Practice Free HPE7-A02 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
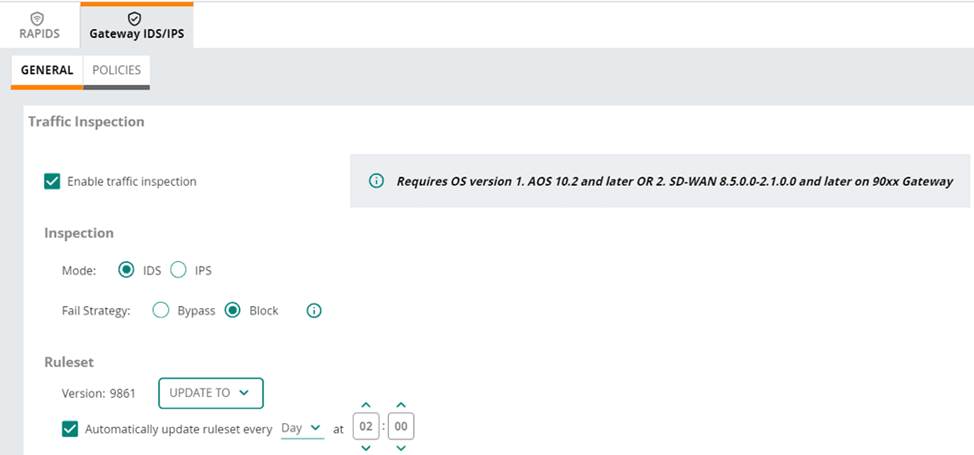
(Note that the HPE Aruba Networking Central interface shown here might look slightly different from what you see in your HPE Aruba Networking Central interface as versions change; however, similar concepts continue to apply.)
An HPE Aruba Networking 9×00 gateway is part of an HPE Aruba Networking Central group that has the settings shown in the exhibit.
What would cause the gateway to drop traffic as part of its IDPS settings?
- A . Its site-to-site VPN connections failing
- B . Traffic matching a rule in the active ruleset
- C . Its IDPS engine failing
- D . Traffic showing anomalous behavior
B
Explanation:
In the exhibit, the HPE Aruba Networking Central settings for the 9×00 gateway show that traffic inspection is enabled, and the gateway is set to operate in IDS (Intrusion Detection System) mode with the fail strategy set to "Block". This configuration means that the gateway will drop traffic if it matches a rule in the active ruleset.
Refer to the exhibit.

(Note that the HPE Aruba Networking Central interface shown here might look slightly different from what you see in your HPE Aruba Networking Central interface as versions change; however, similar concepts continue to apply.)
An HPE Aruba Networking 9×00 gateway is part of an HPE Aruba Networking Central group that has the settings shown in the exhibit.
What would cause the gateway to drop traffic as part of its IDPS settings?
- A . Its site-to-site VPN connections failing
- B . Traffic matching a rule in the active ruleset
- C . Its IDPS engine failing
- D . Traffic showing anomalous behavior
B
Explanation:
In the exhibit, the HPE Aruba Networking Central settings for the 9×00 gateway show that traffic inspection is enabled, and the gateway is set to operate in IDS (Intrusion Detection System) mode with the fail strategy set to "Block". This configuration means that the gateway will drop traffic if it matches a rule in the active ruleset.
The following firewall role is configured on HPE Aruba Networking Central-managed APs:
wlan access-rule employees
index 3
rule any any match 17 67 67 permit
rule any any match any 53 53 permit
rule 10 5 5.0 255.255 255.0 match any any any deny
rule 10.5 0.0 255.255 0.0 match 6 80 80 permit
rule 10.5 0.0 255.255.0.0 match 6 443 443 permit
rule 10.5.0.0 255.255.0.0 match any any any deny
rule any any match any any any permit
A client has authenticated and been assigned to the employees role. The client has IP address 10.2.2.2.
Which correctly describes behavior in this policy?
- A . HTTPS traffic from 10.2.2.2 to 10.5.5.5 is denied.
- B . HTTPS traffic from 10.2.2.2 to 203.0.113.12 is denied.
- C . Traffic from 10.5.3.3 in an active HTTPS session between 10.2.2.2 and 10.5.3.3 is permitted.
- D . Traffic from 198.51.100.12 in an active HTTP session between 10.2.2.2 and 198.51.100.12 is denied.
A
Explanation:
Policy Analysis:
Rule Evaluation Order: Rules are applied in sequential order until a match is found.
Key Points:
DHCP traffic (UDP 67) is permitted.
DNS traffic (UDP 53) is permitted.
Traffic to 10.5.5.0/24 is explicitly denied.
HTTP traffic (TCP 80) is allowed only to 10.5.0.0/16.
HTTPS traffic (TCP 443) is allowed only to 10.5.0.0/16.
All other traffic to 10.5.0.0/16 is denied.
Any other traffic not matching the above rules is permitted.
Scenario Analysis:
The client IP 10.2.2.2 does not fall within the 10.5.0.0/16 subnet.
Rule 3 denies traffic to 10.5.5.5, regardless of the source IP.
Option A: Correct. HTTPS traffic to 10.5.5.5 is explicitly denied by Rule 3.
Option B: Incorrect. Traffic to 203.0.113.12 is permitted due to the final "permit any" rule.
Option C: Incorrect. The client (10.2.2.2) does not belong to the subnet 10.5.0.0/16, so traffic to 10.5.3.3 is not permitted by Rule 5.
Option D: Incorrect. HTTP traffic to 198.51.100.12 is allowed by the last "permit any" rule.
The following firewall role is configured on HPE Aruba Networking Central-managed APs:
wlan access-rule employees
index 3
rule any any match 17 67 67 permit
rule any any match any 53 53 permit
rule 10 5 5.0 255.255 255.0 match any any any deny
rule 10.5 0.0 255.255 0.0 match 6 80 80 permit
rule 10.5 0.0 255.255.0.0 match 6 443 443 permit
rule 10.5.0.0 255.255.0.0 match any any any deny
rule any any match any any any permit
A client has authenticated and been assigned to the employees role. The client has IP address 10.2.2.2.
Which correctly describes behavior in this policy?
- A . HTTPS traffic from 10.2.2.2 to 10.5.5.5 is denied.
- B . HTTPS traffic from 10.2.2.2 to 203.0.113.12 is denied.
- C . Traffic from 10.5.3.3 in an active HTTPS session between 10.2.2.2 and 10.5.3.3 is permitted.
- D . Traffic from 198.51.100.12 in an active HTTP session between 10.2.2.2 and 198.51.100.12 is denied.
A
Explanation:
Policy Analysis:
Rule Evaluation Order: Rules are applied in sequential order until a match is found.
Key Points:
DHCP traffic (UDP 67) is permitted.
DNS traffic (UDP 53) is permitted.
Traffic to 10.5.5.0/24 is explicitly denied.
HTTP traffic (TCP 80) is allowed only to 10.5.0.0/16.
HTTPS traffic (TCP 443) is allowed only to 10.5.0.0/16.
All other traffic to 10.5.0.0/16 is denied.
Any other traffic not matching the above rules is permitted.
Scenario Analysis:
The client IP 10.2.2.2 does not fall within the 10.5.0.0/16 subnet.
Rule 3 denies traffic to 10.5.5.5, regardless of the source IP.
Option A: Correct. HTTPS traffic to 10.5.5.5 is explicitly denied by Rule 3.
Option B: Incorrect. Traffic to 203.0.113.12 is permitted due to the final "permit any" rule.
Option C: Incorrect. The client (10.2.2.2) does not belong to the subnet 10.5.0.0/16, so traffic to 10.5.3.3 is not permitted by Rule 5.
Option D: Incorrect. HTTP traffic to 198.51.100.12 is allowed by the last "permit any" rule.
An AOS-CX switch has this admin user account configured on it:
netadmin in the operators group.
You have configured these commands on an AOS-CX switch:
tacacs-server host cp.example.com key plaintext &12xl,powmay7855
aaa authentication login ssh group tacacs local aaa authentication allow-fail-through
A user accesses the switch with SSH and logs in as netadmin with the correct password. When the switch sends a TACACS+ request to the ClearPass server at cp.example.com, the server does not send a response. Authentication times out.
What happens?
- A . The user is logged in and granted operator access.
- B . The user is logged in and allowed to enter auditor commands only.
- C . The user is logged in and granted administrators access.
- D . The user is not allowed to log in.
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive Detailed Explanation
The configuration includes the command aaa authentication allow-fail-through, which specifies that if the TACACS+ server fails to respond (e.g., times out), the switch will proceed to the next authentication method in the sequence, which is local. In this scenario:
The switch first attempts to authenticate the user against the TACACS+ server.
When the TACACS+ server fails to respond, the switch falls back to local authentication.
The user netadmin is a local account configured on the switch and belongs to the operators group.
As a result, the user is successfully authenticated locally and is granted operator level access.
Reference
Aruba AOS-CX User Guide: Authentication fallback mechanisms.
TACACS+ fallback behavior for HPE Aruba switches.
Refer to the exhibit.
Refer to Exhibit:
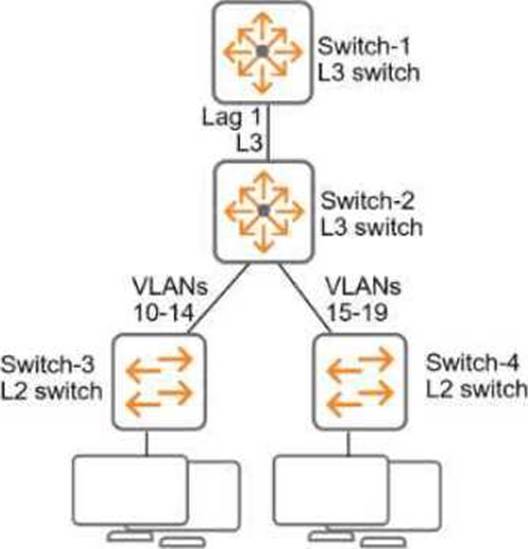
All of the switches in the exhibit are AOS-CX switches.
What is the preferred configuration on Switch-2 for preventing rogue OSPF routers in this network?
- A . Configure OSPF authentication on VLANs 10-19 in password mode.
- B . Configure OSPF authentication on Lag 1 in MD5 mode.
- C . Disable OSPF entirely on VLANs 10-19.
- D . Configure passive-interface as the OSPF default and disable OSPF passive on Lag 1.
B
Explanation:
Why MD5 Authentication on Lag 1 is Preferred:
Lag 1 is the primary link between Switch-2 and Switch-1, both of which are Layer 3 switches running OSPF.
By enabling MD5 authentication, OSPF routers exchange authenticated packets, preventing unauthorized or rogue OSPF routers from forming adjacencies or injecting routes.
MD5 is a secure authentication method and ensures the integrity and authenticity of OSPF communications.
Other Options Analysis:
Refer to the exhibit.
Refer to Exhibit:

All of the switches in the exhibit are AOS-CX switches.
What is the preferred configuration on Switch-2 for preventing rogue OSPF routers in this network?
- A . Configure OSPF authentication on VLANs 10-19 in password mode.
- B . Configure OSPF authentication on Lag 1 in MD5 mode.
- C . Disable OSPF entirely on VLANs 10-19.
- D . Configure passive-interface as the OSPF default and disable OSPF passive on Lag 1.
B
Explanation:
Why MD5 Authentication on Lag 1 is Preferred:
Lag 1 is the primary link between Switch-2 and Switch-1, both of which are Layer 3 switches running OSPF.
By enabling MD5 authentication, OSPF routers exchange authenticated packets, preventing unauthorized or rogue OSPF routers from forming adjacencies or injecting routes.
MD5 is a secure authentication method and ensures the integrity and authenticity of OSPF communications.
Other Options Analysis:
Refer to the exhibit.
Refer to Exhibit:

All of the switches in the exhibit are AOS-CX switches.
What is the preferred configuration on Switch-2 for preventing rogue OSPF routers in this network?
- A . Configure OSPF authentication on VLANs 10-19 in password mode.
- B . Configure OSPF authentication on Lag 1 in MD5 mode.
- C . Disable OSPF entirely on VLANs 10-19.
- D . Configure passive-interface as the OSPF default and disable OSPF passive on Lag 1.
B
Explanation:
Why MD5 Authentication on Lag 1 is Preferred:
Lag 1 is the primary link between Switch-2 and Switch-1, both of which are Layer 3 switches running OSPF.
By enabling MD5 authentication, OSPF routers exchange authenticated packets, preventing unauthorized or rogue OSPF routers from forming adjacencies or injecting routes.
MD5 is a secure authentication method and ensures the integrity and authenticity of OSPF communications.
Other Options Analysis:
Refer to the exhibit.
Refer to Exhibit:

All of the switches in the exhibit are AOS-CX switches.
What is the preferred configuration on Switch-2 for preventing rogue OSPF routers in this network?
- A . Configure OSPF authentication on VLANs 10-19 in password mode.
- B . Configure OSPF authentication on Lag 1 in MD5 mode.
- C . Disable OSPF entirely on VLANs 10-19.
- D . Configure passive-interface as the OSPF default and disable OSPF passive on Lag 1.
B
Explanation:
Why MD5 Authentication on Lag 1 is Preferred:
Lag 1 is the primary link between Switch-2 and Switch-1, both of which are Layer 3 switches running OSPF.
By enabling MD5 authentication, OSPF routers exchange authenticated packets, preventing unauthorized or rogue OSPF routers from forming adjacencies or injecting routes.
MD5 is a secure authentication method and ensures the integrity and authenticity of OSPF communications.
Other Options Analysis:
Refer to the exhibit.
Refer to Exhibit:

All of the switches in the exhibit are AOS-CX switches.
What is the preferred configuration on Switch-2 for preventing rogue OSPF routers in this network?
- A . Configure OSPF authentication on VLANs 10-19 in password mode.
- B . Configure OSPF authentication on Lag 1 in MD5 mode.
- C . Disable OSPF entirely on VLANs 10-19.
- D . Configure passive-interface as the OSPF default and disable OSPF passive on Lag 1.
B
Explanation:
Why MD5 Authentication on Lag 1 is Preferred:
Lag 1 is the primary link between Switch-2 and Switch-1, both of which are Layer 3 switches running OSPF.
By enabling MD5 authentication, OSPF routers exchange authenticated packets, preventing unauthorized or rogue OSPF routers from forming adjacencies or injecting routes.
MD5 is a secure authentication method and ensures the integrity and authenticity of OSPF communications.
Other Options Analysis:
