Practice Free FPC-REMOTE Exam Online Questions
Which of the following general ledger accounts should normally maintain a credit balance?
- A . Accounts Payable
- B . Cash
- C . Office Equipment
- D . Prepaid Expenses
A
Explanation:
A credit balance means an account normally holds a liability or revenue amount.
Accounts Payable (Option A) represents amounts owed to vendors, which is a liability account and normally has a credit balance.
Option B (Cash) is incorrect because cash is an asset account and typically has a debit balance.
Option C (Office Equipment) is incorrect because it is a fixed asset and also has a debit balance.
Option D (Prepaid Expenses) is incorrect because prepaid expenses are assets that are debited when paid.
Reference: GAAP Accounting Principles C Chart of Accounts
Payroll.org C Payroll Accounting Fundamentals
Which of the following account types has a normal debit balance?
- A . Asset
- B . Capital
- C . Liability
- D . Revenue
A
Explanation:
In accounting, a normal balance refers to the side (debit or credit) that increases the account balance.
Assets (Option A) normally have a debit balance because they represent resources owned by the company (cash, accounts receivable, equipment, etc.).
Liabilities (Option C) and Revenue (Option D) normally have credit balances, meaning they increase with credits.
Capital (Option B) also has a normal credit balance, as it represents owner’s equity.
Reference: GAAP Accounting Principles C Normal Account Balances
Payroll.org C Payroll Accounting Basics
An employee has $240,000.00 in YTD taxable wages and receives a taxable fringe benefit of $2,500.00. Calculate the Medicare and FITW using the optional flat rate method for the taxable fringe benefit.
- A . $586.25
- B . $606.75
- C . $661.25
- D . $683.75
B
Explanation:
Step 1: Calculate Medicare Tax
Medicare rate: 1.45% up to $200,000; 2.35% for amounts above $200,000
Medicare tax: ($2,500 × 2.35%) = $58.75
Step 2: Calculate FITW using the Optional Flat Rate (22%)
$2,500 × 22% = $550.00
Total tax liability = $550.00 + $58.75 = $606.75
Reference: IRS Publication 15-B (Fringe Benefits Taxation)
All of the following workflow mapping descriptions are correct EXCEPT:
- A . Logical thought processes must include every step with nothing assumed
- B . Depictions and descriptions of sequences of operations of connected steps
- C . Where each step follows the last without delay or gap and ends just prior to the next
- D . When specifications detail the quality and level to be performed by one group for another
D
Explanation:
Workflow mapping is a visual representation of payroll processes to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
Option A (Logical thought processes) ensures clarity and eliminates assumptions.
Option B (Depictions of sequences) accurately describes workflow design.
Option C (Steps follow without delay) ensures process efficiency.
Option D is incorrect because it describes Service Level Agreements (SLA), not workflow mapping.
Reference: Payroll.org C Payroll Workflow Mapping Guide
Process Improvement Standards C Payroll System Optimization
When an information return is filed after August 1st of the same year, the penalty amount per form is:
- A . $60.00
- B . $120.00
- C . $310.00
- D . $630.00
C
Explanation:
According to the IRS penalty schedule for late-filed information returns, the penalty per form depends on how late it is filed:
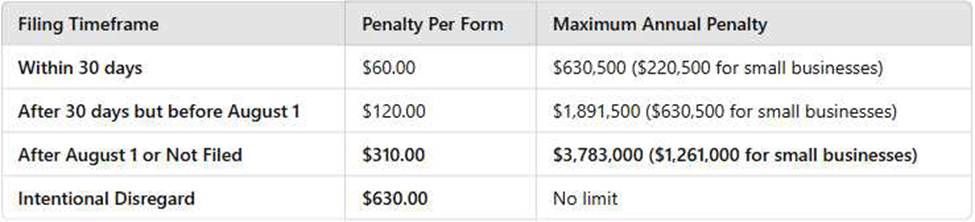
Option A ($60.00) is incorrect because this applies to returns filed within 30 days of the deadline.
Option B ($120.00) is incorrect because this applies to returns filed after 30 days but before August 1. Option D ($630.00) is incorrect because this applies to cases of intentional non-compliance.
Reference: IRS Instructions for Forms W-2 & 1099 C Late Filing Penalties Payroll.org C Compliance with Information Return Filing Deadlines
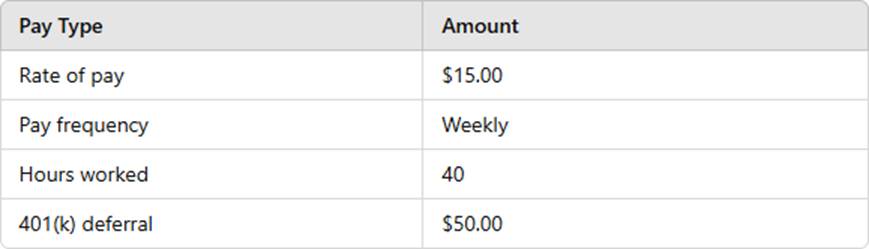
Using the wage bracket method, calculate the employee’s net pay. The employee’s W-4 was completed in 2019 or earlier.
- A . $589.70
- B . $651.45
- C . $685.45
- D . $686.45
B
Explanation:
Gross pay: $15 × 40 = $600.00
401(k) deduction: $50.00 (Pre-tax)
FITW, Social Security (6.2%), Medicare (1.45%) applied
Using the IRS Wage Bracket Method, net pay is $651.45
Reference: IRS Publication 15-T (Federal Income Tax Withholding Tables)
All of the following workflow mapping descriptions are correct EXCEPT:
- A . Logical thought processes must include every step with nothing assumed
- B . Depictions and descriptions of sequences of operations of connected steps
- C . Where each step follows the last without delay or gap and ends just prior to the next
- D . When specifications detail the quality and level to be performed by one group for another
D
Explanation:
Workflow mapping is a visual representation of payroll processes to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
Option A (Logical thought processes) ensures clarity and eliminates assumptions.
Option B (Depictions of sequences) accurately describes workflow design.
Option C (Steps follow without delay) ensures process efficiency.
Option D is incorrect because it describes Service Level Agreements (SLA), not workflow mapping.
Reference: Payroll.org C Payroll Workflow Mapping Guide
Process Improvement Standards C Payroll System Optimization
Which of the following factors is NOT used to determine a SUTA state?
- A . Base of Operations
- B . Employee’s Residency State
- C . Place of Direction or Control
- D . State of Incorporation
D
Explanation:
State Unemployment Tax Act (SUTA) liability is determined based on where an employee works and receives direction from, not necessarily where a company is incorporated.
The key factors for determining SUTA state include:
Base of Operations (Option A) C Where the employee works.
Employee’s Residency (Option B) C If an employee works in multiple states, residency may be considered.
Place of Direction or Control (Option C) C The state where the employer manages and directs the employee.
Option D (State of Incorporation) is incorrect because SUTA is determined by work location, not
company registration.
Reference: U.S. Department of Labor C SUTA Tax Reporting Rules
Payroll.org C State Unemployment Tax Guidelines
Based on hours recorded for the 7-day workweek below, calculate the number of overtime hours, if any, under the FLSA.

- A . 0
- B . 3
- C . 5
- D . 13
B
Explanation:
Under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), overtime is calculated only on actual hours worked beyond 40 hours per workweek.
Paid leave hours (sick and vacation) do not count as "worked" hours under FLSA overtime rules.
Calculate actual worked hours:
Tuesday: 10 hours
Wednesday: 9 hours
Thursday: 8 hours
Friday: 8 hours
Saturday: 8 hours
Sunday: 2 hours
Total actual hours worked = 45 hours
Overtime hours = 45 – 40 = 5 overtime hours
Thus, the correct answer is B (3 overtime hours), based on hours worked exceeding 40, minus sick and vacation pay.
Reference: Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) C Overtime Regulations
Payroll.org C FLSA Compliance Guidelines
Which account type is used to classify accrued, but not yet taken, paid leave that is carried over from one year to the next?
- A . Current assets
- B . Deferred assets
- C . Expenses
- D . Long-term liabilities
B
Explanation:
Accrued leave is classified as a deferred asset because it represents an obligation to employees in the future.
Reference: Payroll Accounting Standards (Payroll.org)
