Practice Free DP-300 Exam Online Questions
DRAG DROP
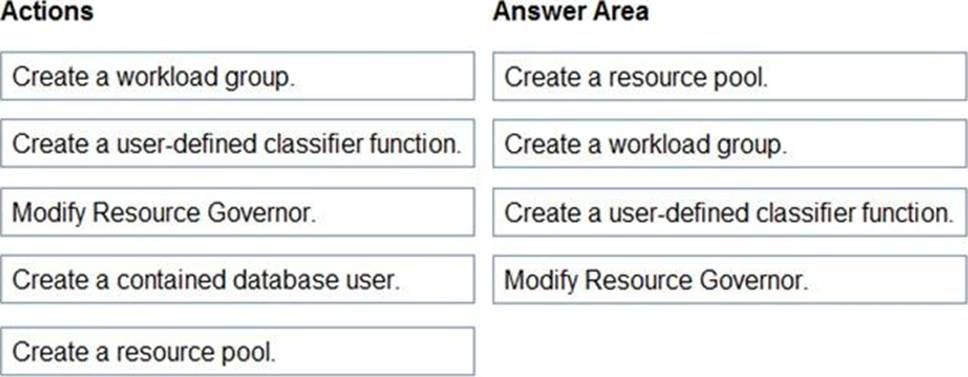
You have an Azure SQL managed instance named SQLMI1 that has Resource Governor enabled and is used by two apps named App1 and App2.
You need to configure SQLMI1 to limit the CPU and memory resources that can be allocated to App1.
Which four actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Explanation:
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/resource-governor/resource-governor?view=sql-server-ver15
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/resource-governor/create-and-test-a-classifier-user-defined-function?view=sql-server-ver15
HOTSPOT
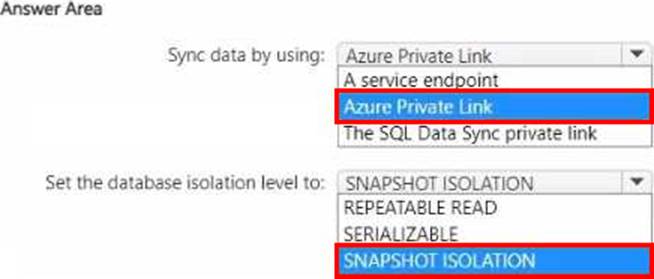
You have an Azure virtual machine named Server1 that has Microsoft SQL Server installed. Server1 contains a database named DB1.
You have a logical SQL server named ASVR1 that contains an Azure SQL database named ADB1.
You plan to use SQL Data Sync to migrate DB1 from Server! to ASVR1.
You need to prepare the environment for the migration. The solution must ensure that the connection from Server1 to ADB1 does NOT use a public endpoint.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
What should you implement to meet the disaster recovery requirements for the PaaS solution?
- A . Availability Zones
- B . failover groups
- C . Always On availability groups
- D . geo-replication
B
Explanation:
Scenario: In the event of an Azure regional outage, ensure that the customers can access the PaaS
solution with minimal downtime. The solution must provide automatic failover.
The auto-failover groups feature allows you to manage the replication and failover of a group of databases on a server or all databases in a managed instance to another region. It is a declarative abstraction on top of the existing active geo-replication feature, designed to simplify deployment and management of geo-replicated databases at scale. You can initiate failover manually or you can delegate it to the Azure service based on a user-defined policy.
The latter option allows you to automatically recover multiple related databases in a secondary region after a catastrophic failure or other unplanned event that results in full or partial loss of the SQL Database or SQL Managed Instance availability in the primary region.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/auto-failover-group-overview
You have SQL Server 2019 on an Azure virtual machine that runs Windows Server 2019. The virtual machine has 4 vCPUs and 28 GB of memory.
You scale up the virtual machine to 16 vCPUSs and 64 GB of memory.
You need to provide the lowest latency for tempdb.
What is the total number of data files that tempdb should contain?
- A . 2
- B . 4
- C . 8
- D . 64
D
Explanation:
The number of files depends on the number of (logical) processors on the machine. As a general rule, if the number of logical processors is less than or equal to eight, use the same number of data files as logical processors. If the number of logical processors is greater than eight, use eight data files and then if contention continues, increase the number of data files by multiples of 4 until the contention is reduced to acceptable levels or make changes to the workload/code.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/databases/tempdb-database
You have an Azure subscription.
You plan to deploy four SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines instances to two Azure regions. Two instances will be deployed to each region. Each region will host a domain-independent availability group. You need to recommend a high availability, disaster recovery (HA/DR) solution for the planned deployment. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
What should you include in the recommendation?
- A . a Network Load Balancing (NLB) cluster
- B . a workgroup cluster
- C . an Active Directory-detached cluster
- D . a Hyper-V cluster
You have a Microsoft SQL Server 2019 database named DB1 and an Azure SQL managed instance named SQLMI1. You need to move a SQL Server Agent job from DB1 to SQLMI1.
Which job attribute is unsupported in SQLMI1?
- A . log to table
- B . email notifications
- C . schedules
- D . output files
You have an on-premises datacenter that contains a 2-TB Microsoft SQL Server 2019 database named DB1.
You need to recommend a solution to migrate DB1 to an Azure SQL managed instance. The solution must minimize downtime and administrative effort.
What should you include in the recommendation?
- A . Log Replay Service (LRS)
- B . log shipping
- C . transactional replication
- D . SQL Data Sync
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1.
You need to ensure that DB1 will support automatic failover without data loss if a datacenter fails.
The solution must minimize costs.
Which deployment option and pricing tier should you configure?
- A . Azure SQL Database Hyperscale
- B . Azure SQL Database managed instance General Purpose
- C . Azure SQL Database Premium
- D . Azure SQL Database Basic
C
Explanation:
By default, the cluster of nodes for the premium availability model is created in the same datacenter. With the introduction of Azure Availability Zones, SQL Database can place different replicas of the Business Critical database to different availability zones in the same region. To eliminate a single point of failure, the control ring is also duplicated across multiple zones as three gateway rings (GW). The routing to a specific gateway ring is controlled by Azure Traffic Manager (ATM). Because the zone redundant configuration in the Premium or Business Critical service tiers does not create additional database redundancy, you can enable it at no extra cost. By selecting a zone redundant configuration, you can make your Premium or Business Critical databases resilient to a much larger set of failures, including catastrophic datacenter outages, without any changes to the application logic. You can also convert any existing Premium or Business Critical databases or pools to the zone redundant configuration.
Incorrect Answers:
C. This feature is not available in SQL Managed Instance.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/high-availability-sla
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure Data Factory instance named ADF1 and two Azure Synapse Analytics workspaces named WS1 and WS2.
ADF1 contains the following pipelines:
✑ P1: Uses a copy activity to copy data from a nonpartitioned table in a dedicated SQL pool of WS1 to an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account
✑ P2: Uses a copy activity to copy data from text-delimited files in an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account to a nonpartitioned table in a dedicated SQL pool of WS2
You need to configure P1 and P2 to maximize parallelism and performance.
Which dataset settings should you configure for the copy activity of each pipeline? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.


Explanation:
P1: Set the Partition option to Dynamic Range.
The SQL Server connector in copy activity provides built-in data partitioning to copy data in parallel.
P2: Set the Copy method to PolyBase
Polybase is the most efficient way to move data into Azure Synapse Analytics. Use the staging blob feature to achieve high load speeds from all types of data stores, including Azure Blob storage and Data Lake Store. (Polybase supports Azure Blob storage and Azure Data Lake Store by default.)
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-factory/connector-azure-sql-data-warehouse
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-factory/load-azure-sql-data-warehouse
You receive numerous alerts from Azure Monitor for an Azure SQL database.
You need to reduce the number of alerts. You must only receive alerts if there is a significant change in usage patterns for an extended period.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A . Set Threshold Sensitivity to High
- B . Set the Alert logic threshold to Dynamic
- C . Set the Alert logic threshold to Static
- D . Set Threshold Sensitivity to Low
- E . Set Force Plan to On
BD
Explanation:
B: Dynamic Thresholds continuously learns the data of the metric series and tries to model it using a set of algorithms and methods. It detects patterns in the data such as seasonality (Hourly / Daily / Weekly), and is able to handle noisy metrics (such as machine CPU or memory) as well as metrics with low dispersion (such as availability and error rate).
D: Alert threshold sensitivity is a high-level concept that controls the amount of deviation from metric behavior required to trigger an alert.
Low C The thresholds will be loose with more distance from metric series pattern. An alert rule will only trigger on large deviations, resulting in fewer alerts.
Incorrect Answers:
A: High C The thresholds will be tight and close to the metric series pattern. An alert rule will be triggered on the smallest deviation, resulting in more alerts.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/platform/alerts-dynamic-thresholds
