with a personal device.
- B . A DMCP failure caused an incorrect IP address to be distributed
- C . An administrator bypassed the security controls for testing.
- D . DNS hijacking let an attacker intercept the captive portal traffic.
Which of the following security principles most likely requires validation before allowing traffic between systems?
- A . Policy enforcement
- B . Authentication
- C . Zero Trust architecture
- D . Confidentiality
C
Explanation:
Zero Trust architecture is based on the principle of "never trust, always verify," meaning all traffic between systems must be authenticated and authorized before communication is allowed, regardless of network location.
Policy enforcement (A) is important but broader. Authentication (B) is a component of Zero Trust, and confidentiality (D) refers to data protection, not access validation.
Zero Trust is a modern security framework emphasized in Security Architecture for securing enterprise environments 【 6:Chapter 3†CompTIA Security+ Study Guide 】 .
Which of the following would be the best way to handle a critical business application that is running on a legacy server?
- A . Segmentation
- B . Isolation
- C . Hardening
- D . Decommissioning
C
Explanation:
A legacy server is a server that is running outdated or unsupported software or hardware, which may pose security risks and compatibility issues. A critical business application is an application that is essential for the operation and continuity of the business, such as accounting, payroll, or inventory management. A legacy server running a critical business application may be difficult to replace or upgrade, but it should not be left unsecured or exposed to potential threats.
One of the best ways to handle a legacy server running a critical business application is to harden it. Hardening is the process of applying security measures and configurations to a system to reduce its attack surface and vulnerability. Hardening a legacy server may involve steps such as:
Applying patches and updates to the operating system and the application, if available
Removing or disabling unnecessary services, features, or accounts
Configuring firewall rules and network access control lists to restrict inbound and outbound traffic
Enabling encryption and authentication for data transmission and storage
Implementing logging and monitoring tools to detect and respond to anomalous or malicious activity
Performing regular backups and testing of the system and the application
Hardening a legacy server can help protect the critical business application from unauthorized access, modification, or disruption, while maintaining its functionality and availability. However, hardening a legacy server is not a permanent solution, and it may not be sufficient to address all the security issues and challenges posed by the outdated or unsupported system. Therefore, it is advisable to plan for the eventual decommissioning or migration of the legacy server to a more secure and modern platform, as soon as possible.
: CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 Certification Study Guide, Chapter 3: Architecture and Design, Section 3.2: Secure System Design, Page 133 1; CompTIA Security+ Certification Exam Objectives, Domain 3: Architecture and Design, Objective 3.2: Explain the importance of secure system design, Subobjective: Legacy systems 2
A company is implementing a policy to allow employees to use their personal equipment for work.
However, the company wants to ensure that only company-approved applications can be installed.
Which of the following addresses this concern?
- A . MDM
- B . Containerization
- C . DLP
- D . FIM
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
Mobile Device Management (MDM) is a security solution that allows organizations to enforce policies on employee-owned or company-issued mobile devices. It can restrict the installation of unauthorized applications, ensuring that only company-approved apps are used. Containerization isolates work applications from personal applications but does not enforce app restrictions.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)focuses on preventing sensitive data leaks rather than managing app installations.
File Integrity Monitoring (FIM)tracks changes to files and system configurations but does not control app installations.
Therefore, MDM is the best solution for restricting unauthorized applications on personal devices.
An organization would like to store customer data on a separate part of the network that is not accessible to users on the main corporate network.
Which of the following should the administrator
use to accomplish this goal?
- A . Segmentation
- B . Isolation
- C . Patching
- D . Encryption
A
Explanation:
Segmentation is a network design technique that divides the network into smaller and isolated segments based on logical or physical boundaries. Segmentation can help improve network security by limiting the scope of an attack, reducing the attack surface, and enforcing access control policies. Segmentation can also enhance network performance, scalability, and manageability. To accomplish the goal of storing customer data on a separate part of the network, the administrator can use segmentation technologies such as subnetting, VLANs, firewalls, routers, or switches.: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide: Exam SY0-701, 9th Edition, page 308-309 1
Which of the following describes effective change management procedures?
- A . Approving the change after a successful deployment
- B . Having a backout plan when a patch fails
- C . Using a spreadsheet for tracking changes
- D . Using an automatic change control bypass for security updates
B
Explanation:
Effective change management requires structured planning, testing, review, approval, deployment, and rollback capabilities. According to CompTIA Security+ SY0-701, one of the most critical components of change management is having a backout plan, which allows the organization to safely revert changes if the update or patch causes issues, operational disruption, or security instability. A proper backout plan reduces downtime, maintains system availability, and protects against unexpected failures.
Approving a change after deployment (A) violates standard change management protocols. Approval must occur before live implementation. Using a spreadsheet (C) is not considered an effective or secure change management mechanism. Automatic bypassing of change controls (D) is dangerous, even for security patches, because changes must be tested to avoid service outages or unintended vulnerabilities.
Therefore, the best description of effective change management is B: Having a backout plan when a patch fails.
A company is developing a critical system for the government and storing project information on a file share.
Which of the following describes how this data will most likely be classified? (Select two).
- A . Private
- B . Confidential
- C . Public
- D . Operational
- E . Urgent
- F . Restricted
B,F
Explanation:
Data classification is the process of assigning labels to data based on its sensitivity and business impact. Different organizations and sectors may have different data classification schemes, but a common one is the following1:
Public: Data that can be freely disclosed to anyone without any harm or risk.
Private: Data that is intended for internal use only and may cause some harm or risk if disclosed.
Confidential: Data that is intended for authorized use only and may cause significant harm or risk if disclosed.
Restricted: Data that is intended for very limited use only and may cause severe harm or risk if disclosed.
In this scenario, the company is developing a critical system for the government and storing project information on a file share. This data is likely to be classified as confidential and restricted, because it is not meant for public or private use, and it may cause serious damage to national security or public safety if disclosed. The government may also have specific requirements or regulations for handling such data, such as encryption, access control, and auditing2.: 1: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide:
Exam SY0-701, 9th Edition, page 16-17 2: Data Classification Practices: Final Project Description Released
A company’s web filter is configured to scan the URL for strings and deny access when matches are found.
Which of the following search strings should an analyst employ to prohibit access to non-encrypted websites?
- A . encryption=off
- B . http://
- C . www.*.com
- D . :443
B
Explanation:
A web filter is a device or software that can monitor, block, or allow web traffic based on predefined rules or policies. One of the common methods of web filtering is to scan the URL for strings and deny access when matches are found. For example, a web filter can block access to websites that contain the words “gambling”, “porn”, or “malware” in their URLs. A URL is a uniform resource locator that identifies the location and protocol of a web resource. A URL typically consists of the following components: protocol://domain:port/path?query#fragment.The protocol specifies the communication method used to access the web resource, such as HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, or SMTP. The domain is the name of the web server that hosts the web resource, such as www.google.com or www.bing.com. The port is an optional number that identifies the specific service or application running on the web server, such as 80 for HTTP or 443 for HTTPS. The path is the specific folder or file name of the web resource, such as /index.html or /images/logo.png. The query is an optional string that contains additional information or parameters for the web resource, such as ?q=security or ?lang=en. The fragment is an optional string that identifies a specific part or section of the web resource, such as #introduction or #summary.
To prohibit access to non-encrypted websites, an analyst should employ a search string that matches the protocol of non-encrypted web traffic, which is HTTP. HTTP stands for hypertext transfer protocol,
and it is a standard protocol for transferring data between web servers and web browsers. However, HTTP does not provide any encryption or security for the data, which means that anyone who intercepts the web traffic can read or modify the data. Therefore, non-encrypted websites are vulnerable to eavesdropping, tampering, or spoofing attacks. To access a non-encrypted website, the URL usually starts with http://, followed by the domain name and optionally the port number. For example, http://www.example.com or http://www.example.com:80. By scanning the URL for the string http://, the web filter can identify and block non-encrypted websites.
The other options are not correct because they do not match the protocol of non-encrypted web traffic. Encryption=off is a possible query string that indicates the encryption status of the web resource, but it is not a standard or mandatory parameter. Https:// is the protocol of encrypted web traffic, which uses hypertext transfer protocol secure (HTTPS) to provide encryption and security for the data. Www.*.com is a possible domain name that matches any website that starts with www and ends with .com, but it does not specify the protocol. :443 is the port number of HTTPS, which is the protocol of encrypted web traffic. = CompTIA Security+ Study Guide (SY0-701), Chapter 2: Securing Networks, page 69. Professor Messer’s CompTIA SY0-701 Security+ Training Course, Section 2.1: Network Devices and Technologies, video: Web Filter (5:16).
