Practice Free DP-700 Exam Online Questions
HOTSPOT
You are building a data loading pattern for Fabric notebook workloads.
You have the following code segment:

For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Topic 2, Litware, Inc
Case Study
Overview
This is a case study. Case studies are not timed separately. You can use as much exam time as you would like to complete each case. However, there may be additional case studies and sections on this exam. You must manage your time to ensure that you are able to complete all questions included on this exam in the time provided.
To answer the questions included in a case study, you will need to reference information that is provided in the case study. Case studies might contain exhibits and other resources that provide more information about the scenario that is described in the case study. Each question is independent of the other questions in this case study.
At the end of this case study, a review screen will appear. This screen allows you to review your answers and to make changes before you move to the next section of the exam. After you begin a new section, you cannot return to this section.
To start the case study
To display the first question in this case study, click the Next button. Use the buttons in the left pane to explore the content of the case study before you answer the questions. Clicking these buttons displays information such as business requirements, existing environment, and problem statements. If the case study has an All Information tab, note that the information displayed is identical to the information displayed on the subsequent tabs. When you are ready to answer a question, click the Question button to return to the question.
Overview
Litware, Inc. is a publishing company that has an online bookstore and several retail bookstores worldwide. Litware also manages an online advertising business for the authors it represents.
Existing Environment. Fabric Environment
Litware has a Fabric workspace named Workspace1. High concurrency is enabled for Workspace1.
The company has a data engineering team that uses Python for data processing.
Existing Environment. Data Processing
The retail bookstores send sales data at the end of each business day, while the online bookstore constantly provides logs and sales data to a central enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
Litware implements a medallion architecture by using the following three layers: bronze, silver, and gold. The sales data is ingested from the ERP system as Parquet files that land in the Files folder in a lakehouse. Notebooks are used to transform the files in a Delta table for the bronze and silver layers. The gold layer is in a warehouse that has V-Order disabled.
Litware has image files of book covers in Azure Blob Storage. The files are loaded into the Files folder.
Existing Environment. Sales Data
Month-end sales data is processed on the first calendar day of each month. Data that is older than one month never changes.
In the source system, the sales data refreshes every six hours starting at midnight each day.
The sales data is captured in a Dataflow Gen1 dataflow. When the dataflow runs, new and historical data is captured.
The dataflow captures the following fields of the source:
– Sales Date
– Author
– Price
– Units
– SKU
A table named AuthorSales stores the sales data that relates to each author. The table contains a column named AuthorEmail. Authors authenticate to a guest Fabric tenant by using their email address.
Existing Environment. Security Groups
Litware has the following security groups:
– Sales
– Fabric Admins
– Streaming Admins
Existing Environment. Performance Issues
Business users perform ad-hoc queries against the warehouse. The business users indicate that reports against the warehouse sometimes run for two hours and fail to load as expected. Upon further investigation, the data engineering team receives the following error message when the reports fail to load: “The SQL query failed while running.”
The data engineering team wants to debug the issue and find queries that cause more than one failure.
When the authors have new book releases, there is often an increase in sales activity. This increase slows the data ingestion process.
The company’s sales team reports that during the last month, the sales data has NOT been up-to-date when they arrive at work in the morning.
Requirements. Planned Changes
Litware recently signed a contract to receive book reviews. The provider of the reviews exposes the data in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets.
Litware plans to manage Search Engine Optimization (SEO) for the authors. The SEO data will be streamed from a REST API.
Requirements. Version Control
Litware plans to implement a version control solution in Fabric that will use GitHub integration and follow the principle of least privilege.
Requirements. Governance Requirements
To control data platform costs, the data platform must use only Fabric services and items. Additional Azure resources must NOT be provisioned.
Requirements. Data Requirements
Litware identifies the following data requirements:
– Process the SEO data in near-real-time (NRT).
– Make the book reviews available in the lakehouse without making a copy of the data.
– When a new book cover image arrives in the Files folder, process the image as soon as possible.
You need to implement the solution for the book reviews.
Which should you do?
- A . Create a Dataflow Gen2 dataflow.
- B . Create a shortcut.
- C . Enable external data sharing.
- D . Create a data pipeline.
B
Explanation:
The requirement specifies that Litware plans to make the book reviews available in the lakehouse without making a copy of the data. In this case, creating a shortcut in Fabric is the most appropriate solution. A shortcut is a reference to the external data, and it allows Litware to access the book reviews stored in Amazon S3 without duplicating the data into the lakehouse.
You need to schedule the population of the medallion layers to meet the technical requirements.
What should you do?
- A . Schedule a data pipeline that calls other data pipelines.
- B . Schedule a notebook.
- C . Schedule an Apache Spark job.
- D . Schedule multiple data pipelines.
A
Explanation:
The technical requirements specify that:
Medallion layers must be fully populated sequentially (bronze → silver → gold). Each layer must be populated before the next.
If any step fails, the process must notify the data engineers.
Data imports should run simultaneously when possible.
Why Use a Data Pipeline That Calls Other Data Pipelines?
A data pipeline provides a modular and reusable approach to orchestrating the sequential population of medallion layers.
By calling other pipelines, each pipeline can focus on populating a specific layer (bronze, silver, or gold), simplifying development and maintenance.
A parent pipeline can handle:
– Sequential execution of child pipelines.
– Error handling to send email notifications upon failures.
– Parallel execution of tasks where possible (e.g., simultaneous imports into the bronze layer).
You have a Fabric warehouse named DW1 that contains a Type 2 slowly changing dimension (SCD) dimension table named DimCustomer. DimCustomer contains 100 columns and 20 million rows. The columns are of various data types, including int, varchar, date, and varbinary.
You need to identify incoming changes to the table and update the records when there is a change.
The solution must minimize resource consumption.
What should you use to identify changes to attributes?
- A . a direct attributes comparison for the attributes in the source table.
- B . a hash function to compare the attributes in the DimCustomer table.
- C . a direct attributes comparison across the attributes in the DimCustomer table.
- D . a hash function to compare the attributes in the source table.
You have five Fabric workspaces.
You are monitoring the execution of items by using Monitoring hub.
You need to identify in which workspace a specific item runs.
Which column should you view in Monitoring hub?
- A . Start time
- B . Capacity
- C . Activity name
- D . Submitter
- E . Item type
- F . Job type
- G . Location
G
Explanation:
To identify in which workspace a specific item runs in Monitoring hub, you should view the Location column. This column indicates the workspace where the item is executed. Since you have multiple workspaces and need to track the execution of items across them, the Location column will show you the exact workspace associated with each item or job execution.
You have a Fabric workspace named Workspace1 that contains a warehouse named DW1 and a data pipeline named Pipeline1.
You plan to add a user named User3 to Workspace1.
You need to ensure that User3 can perform the following actions:
View all the items in Workspace1.
Update the tables in DW1.
The solution must follow the principle of least privilege.
You already assigned the appropriate object-level permissions to DW1.
Which workspace role should you assign to User3?
- A . Admin
- B . Member
- C . Viewer
- D . Contributor
D
Explanation:
To ensure User3 can view all items in Workspace1 and update the tables in DW1, the most appropriate workspace role to assign is the Contributor role.
This role allows User3 to:
View all items in Workspace1: The Contributor role provides the ability to view all objects within the workspace, such as data pipelines, warehouses, and other resources.
Update the tables in DW1: The Contributor role allows User3 to modify or update resources within the workspace, including the tables in DW1, assuming that appropriate object-level permissions are set for the warehouse.
This role adheres to the principle of least privilege, as it provides the necessary permissions without granting broader administrative rights.
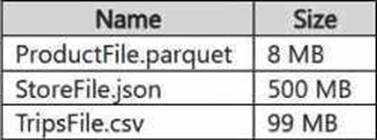
You have a Google Cloud Storage (GCS) container named storage1 that contains the files shown in the following table.
You have a Fabric workspace named Workspace1 that has the cache for shortcuts enabled. Workspace1 contains a lakehouse named Lakehouse1.
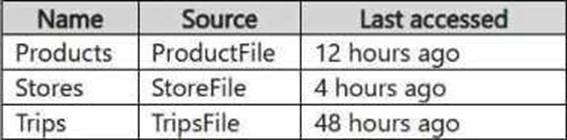
Lakehouse1 has the shortcuts shown in the following table.
You need to read data from all the shortcuts.
Which shortcuts will retrieve data from the cache?
- A . Stores only
- B . Products only
- C . Stores and Products only
- D . Products, Stores, and Trips
- E . Trips only
- F . Products and Trips only
C
Explanation:
When reading data from shortcuts in Fabric (in this case, from a lakehouse like Lakehouse1), the cache for shortcuts helps by storing the data locally for quick access. The last accessed timestamp and the cache expiration rules determine whether data is fetched from the cache or from the source (Google Cloud Storage, in this case).
Products: The ProductFile.parquet was last accessed 12 hours ago. Since the cache has data available for up to 12 hours, it is likely that this data will be retrieved from the cache, as it hasn’t been too long since it was last accessed.
Stores: The StoreFile.json was last accessed 4 hours ago, which is within the cache retention period.
Therefore, this data will also be retrieved from the cache.
Trips: The TripsFile.csv was last accessed 48 hours ago. Given that it’s outside the typical caching window (assuming the cache has a maximum retention period of around 24 hours), it would not be retrieved from the cache. Instead, it will likely require a fresh read from the source.
You have a Fabric workspace that contains a warehouse named Warehouse1.
You have an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server database named Database1 that is accessed by using an on-premises data gateway.
You need to copy data from Database1 to Warehouse1.
Which item should you use?
- A . an Apache Spark job definition
- B . a data pipeline
- C . a Dataflow Gen1 dataflow
- D . an eventstream
B
Explanation:
To copy data from an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server database (Database1) to a warehouse (Warehouse1) in Fabric, a data pipeline is the most appropriate tool. A data pipeline in Fabric is designed to move data between various data sources and destinations, including on-premises databases like SQL Server, and cloud-based storage like Fabric warehouses. The data pipeline can handle the connection through an on-premises data gateway, which is required to access on-premises data. This solution facilitates the orchestration of data movement and transformations if needed.
HOTSPOT
You have a Fabric workspace that contains a lakehouse named Lakehousel.
Lakehousel contains a table named Status_Target that has the following columns:
• Key
• Status
• LastModified
The data source contains a table named Status.Source that has the same columns as Status_Target.
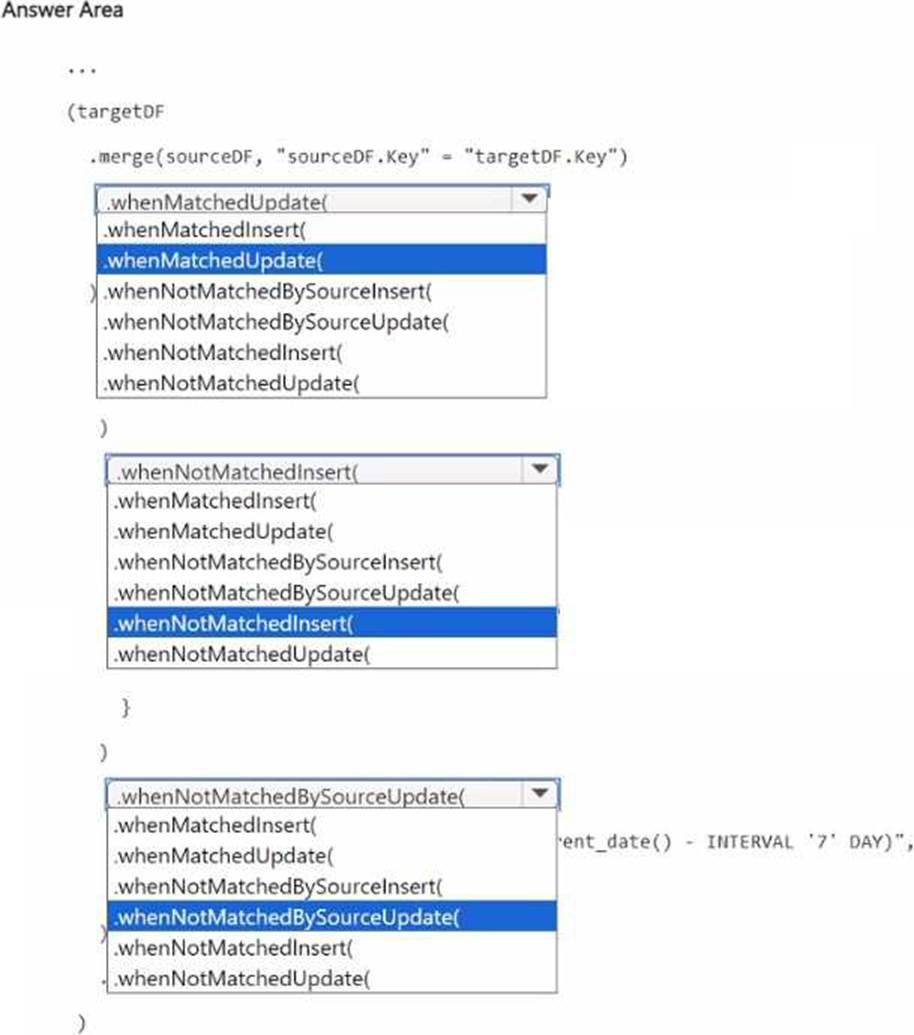
Status.Source is used to populate Status_Target. In a notebook name Notebook!, you load Status_Source to a DataFrame named sourceDF and Status_Target to a DataFrame named targetDF.
You need to implement an incremental loading pattern by using Notebook-!. The solution must meet
the following requirements:
• For all the matching records that have the same value of key, update the value of LastModified in Status_Target to the value of LastModified in Status_Source.
• Insert all the records that exist in Status_Source that do NOT exist in Status_Target.
• Set the value of Status in Status_Target to inactive for all the records that were last modified more than seven days ago and that do NOT exist in Status.Source.
How should you complete the statement? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

You have a Fabric workspace that contains a lakehouse named Lakehouse1.
In an external data source, you have data files that are 500 GB each. A new file is added every day.
You need to ingest the data into Lakehouse1 without applying any transformations.
The solution must meet the following requirements
Trigger the process when a new file is added.
Provide the highest throughput.
Which type of item should you use to ingest the data?
- A . Data pipeline
- B . Environment
- C . KQL queryset
- D . Dataflow Gen2
A
Explanation:
To efficiently ingest large data files (500 GB each) into Lakehouse1 with high throughput and trigger the process when a new file is added, a Data pipeline is the most suitable solution. Data pipelines in Fabric are ideal for orchestrating data movement and can be configured to automatically trigger based on file arrivals or other events. This solution meets both requirements: ingesting the data without transformations (since you just need to copy the data) and triggering the process when new files are added.
