Practice Free JN0-232 Exam Online Questions
You have a situation where legitimate traffic is incorrectly identified as malicious by your screen options.
In this scenario, what should you do?
- A . Enable all screen options.
- B . Discard the traffic immediately.
- C . Increase the sensitivity of the screen options.
- D . Use the alarm-without-drop configuration parameter.
D
Explanation:
Screen options are used to detect and prevent attacks such as floods, scans, and malformed packets. In some cases, false positives may occur, where legitimate traffic is mistakenly identified as malicious.
To address this, administrators can configure the alarm-without-drop option (Option D). This setting generates alarms/logs for suspicious traffic without actually dropping it, allowing verification before taking further action.
Enabling all screen options (Option A) may increase false positives further.
Discarding traffic immediately (Option B) risks disrupting legitimate communication.
Increasing sensitivity (Option C) worsens the problem, since false positives would increase.
Correct Action: Use alarm-without-drop to log the traffic without dropping it.
Reference: Juniper Networks CJunos OS Screen Options and Troubleshooting, Junos OS Security Fundamentals.
Which two addresses are valid address book entries? (Choose two.)
- A . 173.145.5.21/255.255.255.0
- B . 153.146.0.145/255.255.0.255
- C . 203.150.108.10/24
- D . 191.168.203.0/24
A, C
Explanation:
The correct address book entries are:
Which statement is correct about source NAT?
- A . It translates MAC addresses to private IP addresses.
- B . It translates private IP addresses to public IP addresses.
- C . It performs bidirectional IP address translation.
- D . It performs translation on ingress traffic only.
B
Explanation:
Source NAT (Network Address Translation) is used on SRX devices to allow hosts with private IP addresses to access external networks, such as the Internet. The SRX translates the private IP address of the source host into a public IP address before forwarding traffic toward the destination.
It does not translate MAC addresses (Option A).
NAT is unidirectional in this case: it specifically translates private-to-public in the outbound direction, while the reverse (return traffic) is handled automatically through the session table. It is not a bidirectional translation (Option C).
NAT processing occurs as part of the flow module, not limited only to ingress traffic (Option D).
Therefore, the correct statement is that source NAT translates private IP addresses to public IP addresses.
Reference: Juniper Networks CJunos OS Security Fundamentals, NAT Concepts and Source NAT Processing.
Which two statements are correct about IKE security associations? (Choose two.)
- A . IKE security associations are established during IKE Phase 1 negotiations.
- B . IKE security associations are unidirectional.
- C . IKE security associations are established during IKE Phase 2 negotiations.
- D . IKE security associations are bidirectional.
Which two statements are correct about screens? (Choose two.)
- A . Screens process inbound packets.
- B . Screens are processed on the routing engine.
- C . Screens process outbound packets.
- D . Screens are processed on the flow module.
Which two UTM features should be used for tracking productivity and corporate user behavior? (Choose two.)
- A . the content filtering UTM feature
- B . the antivirus UTM feature
- C . the Web filtering UTM feature
- D . the antispam UTM feature
Click the Exhibit button.
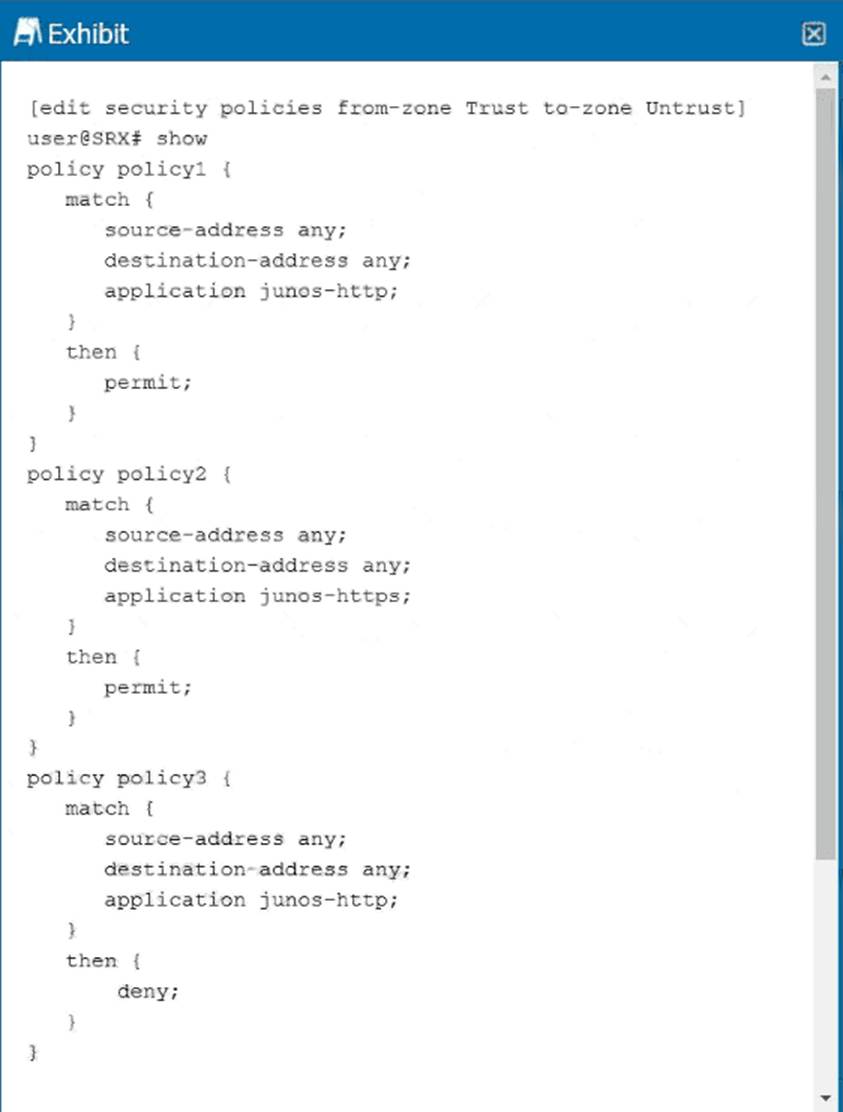
Referring to the exhibit, which statement is correct?
- A . policy3 will be shadowed because it matches the same application as policy1.
- B . None of the policies will be shadowed.
- C . policy1 will be shadowed because it matches the same application as policy3.
- D . policy2 will be shadowed because it matches the same application as policy1.
A
Explanation:
Juniper SRX evaluates security policies in order, top to bottom. The first matching policy determines the action, and no further policies are evaluated. This behavior can lead to shadowed policies if later policies match the same conditions as earlier ones.
From the exhibit:
Policy1: Matches application junos-http and permits traffic.
Policy2: Matches application junos-https and permits traffic.
Policy3: Matches application junos-http again, but denies traffic.
Sincepolicy1already matches all HTTP traffic and permits it, traffic never reachespolicy3. This makespolicy3 shadowed because it has the same match condition as policy1 but is evaluated later in the list.
Other options:
Policy1 is not shadowed because it is evaluated first.
Policy2 is independent (application = HTTPS) and therefore unaffected.
Only policy3 is shadowed by policy1.
Correct Statement: Policy3 will be shadowed because it matches the same application as policy1.
Reference: Juniper Networks CSecurity Policy Evaluation Order and Shadowed Policies, Junos OS Security Fundamentals.
Which two statements are correct about unified security policies? (Choose two.)
- A . Traffic that matches a unified policy will not be evaluated by traditional security policy.
- B . Dynamic applications in unified security policies analyze traffic based on Layer 4 information.
- C . Traffic that matches a traditional policy will not be evaluated by unified security policy.
- D . Dynamic applications in unified security policies analyze traffic based on Layer 7 information.
A D
Explanation:
Unified security policies (USPs) provide integrated application-aware controls using AppID and extend traditional zone-based policy enforcement.
Option A: Correct. If traffic matches a unified security policy, it is not re-evaluated by traditional security policies. Unified policies take precedence for matched flows.
Option B: Incorrect. Traditional policies rely on Layer 3/4 attributes. Unified policies go deeper by leveraging AppID, which inspects traffic up to Layer 7.
Option C: Incorrect. Traffic matching a traditional policy is unaffected by unified policy unless unified mode is explicitly configured for those flows.
Option D: Correct. Dynamic application recognition in unified policies uses Layer 7 (application-layer) inspection via AppID.
Correct Statements: A and D
Reference: Juniper Networks CUnified Security Policies and App Secure AppID, Junos OS Security Fundamentals.
You are deploying an SRX Series firewall with multiple NAT scenarios.
In this situation, which NAT scenario takes priority?
- A . interface NAT
- B . source NAT
- C . static NAT
- D . destination NAT
A
Explanation:
This is because the interface NAT would allow the connections to pass through the firewall – and thus, would ensure that the appropriate ports are open in order to allow for the connections to be established.
This is a really important step in order to ensure that all of the appropriate traffic is allowed through the SRX Series firewall – and thus, it must be a priority when deploying the firewall.
Which IPsec protocol is used to encrypt the data payload?
- A . ESP
- B . IKE
- C . AH
- D . TCP
