Practice Free 220-1201 Exam Online Questions
Which of the following cable types can be used to transfer data and video?
- A . USB-C
- B . HDMI
- C . DisplayPort
- D . VGA
A
Explanation:
USB-Cis a versatile connector capable of transmitting data, video, audio, and power. With standards like Display Port over USB-C or Thunderbolt 3/4, it can be used for external displays, file transfers, charging, and more all through one cable.
Option B (HDMI): Supports video and audio but not general data transfer.
Option C (DisplayPort): Similar to HDMI supports video/audio but not general file transfer.
Option D (VGA): Legacy analog video only no data or audio support. CompTIA A+ Core 1 Exam Objective
Reference: Objective 3.1: Identify common connector types.
A user prints a job from a laser printer. The user wipes the page, and the words and images come off of it. The technician replaces the toner cartridge, but the issue persists.
Which of the following components should the technician replace next?
- A . Fuser
- B . Drum
- C . Developer roller
- D . Discharge lamp
A
Explanation:
In laser printers, the fuser unit is responsible formelting the toner onto the paper using heat and pressure. If the toner rubs off easily, it’s a clear sign the fuser is failing or not heating properly. Replacing the fuser will ensure the toner bonds correctly to the paper.
Option B (Drum): Transfers the image, but doesn’t fuse the toner.
Option C (Developer roller): Applies toner to the drum wouldn’t cause toner to rub off.
Option D (Discharge lamp): Prepares the drum for a new image; not related to toner adhesion.
CompTIA A+ Core 1 Exam Objective
Reference: Objective 3.7: Given a scenario, troubleshoot common printer problems.
While reviewing options in the BIOS/UEFI settings page to fix a laptop issue, a support technician notices an option to clear existing TPM keys.
Which of the following would most likely happen if the TPM is cleared?
- A . Encrypted hard drives would probably not be accessible.
- B . All security certificates would need to be reinstalled from trusted roots.
- C . The device would need to be reenrolled in the MDM platform
- D . The laptop would need to be registered to the domain as a new client.
A
Explanation:
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a hardware-based security feature used to store cryptographic keys, such as those used for encryption, authentication, or device identification. It plays a critical role in ensuring secure operations for encrypted drives, BitLocker, and secure boot processes. Clearing TPM keys involves wiping all stored cryptographic data, which can lead to several consequences depending on what the TPM was being used for. Let’s break it down:
Correct Answer
Some users are unable to access their workstations.
An administrator runs ipconfig on one of the workstations and sees the following:
![]()
The administrator runs the following command and receives this output:

Which of the following is the source of issue?
- A . Web server
- B . Router
- C . DNS
- D . DHCP
B
Explanation:
The workstation’s IP configuration (192.168.1.27/24 with gateway 192.168.1.1) shows that it has a correct IP address, correct subnet mask, and expected default gateway for a typical small office network. Because the IP is in the correct private range and not an APIPA address (169.254.x.x), this also confirms that DHCP is functioning properly. Therefore, option D (DHCP) cannot be the cause.
The user then pings the default gateway at 192.168.1.1, which should be the router―the device providing routing between local devices and outside networks. The repeated "Request timed out" responses indicate the workstation cannot reach the router at all. This type of failure points directly to a router outage, a powered-off router, a failed router interface, or a physical disconnection of the router from the switch.
If DNS (C) were the issue, the user would still be able to ping the IP address of the gateway because DNS is not required for IP-to-IP connectivity. A web server (A) has no relation to local gateway communication and does not affect workstation access.
Since the workstation has a valid IP but cannot reach its default gateway, the failure point is the router.
A user reports that the print quality of their desk printer is poor. A technician replaces the ink cartridge, but this does not resolve the issue.
Which of the following should the technician do next?
- A . Replace the pickup rollers
- B . Clean the printheads
- C . Switch the paper type
- D . Change the ribbon
B
Explanation:
If print quality remains poor after replacing the ink cartridge, the next step is to clean the printheads. Printheads can become clogged with dried ink, especially in inkjet printers, causing streaks or faded output.
From the CompTIA A+ 220-1101 Official Study Guide, Objective 4.3 C Troubleshoot printing problems:
“Poor print quality after replacing cartridges is commonly caused by clogged or dirty printheads. Use the printer’s cleaning cycle or manually clean the printheads as needed.”
Verified Source:
CompTIA A+ Core 1 (220-1101) Official Study Guide, Chapter 4: Printer Troubleshooting CompTIA Exam Objectives 220-1101, Domain 4.3
Which of the following should a technician create to assign a permanent IP address to a PC using DHCP?
- A . Reservation
- B . Lease
- C . Exclusion
- D . Scope option
A
Explanation:
DHCP normally assigns IP addresses dynamically using timed leases, meaning the address may change after expiration. However, many devices―such as servers, printers, or specialized workstations―require permanent, predictable IP addresses. CompTIA A+ identifies a DHCP reservation as the correct method for assigning a consistent IP while still using DHCP.
A reservation binds a device’s MAC address to a specific IP address in the DHCP server. Each time the device requests an address, the DHCP server recognizes the MAC address and issues the same IP. This provides reliability while still allowing centralized management of network addressing.
A lease is temporary and not permanent. An exclusion simply removes certain IP addresses from the assignable pool―it does not assign any device a fixed address. A scope option configures additional network parameters such as DNS, gateway, or WINS settings but does not assign static IPs.
Therefore, a reservation is the correct method to permanently assign an IP address using DHCP without requiring static configuration on the device itself.
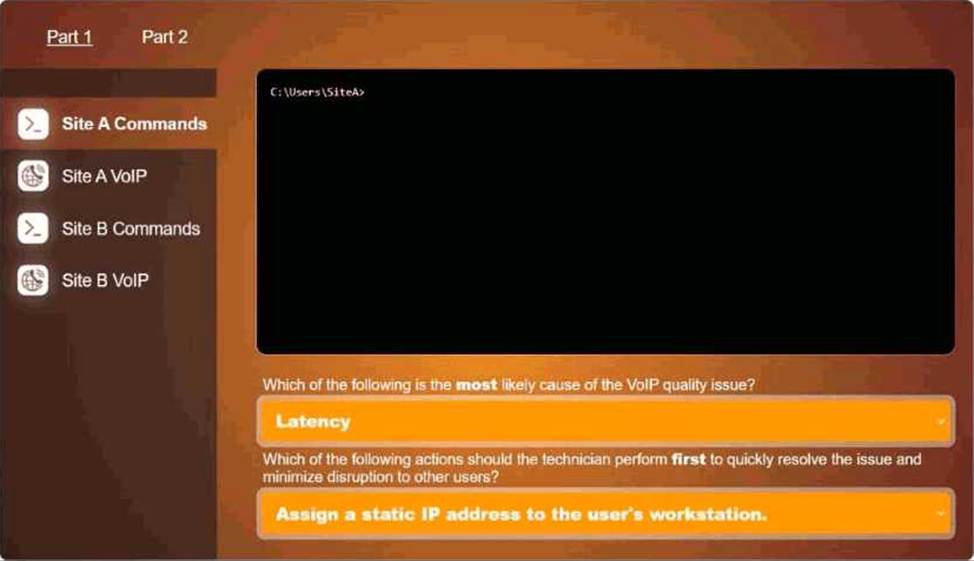
HOTSPOT
User at site A is reporting dropped VolP calls when using a softphone application.
However, users at site B are not experiencing any issues. The VolP provider has a tool to troubleshoot connectivity Issues.
Click on each tab to investigate the cause of the dropped calls. In Part 1, type help in each terminal to view a list of available commands. Then, select the correct answer for each question. In Part 2, make unnecessary network configuration changes to resolve reported issue.
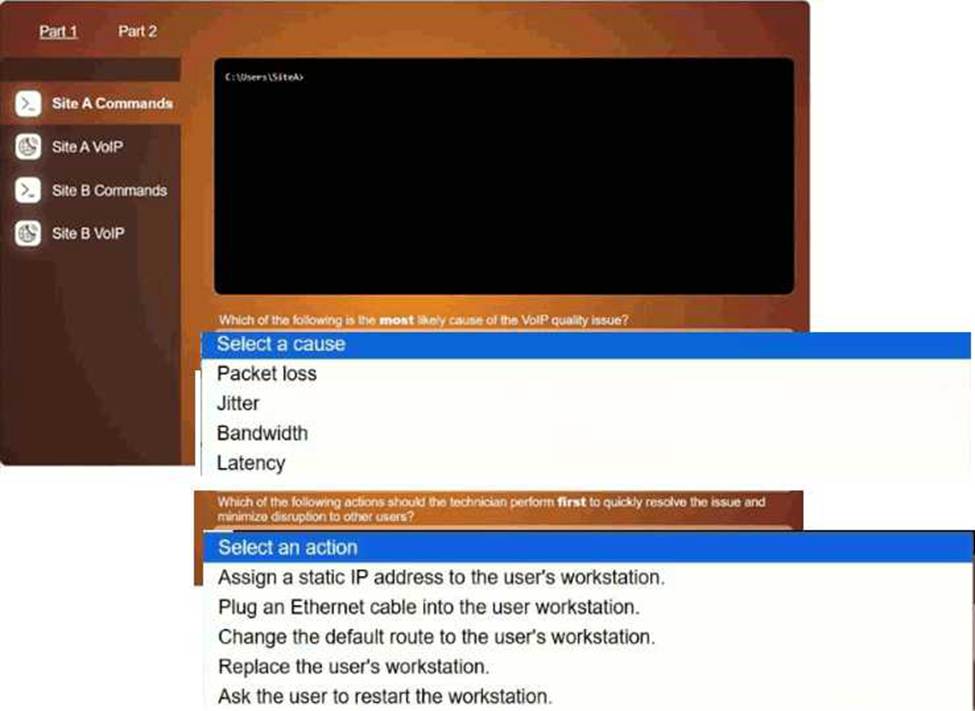
Plug an Ethernet cable into the workstation
A screenshot of a computer AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A user reports cursor issues on a company laptop. Technician finds a bulge under the trackpad.
Which component should be replaced first?
- A . Motherboard
- B . Heat sink
- C . Battery
- D . Trackpad
C
Explanation:
A physical bulge under the trackpad is a classic CompTIA-identified symptom of a swollen lithium-ion battery. As batteries degrade, internal gas buildup expands the casing, pushing upward on the laptop chassis―often distorting the trackpad, keyboard, or bottom shell. This can cause cursor issues, clicking problems, and safety hazards.
Replacing the battery first is essential because swollen batteries can rupture, leak, or ignite. Only after the battery is removed and replaced should the technician evaluate whether the trackpad suffered permanent damage.
Replacing the trackpad (D) without addressing the battery fails to correct the root cause. The motherboard (A) and heat sink (B) are unrelated to the physical bulge.
Thus, the correct first step is replacing the battery.
A customer needs to install a new printer in their network. The customer reports that users had intermittent connectivity issues with previous printers.
Which of the following should the technician configure on the new printer to prevent this issue?
- A . Gateway IP address
- B . DHCP IP address
- C . Static IP address
- D . Public IP address
C
Explanation:
Intermittent connectivity issues with network printers are commonly caused by changing IP addresses when using DHCP. Assigning a static IP address ensures that the printer is always reachable at the same IP address by client machines.
Reference: "CompTIA A+ Complete Study Guide" by Quentin Docter C Chapter 4, "Printers and Multifunction Devices", page 241.
A user has two SSDs of the same size in their PC. The user wants to configure both SSDs to have a copy of all data so there will be no data loss if one drive fails.
Which of the following is this an example of?
- A . RAID 0
- B . RAID 1
- C . RAID 5
- D . RAID 10
B
Explanation:
This scenario describes disk mirroring, which is RAID 1. With RAID 1, the same data is written to two drives simultaneously, creating an exact duplicate on each SSD. If one drive fails, the system can continue to operate using the remaining drive with no loss of data, which directly matches the requirement “no data loss if one drive fails.” RAID 1 is commonly used when fault tolerance and data redundancy are the priority. A key trade-off is capacity: because the data is duplicated, the usable storage is essentially the size of one of the drives (two 1TB drives in RAID 1 provide about 1TB usable). Performance can vary: read performance may improve slightly in some implementations, but write performance is generally similar to a single drive because data must be written to both drives.
RAID 0 is striping with no redundancy, so a single drive failure causes total data loss. RAID 5 requires at least three drives and uses parity. RAID 10 requires at least four drives and combines mirroring and striping. Therefore, the correct answer is RAID 1.
