Practice Free HPE7-A02 Exam Online Questions
A company has AOS-CX switches and HPE Aruba Networking APs, which run AOS-10 and bridge their SSIDs. Company security policies require 802.1X on all edge ports, some of which connect to APs.
How should you configure the auth-mode on AOS-CX switches?
- A . Leave all edge ports in client auth-mode and configure device auth-mode in the AP role.
- B . Configure all edge ports in client auth-mode.
- C . Configure all edge ports in device auth-mode.
- D . Leave all edge ports in device auth-mode and configure client auth-mode in the AP role.
A
Explanation:
Refer to the exhibit.
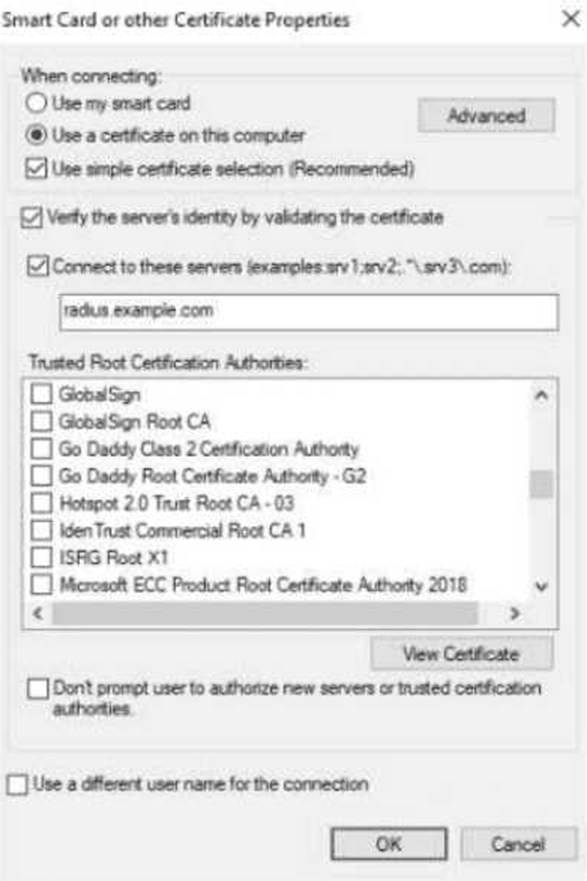
The exhibit shows the 802.1X-related settings for Windows domain clients.
What should admins change to make the settings follow best security practices?
- A . Specify at least two server names under the "Connect to these servers" field.
- B . Select the desired Trusted Root Certificate Authority and select the check box next to "Don’t prompt users."
- C . Under the "Connect to these servers" field, use a wildcard in the server name.
- D . Clear the check box for using simple certificate selection and select the desired certificate manually.
A
Explanation:
To follow best security practices for 802.1X authentication settings in Windows domain clients:
Specify at least two server names under "Connect to these servers":
Admins should explicitly list trusted RADIUS server names (e.g., radius.example.com) to prevent the client from connecting to unauthorized or rogue servers.
This mitigates man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks where an attacker attempts to present their own RADIUS server.
Select the desired Trusted Root Certificate Authority and "Don’t prompt users":
Select the Trusted Root CA that issued the RADIUS server’s certificate. This ensures clients validate the correct server certificate during the EAP-TLS/PEAP authentication process.
Enabling "Don’t prompt users" ensures end users are not confused or tricked into accepting certificates from untrusted servers.
Why the other options are incorrect:
Option C: Incorrect. Wildcards in server names (e.g., *.example.com) weaken security and allow broader matching, increasing the risk of rogue servers.
Option D: Incorrect. Clearing "Use simple certificate selection" requires users to select certificates manually, which can lead to errors and usability issues. Simple certificate selection is recommended when properly configured.
Recommended Settings for Best Security Practices:
Server Validation: Specify the exact RADIUS server names in the "Connect to these servers" field.
Root CA Validation: Ensure only the correct Trusted Root Certificate Authority is selected.
User Prompts: Enable "Don’t prompt users" to enforce automatic and secure authentication without user intervention.
Refer to the exhibit.

The exhibit shows the 802.1X-related settings for Windows domain clients.
What should admins change to make the settings follow best security practices?
- A . Specify at least two server names under the "Connect to these servers" field.
- B . Select the desired Trusted Root Certificate Authority and select the check box next to "Don’t prompt users."
- C . Under the "Connect to these servers" field, use a wildcard in the server name.
- D . Clear the check box for using simple certificate selection and select the desired certificate manually.
A
Explanation:
To follow best security practices for 802.1X authentication settings in Windows domain clients:
Specify at least two server names under "Connect to these servers":
Admins should explicitly list trusted RADIUS server names (e.g., radius.example.com) to prevent the client from connecting to unauthorized or rogue servers.
This mitigates man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks where an attacker attempts to present their own RADIUS server.
Select the desired Trusted Root Certificate Authority and "Don’t prompt users":
Select the Trusted Root CA that issued the RADIUS server’s certificate. This ensures clients validate the correct server certificate during the EAP-TLS/PEAP authentication process.
Enabling "Don’t prompt users" ensures end users are not confused or tricked into accepting certificates from untrusted servers.
Why the other options are incorrect:
Option C: Incorrect. Wildcards in server names (e.g., *.example.com) weaken security and allow broader matching, increasing the risk of rogue servers.
Option D: Incorrect. Clearing "Use simple certificate selection" requires users to select certificates manually, which can lead to errors and usability issues. Simple certificate selection is recommended when properly configured.
Recommended Settings for Best Security Practices:
Server Validation: Specify the exact RADIUS server names in the "Connect to these servers" field.
Root CA Validation: Ensure only the correct Trusted Root Certificate Authority is selected.
User Prompts: Enable "Don’t prompt users" to enforce automatic and secure authentication without user intervention.
A company uses both HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI).
What is one way integrating the two solutions can help the company implement Zero Trust Security?
- A . CPPM can provide CPDI with custom device fingerprint definitions in order to enhance the
company’s total visibility. - B . CPDI can provide CPPM with extra information about users’ identity; CPPM can then use that information to apply the correct identity-based enforcement.
- C . CPPM can inform CPDI that it has assigned a particular Aruba-User-Role to a client; CPDI can then use that information to reclassify the client.
- D . CPDI can use tags to inform CPPM that clients are using prohibited applications; CPPM can then tell the network infrastructure to quarantine those clients.
D
Explanation:
Integrating HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI) can help a company implement Zero Trust Security by allowing CPDI to use tags to inform CPPM that clients are using prohibited applications. CPPM can then take action, such as telling the network infrastructure to quarantine those clients, ensuring that only compliant and trusted devices have network access.
A company uses both HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI).
What is one way integrating the two solutions can help the company implement Zero Trust Security?
- A . CPPM can provide CPDI with custom device fingerprint definitions in order to enhance the
company’s total visibility. - B . CPDI can provide CPPM with extra information about users’ identity; CPPM can then use that information to apply the correct identity-based enforcement.
- C . CPPM can inform CPDI that it has assigned a particular Aruba-User-Role to a client; CPDI can then use that information to reclassify the client.
- D . CPDI can use tags to inform CPPM that clients are using prohibited applications; CPPM can then tell the network infrastructure to quarantine those clients.
D
Explanation:
Integrating HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI) can help a company implement Zero Trust Security by allowing CPDI to use tags to inform CPPM that clients are using prohibited applications. CPPM can then take action, such as telling the network infrastructure to quarantine those clients, ensuring that only compliant and trusted devices have network access.
A company uses both HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI).
What is one way integrating the two solutions can help the company implement Zero Trust Security?
- A . CPPM can provide CPDI with custom device fingerprint definitions in order to enhance the
company’s total visibility. - B . CPDI can provide CPPM with extra information about users’ identity; CPPM can then use that information to apply the correct identity-based enforcement.
- C . CPPM can inform CPDI that it has assigned a particular Aruba-User-Role to a client; CPDI can then use that information to reclassify the client.
- D . CPDI can use tags to inform CPPM that clients are using prohibited applications; CPPM can then tell the network infrastructure to quarantine those clients.
D
Explanation:
Integrating HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI) can help a company implement Zero Trust Security by allowing CPDI to use tags to inform CPPM that clients are using prohibited applications. CPPM can then take action, such as telling the network infrastructure to quarantine those clients, ensuring that only compliant and trusted devices have network access.
A company uses both HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI).
What is one way integrating the two solutions can help the company implement Zero Trust Security?
- A . CPPM can provide CPDI with custom device fingerprint definitions in order to enhance the
company’s total visibility. - B . CPDI can provide CPPM with extra information about users’ identity; CPPM can then use that information to apply the correct identity-based enforcement.
- C . CPPM can inform CPDI that it has assigned a particular Aruba-User-Role to a client; CPDI can then use that information to reclassify the client.
- D . CPDI can use tags to inform CPPM that clients are using prohibited applications; CPPM can then tell the network infrastructure to quarantine those clients.
D
Explanation:
Integrating HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI) can help a company implement Zero Trust Security by allowing CPDI to use tags to inform CPPM that clients are using prohibited applications. CPPM can then take action, such as telling the network infrastructure to quarantine those clients, ensuring that only compliant and trusted devices have network access.
A company uses both HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI).
What is one way integrating the two solutions can help the company implement Zero Trust Security?
- A . CPPM can provide CPDI with custom device fingerprint definitions in order to enhance the
company’s total visibility. - B . CPDI can provide CPPM with extra information about users’ identity; CPPM can then use that information to apply the correct identity-based enforcement.
- C . CPPM can inform CPDI that it has assigned a particular Aruba-User-Role to a client; CPDI can then use that information to reclassify the client.
- D . CPDI can use tags to inform CPPM that clients are using prohibited applications; CPPM can then tell the network infrastructure to quarantine those clients.
D
Explanation:
Integrating HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Device Insight (CPDI) can help a company implement Zero Trust Security by allowing CPDI to use tags to inform CPPM that clients are using prohibited applications. CPPM can then take action, such as telling the network infrastructure to quarantine those clients, ensuring that only compliant and trusted devices have network access.
Refer to the exhibit.
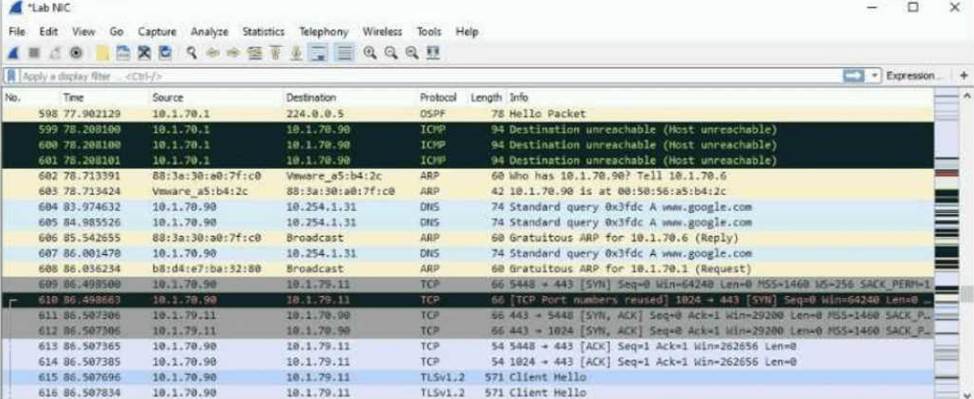
The exhibit shows a saved packet capture, which you have opened in Wireshark. You want to focus on the complete conversation between 10.1.70.90 and 10.1.79.11 that uses source port 5448.
What is a simple way to do this in Wireshark?
- A . Apply a capture filter that selects for both the 10.1.70.90 and 10.1.79.11 IP addresses.
- B . Click the Source column and then the Destination column to sort the packets into the desired order.
- C . Apply a capture filter that selects for TCP port 5448.
- D . Right-click one of the packets between those addresses and choose to follow the stream.
D
Explanation:
Wireshark: Follow TCP Stream:
Wireshark provides an intuitive feature to filter and display a complete TCP conversation.
By right-clicking any packet within the conversation and selecting "Follow → TCP Stream", Wireshark isolates and displays the entire conversation.
This feature allows you to view the communication in a simplified, sequential manner, including requests and responses.
Option Analysis:
Option A: Incorrect. Capture filters only apply during packet capturing, not for analyzing already saved packet captures.
Option B: Incorrect. Sorting packets helps with organizing data but does not isolate a complete conversation.
Option C: Incorrect. A capture filter for TCP port 5448 would have to be applied before capturing; it does not work for saved data.
Option D: Correct. Right-clicking a packet and choosing "Follow TCP Stream" is the simplest way to display the full conversation between 10.1.70.90 and 10.1.79.11 on port 5448.
Steps in Wireshark to Follow a TCP Stream:
Locate any packet within the desired conversation (e.g., between 10.1.70.90 and 10.1.79.11 on TCP port 5448).
Right-click on the packet.
Choose "Follow" → "TCP Stream".
Wireshark will display the entire TCP conversation, including both directions of communication.
This feature is especially useful when troubleshooting or analyzing detailed interactions between hosts.
You have enabled "rogue AP containment" in the Wireless IPS settings for a company’s HPE Aruba Networking APs.
What form of containment does HPE Aruba Networking recommend?
- A . Wireless deauthentication only
- B . Wireless tarpit and wired containment
- C . Wireless tarpit only
- D . Wired containment
A
Explanation:
Rogue AP Containment Methods:
HPE Aruba Networking recommends using wireless deauthentication as the preferred method for rogue AP containment.
Deauthentication sends deauth frames to clients connected to rogue APs, causing them to disconnect. This method is effective without introducing unnecessary disruptions to the wired infrastructure.
Key Points:
Wireless Deauthentication is simple, efficient, and widely supported across client devices.
Tarpit Containment is more aggressive and may cause unintentional disruptions to legitimate clients.
Wired Containment involves blocking traffic at the switch level but is complex and may impact legitimate infrastructure traffic.
Option Analysis:
Option A: Correct. Wireless deauthentication is the recommended method as it targets rogue AP clients without excessive network impact.
Option B: Incorrect. Combining wireless tarpit and wired containment is overkill and not typically recommended.
Option C: Incorrect. Wireless tarpit can be effective but is generally not the first choice due to its aggressive nature.
Option D: Incorrect. Wired containment is more complex and reserved for specific use cases, not general recommendations.
