Practice Free DP-300 Exam Online Questions
You have a new Azure SQL database. The database contains a column that stores confidential information.
You need to track each time values from the column are returned in a query. The tracking information must be stored for 365 days from the date the query was executed.
Which three actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A . Turn on auditing and write audit logs to an Azure Storage account.
- B . Add extended properties to the column.
- C . Turn on Advanced Data Security for the Azure SQL server.
- D . Apply sensitivity labels named Highly Confidential to the column.
- E . Turn on Azure Advanced Threat Protection (ATP).
ACD
Explanation:
C: Advanced Data Security (ADS) is a unified package for advanced SQL security capabilities. ADS is available for Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse Analytics. It includes functionality for discovering and classifying sensitive data
D: You can apply sensitivity-classification labels persistently to columns by using new metadata attributes that have been added to the SQL Server database engine. This metadata can then be used for advanced, sensitivity-based auditing and protection scenarios.
A: An important aspect of the information-protection paradigm is the ability to monitor access to sensitive data. Azure SQL Auditing has been enhanced to include a new field in the audit log called data_sensitivity_information. This field logs the sensitivity classifications (labels) of the data that was returned by a query. Here’s an example:
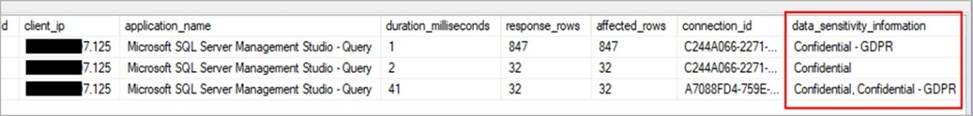
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/data-discovery-and-classification-overview
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1.
A user named User 1 has an Azure AD account.
You need to provide User1 with the ability to add and remove columns from the tables inDBV. The solution must use the principle of least privilege.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point
- A . Assign the database user the db.ddladmm role.
- B . Assign the database user the db.owner role.
- C . Create a contained database user.
- D . Create a login and an associated database user.
DRAG DROP
You plan to create a table in an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool.
Data in the table will be retained for five years. Once a year, data that is older than five years will be deleted.
You need to ensure that the data is distributed evenly across partitions. The solutions must minimize the amount of time required to delete old data.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, drag the appropriate values to the correct targets. Each value may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
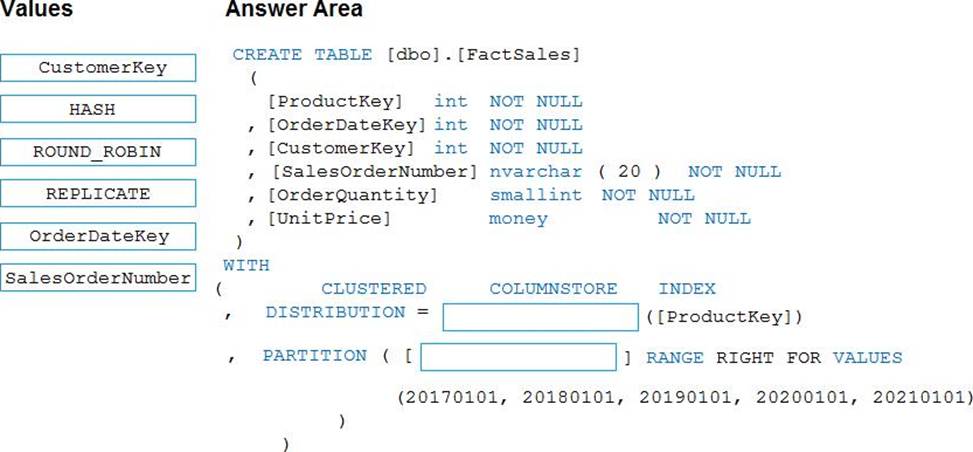
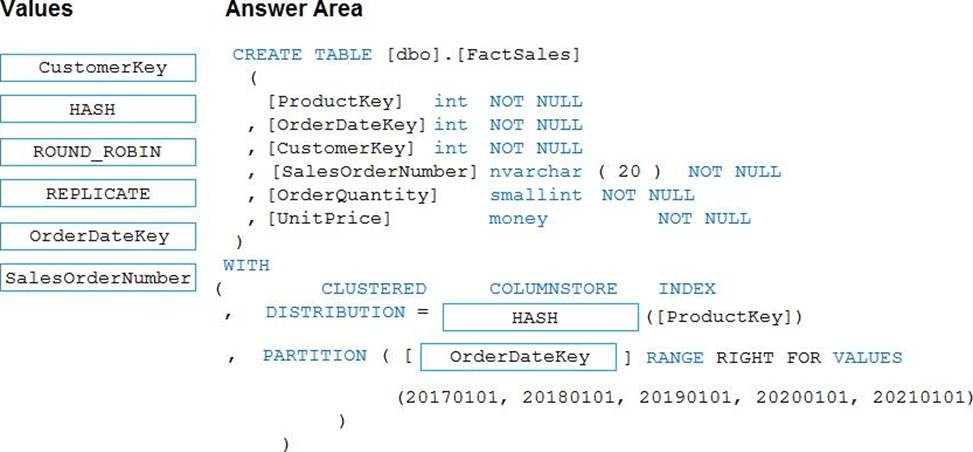
Explanation:
Box 1: HASH
Box 2: OrderDateKey
In most cases, table partitions are created on a date column.
A way to eliminate rollbacks is to use Metadata Only operations like partition switching for data management. For example, rather than execute a DELETE statement to delete all rows in a table where the order_date was in October of 2001, you could partition your data early. Then you can switch out the partition with data for an empty partition from another table.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/create-table-azure-sql-data-warehouse
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql/best-practices-dedicated-sql-pool
You have five on-premises servers that have Microsoft SQL Server 2022 Enterprise installed Each server contains multiple database that store data for web apps and are backed up by using a third-party backup solution.
You plan to migrate the databases to Azure.
You need to recommend a solution to host the databases.
The solution must meet the following requirements:
• Compute and storage resources must be shared across the databases.
• Costs must be minimized.
What should you include in the recommendation?
- A . SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines
- B . in Azure SQL Database elastic pool
- C . Azure SQL Database
- D . Azure SQL Managed Instance
SIMULATION
Task 5
You need to configure a disaster recovery solution for db1. When a failover occurs, the connection strings to the database must remain the same. The secondary server must be in the West US 3 Azure region.
Here are the steps to create a failover group for db1 with the secondary server in the West US 3 region:
Using the Azure portal:
Go to the Azure portal and select your Azure SQL Database server that hosts db1.
Select Failover groups in the left menu and click on Add group.
Enter a name for the failover group and select West US 3 as the secondary region.
Click on Create a new server and enter the details for the secondary server, such as server name, admin login, password, and subscription.
Click on Select existing database(s) and choose db1 from the list of databases on the primary server.
Click on Configure failover policy and select the failover mode, grace period, and read-write failover endpoint mode according to your preferences.
Click on Create to create the failover group and start the replication of db1 to the secondary server.
Using PowerShell commands:
Install the Azure PowerShell module and log in with your Azure account.
Run the following command to create a new server in the West US 3 region: New-AzSqlServer – ResourceGroupName <your-resource-group-name> -ServerName <your-secondary-server-name> – Location "West US 3" -SqlAdministratorCredentials $(New-Object -TypeName System.Management.Automation.PSCredential -ArgumentList "<your-admin-login>", $(ConvertTo-SecureString -String "<your-password>" -AsPlainText -Force))
Run the following command to create a new failover group with db1: New-AzSqlDatabaseFailoverGroup -ResourceGroupName <your-resource-group-name> -ServerName <your-primary-server-name> -PartnerResourceGroupName <your-resource-group-name> – PartnerServerName <your-secondary-server-name> -FailoverGroupName <your-failover-group-name> -Database db1 -FailoverPolicy Manual -GracePeriodWithDataLossHours 1 – ReadWriteFailoverEndpoint "Enabled"
You can modify the parameters of the command according to your preferences, such as the failover policy, grace period, and read-write failover endpoint mode.
These are the steps to create a failover group for db1 with the secondary server in the West US 3 region.
HOTSPOT
You need to recommend the appropriate purchasing model and deployment option for the 30 new databases. The solution must meet the technical requirements and the business requirements.
What should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
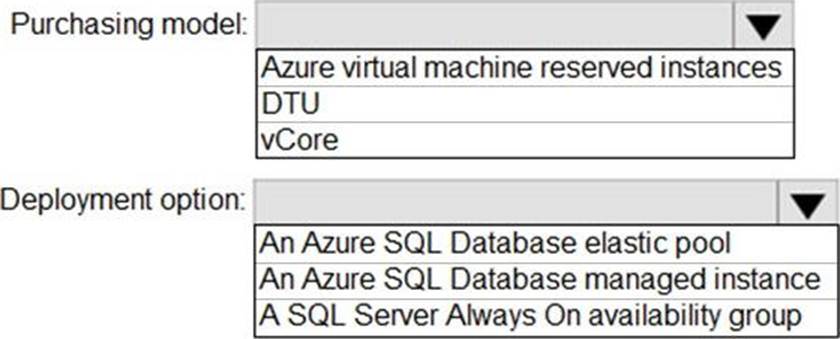
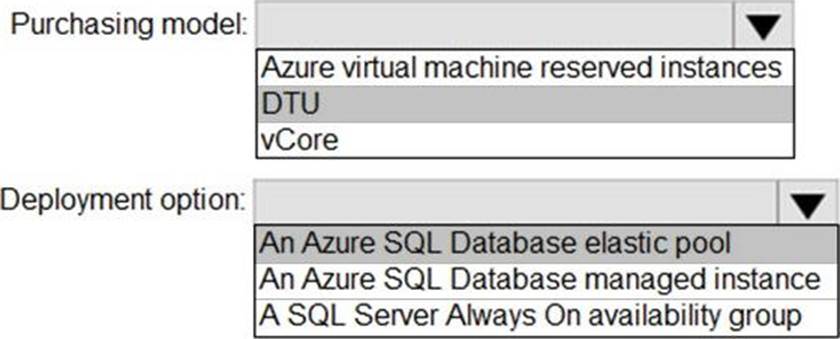
Explanation:
Box 1: DTU
Scenario:
✑ The 30 new databases must scale automatically.
✑ Once all requirements are met, minimize costs whenever possible.
You can configure resources for the pool based either on the DTU-based purchasing model or the vCore-based purchasing model.
In short, for simplicity, the DTU model has an advantage. Plus, if you’re just getting started with Azure SQL Database, the DTU model offers more options at the lower end of performance, so you can get started at a lower price point than with vCore.
Box 2: An Azure SQL database elastic pool
Azure SQL Database elastic pools are a simple, cost-effective solution for managing and scaling multiple databases that have varying and unpredictable usage demands. The databases in an elastic pool are on a single server and share a set number of resources at a set price. Elastic pools in Azure SQL Database enable SaaS developers to optimize the price performance for a group of databases within a prescribed budget while delivering performance elasticity for each database.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/elastic-pool-overview
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/reserved-capacity-overview
What should you do after a failover of SalesSQLDb1 to ensure that the database remains accessible to SalesSQLDb1App1?
- A . Configure SalesSQLDb1 as writable.
- B . Update the connection strings of SalesSQLDb1App1.
- C . Update the firewall rules of SalesSQLDb1.
- D . Update the users in SalesSQLDb1.
B
Explanation:
Scenario: SalesSQLDb1 uses database firewall rules and contained database users.
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure SQL database named DB 1 in the General Purpose service tier.
You need to monitor DB 1 by using SQL Insights.
What should you include in the solution? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
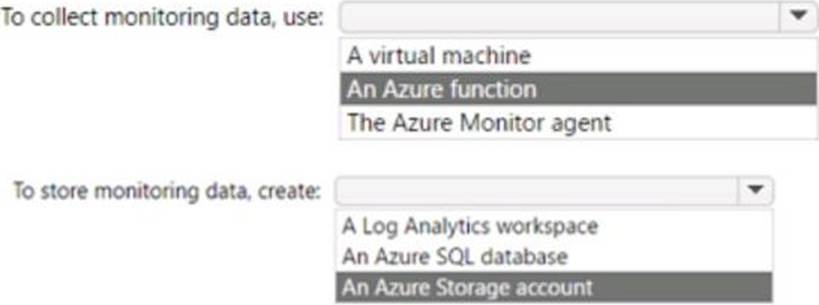
Explanation:
Box 1 = Azure Monitor Agent
Box 2 = An Azure SQL database
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/sql-database-paas-overview?view=azuresql
You have an Azure Databricks workspace named workspace1 in the Standard pricing tier. Workspace1 contains an all-purpose cluster named cluster1.
You need to reduce the time it takes for cluster1 to start and scale up. The solution must minimize costs.
What should you do first?
- A . Upgrade workspace1 to the Premium pricing tier.
- B . Configure a global init script for workspace1.
- C . Create a pool in workspace1.
- D . Create a cluster policy in workspace1.
C
Explanation:
You can use Databricks Pools to Speed up your Data Pipelines and Scale Clusters Quickly. Databricks Pools, a managed cache of virtual machine instances that enables clusters to start and scale 4 times faster.
Reference: https://databricks.com/blog/2019/11/11/databricks-pools-speed-up-data-pipelines.html
Topic 5, Lab / Simulation Tasks
SIMULATION
Task 1
In an Azure SQL database named db1, you need to enable page compression on the PK_SalesOrderHeader_SalesOrderlD clustered index of the SalesLT.SalesOrderHeader table.
— Connect to the Azure SQL database named db1 USE db1;
GO
— Enable page compression on the clustered index
ALTER INDEX PK_SalesOrderHeader_SalesOrderlD ON SalesLT.SalesOrderHeader
REBUILD WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE);
GO
This script will rebuild the clustered index with page compression, which can reduce the storage space and improve the query performance
The script solution consists of three parts:
The first part is USE db1; GO. This part connects to the Azure SQL database named db1, where the SalesLT.SalesOrderHeader table is located. The GO command separates the batches of Transact-SQL statements and sends them to the server.
The second part is ALTER INDEX PK_SalesOrderHeader_SalesOrderlD ON SalesLT.SalesOrderHeader REBUILD WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE); GO. This part enables page compression on the clustered index named PK_SalesOrderHeader_SalesOrderlD, which is defined on the SalesLT.SalesOrderHeader table. The ALTER INDEX statement modifies the properties of an existing index. The REBUILD option rebuilds the index from scratch, which is required to change the compression setting. The DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE option specifies that page compression is applied to the index, which means that both row and prefix compression are used. Page compression can reduce the storage space and improve the query performance by compressing the data at the page level. The GO command ends the batch of statements.
The third part is optional, but it can be useful to verify the compression status of the index. It is SELECT name, index_id, data_compression_desc FROM sys.indexes WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(‘SalesLT.SalesOrderHeader’);. This part queries the sys.indexes catalog view, which contains information about the indexes in the database. The SELECT statement returns the name, index_id, and data_compression_desc columns for the indexes that belong to the SalesLT.SalesOrderHeader table. The OBJECT_ID function returns the object identification number for the table name. The data_compression_desc column shows the compression type of the index, which should be PAGE for the clustered index after the script is executed.
These are the steps of the script solution for enabling page compression on the clustered index of the SalesLT.SalesOrderHeader table in db1.
