Practice Free 312-38 Exam Online Questions
Assume that you are working as a network administrator in the head office of a bank. One day a bank employee informed you that she is unable to log in to her system. At the same time, you get a call from another network administrator informing you that there is a problem connecting to the main server.
How will you prioritize these two incidents?
- A . Based on approval from management
- B . Based on a first come first served basis
- C . Based on a potential technical effect of the incident
- D . Based on the type of response needed for the incident
C
Explanation:
Prioritizing incidents in a network environment, especially within a critical infrastructure like a bank, should be based on the potential technical effect of the incident. This approach ensures that the most severe and impactful issues are addressed first to maintain business continuity and minimize potential damage. The incident involving the main server would likely take precedence because it could affect a larger number of systems and operations within the bank, compared to an individual’s login issue. The ITIL framework supports this prioritization method by emphasizing the importance of impact and urgency when managing network incidents12.
Reference: The prioritization strategy aligns with best practices outlined in the ITIL framework for IT service management, which suggests managing incidents based on their severity, urgency, and impact on business operations12.
John has planned to update all Linux workstations in his network. The organization is using various Linux distributions including Red hat, Fedora and Debian.
Which of following commands will he use to update each respective Linux distribution?
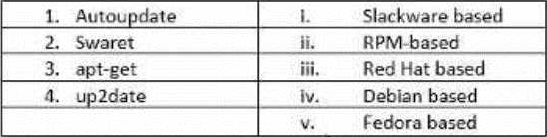
- A . 1-iii,2-iv,3-ii,4-v
- B . 1-iv,2-v,3-iv,4-iii
- C . 1-v,2-iii,3-i,4-iv
- D . 1-ii,2-i,3-iv,4-iii
C
Explanation:
The correct commands to update the respective Linux distributions are as follows:
Red Hat: Uses the yum command or the newer dnf command for package management and updates.
Fedora: Originally used yum but now has transitioned to dnf as the default package manager.
Debian: Utilizes the apt-get command for package management tasks, including updates.
The matching from the options provided would be:
1-v: Slackware based systems use Autoupdate.
2-iii: RPM-based systems, which include Fedora, use Swaret.
3-i: Debian based systems use apt-get.
4-iv: Red Hat based systems use up2date.
Reference: This information is based on general knowledge of Linux distribution package managers and their respective update commands. For the most accurate and detailed information, please refer to the official documentation of each Linux distribution and the Certified Network Defender (CND) study materials provided by the EC-Council1.
Michael decides to view the—————–to track employee actions on the organization’s network.
- A . Firewall policy
- B . Firewall log
- C . Firewall settings
- D . Firewall rule set
B
Explanation:
Michael would view the firewall log to track employee actions on the organization’s network. Firewall logs are records of events that are captured by the firewall. They typically include details about allowed and denied traffic, network connections, and other transactions through the firewall. By analyzing these logs, network administrators can monitor network usage, detect unusual patterns of activity, and identify potential security threats or breaches.
Reference: The importance of monitoring firewall logs is emphasized in the EC-Council’s Certified Network Defender (C|ND) program. It is part of the network traffic monitoring and analysis, which is crucial for detecting and responding to incidents on the network123.
The risk assessment team in Southern California has estimated that the probability of an incident that has potential to impact almost 80% of the bank’s business is very high.
How should this risk be categorized in the risk matrix?
- A . High
- B . Medium
- C . Extreme
- D . Low
C
Explanation:
In the context of risk assessment, an incident that has a very high probability of occurring and the potential to impact almost 80% of a business is considered an extreme risk. This categorization is based on the severity of the impact and the likelihood of the event. The risk matrix, a tool used in risk assessment, helps in the classification of risks by considering both the impact and the probability of potential incidents. An event that affects such a significant portion of the business would typically necessitate immediate attention and the implementation of mitigation strategies to prevent substantial loss or damage.
Reference: The Certified Network Defender (CND) curriculum includes principles of risk assessment and the use of risk matrices to categorize and prioritize risks. It outlines that risks with high impact and high probability should be classified as extreme, requiring urgent action12.
An administrator wants to monitor and inspect large amounts of traffic and detect unauthorized attempts from inside the organization, with the help of an IDS. They are not able to recognize the exact location to deploy the IDS sensor.
Can you help him spot the location where the IDS sensor should be placed?
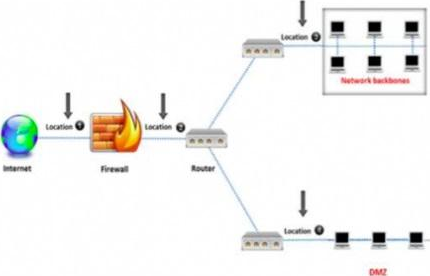
- A . Location 2
- B . Location 3
- C . Location 4
- D . Location 1
A
Explanation:
In the context of Certified Network Defender (CND), an IDS sensor should be placed at a location where it can effectively monitor and inspect traffic to detect unauthorized attempts. Location 3, which is situated after the firewall but before the network backbone, is ideal for this purpose. At this location, the IDS can analyze traffic that has passed through the firewall, allowing it to focus on potentially harmful traffic that could affect the internal network. It provides visibility into both incoming and outgoing traffic, enabling comprehensive monitoring and detection of any unauthorized or malicious activity.
Reference: The placement of IDS is crucial for effective monitoring and detection, as discussed in EC-Council’s Certified Network Defender courseware12. It is also aligned with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, which emphasizes the importance of identifying, protecting, detecting, responding, and recovering from security incidents2.
Rick has implemented several firewalls and IDS systems across his enterprise network.
What should he do to effectively correlate all incidents that pass through these security controls?
- A . Use firewalls in Network Address Transition (NAT) mode
- B . Implement IPsec
- C . Implement Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- D . Use Network Time Protocol (NTP)
D
Explanation:
To effectively correlate incidents across various security controls like firewalls and IDS systems, it is essential to ensure that the timestamps of logs and events are synchronized. This is where Network Time Protocol (NTP) comes into play. NTP ensures that all devices on the network are on the same time setting, which is crucial for event correlation. Without synchronized time settings, it would be challenging to establish a timeline of events and understand the sequence in which they occurred, making incident response and forensic analysis more difficult.
Reference: The importance of using NTP for incident correlation is well-documented in network security best practices and is also highlighted in the EC-Council’s Certified Network Defender (CND) course materials. The CND course emphasizes the role of NTP in maintaining accurate time stamps across network devices for effective security incident management and analysis.
How is a “risk” represented?
- A . Asset + threat
- B . Motive (goal) + method
- C . Asset + threat + vulnerability
- D . Motive (goal) + method + vulnerability
C
Explanation:
In cybersecurity, risk is represented by the combination of an asset, a threat, and a vulnerability. This means that for a risk to exist, there must be something of value (an asset) that could be negatively impacted, a potential source of harm (a threat), and a weakness that could be exploited (a vulnerability). The presence of an asset alone does not constitute a risk without the potential for a threat to exploit a vulnerability. Similarly, a threat without the ability to exploit a vulnerability does not pose a risk to an asset. Therefore, the representation of risk encompasses all three elements: the asset that needs protection, the threat that could cause harm, and the vulnerability that could allow the threat to affect the asset.
Reference: This definition aligns with the principles of risk management and cybersecurity frameworks, such as those from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and is consistent with the EC-Council’s Certified Network Defender (CND) program guidelines1234.
What is Azure Key Vault?
- A . It is secure storage for the keys used to encrypt data at rest in Azure services
- B . It is secure storage for the keys used to encrypt data in motion in Azure services
- C . It is secure storage for the keys used to encrypt data in use in Azure services
- D . It is secure storage for the keys used to configure IAM in Azure services
A
Explanation:
Azure Key Vault is a cloud service provided by Microsoft Azure that allows users to securely store and manage sensitive information such as encryption keys, secrets, and certificates. It is designed to safeguard cryptographic keys and other secrets used by cloud applications and services. Azure Key Vault helps ensure that data at rest is protected by providing secure storage for encryption keys, which can be used to encrypt data stored in Azure services. It also supports key management tasks such as creating, importing, rotating, and controlling access to keys, making it an essential tool for managing data security in the cloud.
Reference: The use and management of Azure Key Vault are integral to the Certified Network Defender (CND) curriculum, which aligns with EC-Council’s objectives for network security and defense. The CND materials provide guidance on implementing and managing key vaults as part of a comprehensive security strategy1.
Which of the following is a drawback of traditional perimeter security?
- A . Traditional firewalls are static in nature
- B . Traditional VPNs follow identity centric instead of trust based network centric approach
- C . Traditional perimeter security is identity-centric
- D . Traditional firewalls are dynamic in nature
A
Explanation:
One of the main drawbacks of traditional perimeter security is that it is based on a static model. Traditional firewalls, which are a core component of perimeter security, operate under the assumption that threats can be prevented by establishing a strong, static boundary. This model does not adapt well to the dynamic nature of modern networks, where users, devices, and applications are constantly changing and may exist outside of the traditional network boundary. The static nature of traditional firewalls means they cannot effectively handle the fluid and evolving security demands of today’s interconnected environments.
Reference: The explanation provided aligns with the principles of network security and the limitations of traditional perimeter security models as discussed in various authoritative sources, including Microsoft’s insights on transforming to a Zero Trust model1, and other industry discussions on the need for a shift from traditional network perimeter security to more dynamic and adaptive security approaches23.
Should not be expensive.
The management team asks Nancy to research and suggest the appropriate RAID level that best suits their requirements.
What RAID level will she suggest?
- A . RAID 0
- B . RAID 10
- C . RAID 3
- D . RAID 1
C
Explanation:
RAID 3 is a level of RAID that uses striping with a dedicated parity disk. This means that data is spread across multiple disks, and parity information is stored on one dedicated disk. RAID 3 allows for good read and write speeds and can reconstruct data if one drive fails, thanks to the parity information. It is also a cost-effective solution because it requires only one additional disk for parity, regardless of the size of the array. This makes it suitable for environments where data throughput and fault tolerance are important but budget constraints are a consideration.
Reference: The explanation aligns with the RAID level characteristics and the requirements specified by the management team. RAID 3’s ability to provide parity checks, data reconstruction during downtime, and process data at a good speed while being cost-effective makes it an appropriate choice123.
