Practice Free DP-300 Exam Online Questions
You have the following Transact-SQL query.
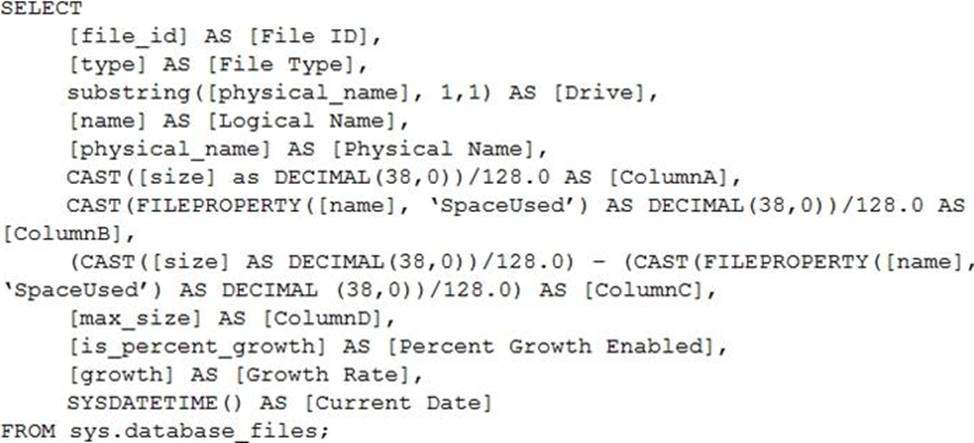
Which column returned by the query represents the free space in each file?
- A . ColumnA
- B . ColumnB
- C . ColumnC
- D . ColumnD
C
Explanation:
Example:
Free space for the file in the below query result set will be returned by the FreeSpaceMB column.
SELECT DB_NAME() AS DbName,
name AS FileName,
type_desc,
size/128.0 AS CurrentSizeMB,
size/128.0 – CAST(FILEPROPERTY(name, ‘SpaceUsed’) AS INT)/128.0 AS FreeSpaceMB
FROM sys.database_files
WHERE type IN (0,1);
Reference: https://www.sqlshack.com/how-to-determine-free-space-and-file-size-for-sql-server-databases/
You need to trigger an Azure Data Factory pipeline when a file arrives in an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 container.
Which resource provider should you enable?
- A . Microsoft.EventHub
- B . Microsoft.EventGrid
- C . Microsoft.Sql
- D . Microsoft.Automation
B
Explanation:
Event-driven architecture (EDA) is a common data integration pattern that involves production, detection, consumption, and reaction to events. Data integration scenarios often require Data Factory customers to trigger pipelines based on events happening in storage account, such as the arrival or deletion of a file in Azure Blob Storage account. Data Factory natively integrates with Azure Event Grid, which lets you trigger pipelines on such events.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-factory/how-to-create-event-trigger
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Data Factory version 2 (V2) data factory named df1.
DF1 contains a linked service.
You have an Azure Key vault named vault1 that contains an encryption kay named key1.
You need to encrypt df1 by using key1.
What should you do first?
- A . Disable purge protection on vault1.
- B . Remove the linked service from df1.
- C . Create a self-hosted integration runtime.
- D . Disable soft delete on vault1.
B
Explanation:
A customer-managed key can only be configured on an empty data Factory. The data factory can’t contain any resources such as linked services, pipelines and data flows. It is recommended to enable customer-managed key right after factory creation.
Note: Azure Data Factory encrypts data at rest, including entity definitions and any data cached while runs are in progress. By default, data is encrypted with a randomly generated Microsoft-managed key that is uniquely assigned to your data factory.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-factory/enable-customer-managed-key
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure Data Lake Storage account that contains a staging zone.
You need to design a daily process to ingest incremental data from the staging zone, transform the data by executing an R script, and then insert the transformed data into a data warehouse in Azure Synapse Analytics.
Solution: You use an Azure Data Factory schedule trigger to execute a pipeline that executes mapping data flow, and then inserts the data into the data warehouse.
Does this meet the goal?
- A . Yes
- B . No
B
Explanation:
If you need to transform data in a way that is not supported by Data Factory, you can create a custom activity, not a mapping flow,5 with your own data processing logic and use the activity in the pipeline. You can create a custom activity to run R scripts on your HDInsight cluster with R installed.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-US/azure/data-factory/transform-data
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure SQL database named DB1 that contains a table named Table 1.
You run a query to load data into Table1.
The performance metrics of Table1 during the load operation are shown in the following exhibit.
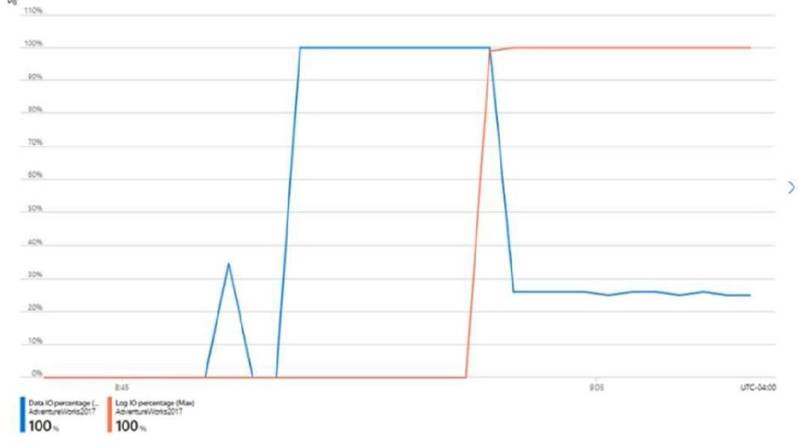
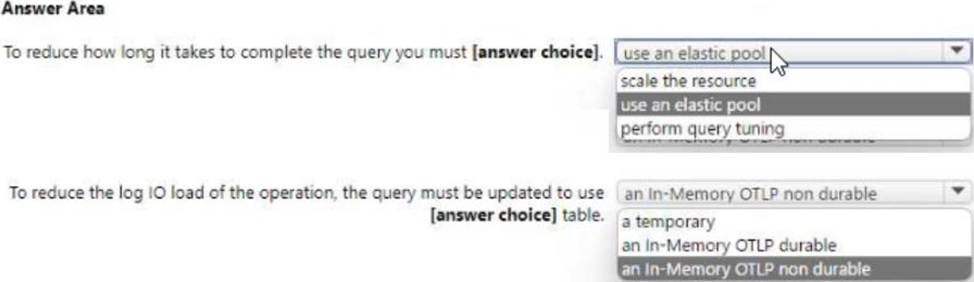
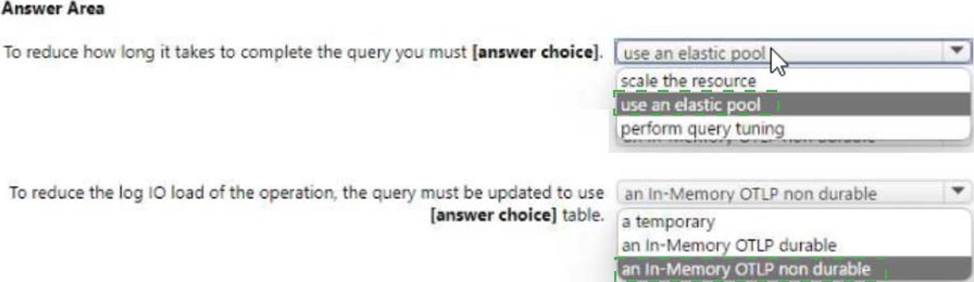
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
You have an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server 2022 instance that hosts a database named DB1. You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure SQL database named SQLDB1. You need to replicate DB1 to SQLDB1.
Which type of replication should you use?
- A . snapshot
- B . peer-to-peer
- C . merge
- D . transactional
You have an Azure Synapse Analytics Apache Spark pool named Pool1.
You plan to load JSON files from an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 container into the tables in Pool1.
The structure and data types vary by file.
You need to load the files into the tables. The solution must maintain the source data types.
What should you do?
- A . Load the data by using PySpark.
- B . Load the data by using the OPENROWSET Transact-SQL command in an Azure Synapse Analytics
serverless SQL pool. - C . Use a Get Metadata activity in Azure Data Factory.
- D . Use a Conditional Split transformation in an Azure Synapse data flow.
B
Explanation:
Serverless SQL pool can automatically synchronize metadata from Apache Spark. A serverless SQL pool database will be created for each database existing in serverless Apache Spark pools.
Serverless SQL pool enables you to query data in your data lake. It offers a T-SQL query surface area that accommodates semi-structured and unstructured data queries.
To support a smooth experience for in place querying of data that’s located in Azure Storage files, serverless SQL pool uses the OPENROWSET function with additional capabilities.
The easiest way to see to the content of your JSON file is to provide the file URL to the OPENROWSET
function, specify csv FORMAT.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql/query-json-files
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql/query-data-storage
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure SQL database.
You have a query and the associated execution plan as shown in the following exhibit.
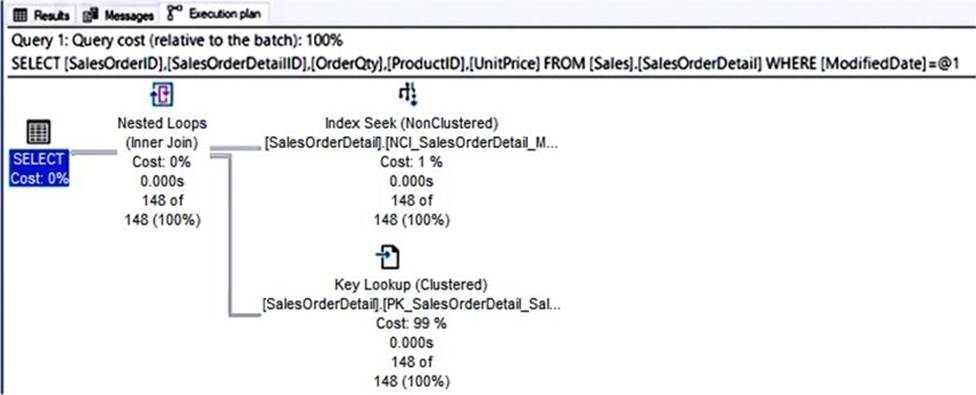
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Explanation:
Box 1: Key Lookup
The Key Lookup cost is 99% so that is the performance bottleneck.
Box 2: nonclustered index
The key lookup on the clustered index is used because the nonclustered index does not include the
required columns to resolve the query. If you add the required columns to the nonclustered index, the key lookup will not be required.
You have an Azure subscription that contains a SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines instance named SQLVMI. SQLVMI hosts a database named OBI.
You need to retrieve query plans from the Query Store on DBI.
What should you do first?
- A . On SQLVM1, install the SQL Server laaS Agent extension.
- B . From Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio, modify the properties of the SQL Server instance.
- C . From Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio, modify the properties of DB 1.
- D . On SQLVM1, install the Azure Monitor agent for Windows.
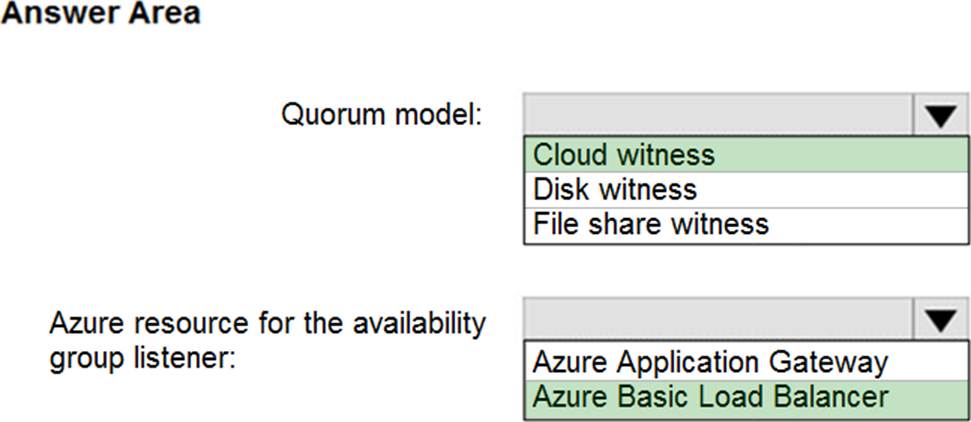
HOTSPOT
You need to recommend a configuration for ManufacturingSQLDb1 after the migration to Azure. The solution must meet the business requirements.
What should you include in the recommendation? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation:
Scenario: Business Requirements
Litware identifies business requirements include: meet an SLA of 99.99% availability for all Azure deployments.
Box 1: Cloud witness
If you have a Failover Cluster deployment, where all nodes can reach the internet (by extension of Azure), it is recommended that you configure a Cloud Witness as your quorum witness resource.
Box 2: Azure Basic Load Balancer
Microsoft guarantees that a Load Balanced Endpoint using Azure Standard Load Balancer, serving two or more Healthy Virtual Machine Instances, will be available 99.99% of the time.
Note: There are two main options for setting up your listener: external (public) or internal. The external (public) listener uses an internet facing load balancer and is associated with a public Virtual IP (VIP) that is accessible over the internet. An internal listener uses an internal load balancer and only supports clients within the same Virtual Network.
Reference:
https://technet.microsoft.com/windows-server-docs/failover-clustering/deploy-cloud-witness
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/support/legal/sla/load-balancer/v1_0/
