Practice Free XK0-005 Exam Online Questions
A Linux administrator needs to create an image named sda.img from the sda disk and store it in the /tmp directory.
Which of the following commands should be used to accomplish this task?
- A . dd of=/dev/sda if=/tmp/sda.img
- B . dd if=/dev/sda of=/tmp/sda.img
- C . dd –if=/dev/sda –of=/tmp/sda.img
- D . dd –of=/dev/sda –if=/tmp/sda.img
B
Explanation:
The command dd if=/dev/sda of=/tmp/sda.img should be used to create an image named sda.img from the sda disk and store it in the /tmp directory. The dd command is a tool for copying and converting data on Linux systems. The if option specifies the input file or device, in this case /dev/sda, which is the disk device. The of option specifies the output file or device, in this case /tmp/sda.img, which is the image file. The command dd if=/dev/sda of=/tmp/sda.img will copy the entire disk data from /dev/sda to /tmp/sda.img and create an image file. This is the correct command to use to accomplish the task. The other options are incorrect because they either use the wrong options (–if or –of instead of if or of) or swap the input and output (dd of=/dev/sda if=/tmp/sda.img or dd –of=/dev/sda –if=/tmp/sda.img). CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 10: Managing Storage, page 323.
Some servers in an organization have been compromised. Users are unable to access to the organization’s web page and other services.
While reviewing the system log, a systems administrator notices messages from the kernel regarding firewall rules:
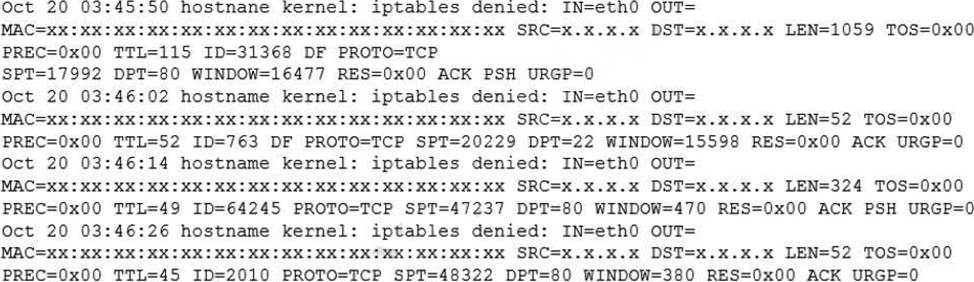
Which of the following commands will remediate and help resolve the issue?
A)
![]()
B)
![]()
C)
![]()
D)
![]()
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
A
Explanation:
The command iptables -F will remediate and help resolve the issue. The issue is caused by the firewall rules that block the access to the organization’s web page and other services. The output of dmesg | grep firewall shows that the kernel has dropped packets from the source IP address 192.168.1.100 to the destination port 80, which is the default port for HTTP. The command iptables – F will flush all the firewall rules and allow the traffic to pass through. This command will resolve the issue and restore the access to the web page and other services. The other options are incorrect because they either do not affect the firewall rules (ip route flush or ip addr flush) or do not exist (iptables -R). CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 18: Securing Linux Systems, page 543.
A systems administrator made some changes in the ~/.bashrc file and added an alias command. When the administrator tried to use the alias command, it did not work.
Which of the following should be executed FIRST?
- A . source ~/.bashrc
- B . read ~/.bashrc
- C . touch ~/.bashrc
- D . echo ~/.bashrc
A
Explanation:
The command source ~/.bashrc should be executed first to use the alias command.
The source command reads and executes commands from a file in the current shell environment. The ~/.bashrc file is a configuration file that contains commands and aliases that are executed when a new bash shell is started. The administrator made some changes in the ~/.bashrc file and added an alias command, but the changes are not effective until the file is sourced or a new shell is started. The command source ~/.bashrc will reload the file and make the alias command available. The other options are incorrect because they either do not execute the commands in the file (read, touch, or echo) or do not affect the current shell environment (read or echo). CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005)
Certification Study Guide, Chapter 9: Working with the Linux Shell, page 295.
An administrator needs to make an application change via a script that must be run only in console mode.
Which of the following best represents the sequence the administrator should execute to accomplish this task?
- A . systemct1 isolate multi-user.targetsh script.shsystemct1 isolate graphical.target
- B . systemct1 isolate graphical.targetsh script.shsystemct1 isolate multi-user.target
- C . sh script.shsystemct1 isolate multi-user.targetsystemct1 isolate graphical.target
- D . systemct1 isolate multi-user.targetsystemct1 isolate graphical.targetsh script.sh
A
Explanation:
The correct answer is A. systemctl isolate multi-user.target sh script.sh systemctl isolate graphical.target This sequence will allow the administrator to switch from the graphical mode to the console mode, run the script, and then switch back to the graphical mode.
The systemctl command is used to control the systemd system and service manager, which manages the boot targets and services on Linux systems. The isolate subcommand starts the unit specified on the command line and its dependencies and stops all others. The multi-user.target is a boot target that provides a text-based console login, while the graphical.target is a boot target that provides a graphical user interface. By using systemctl isolate, the administrator can change the boot target on the fly without rebooting the system.
The sh command is used to run a shell script, which is a file that contains a series of commands that can be executed by the shell. The script.sh is the name of the script that contains the application change that the administrator needs to make. By running sh script.sh, the administrator can execute the script in the console mode.
The other options are incorrect because:
B. systemctl isolate graphical.target sh script.sh systemctl isolate multi-user.target
This sequence will switch from the console mode to the graphical mode, run the script, and then switch back to the console mode. This is not what the administrator wants to do, as the script must be run only in console mode.
C. sh script.sh systemctl isolate multi-user.target systemctl isolate graphical.target
This sequence will run the script in the current mode, which may or may not be console mode, and then switch to console mode and back to graphical mode. This is not what the administrator wants to do, as the script must be run only in console mode.
D. systemctl isolate multi-user.target systemctl isolate graphical.target sh script.sh
This sequence will switch from graphical mode to console mode and then back to graphical mode,
without running the script at all. This is not what the administrator wants to do, as the script must be
run only in console mode.
systemctl(1) – Linux manual page
How to switch between the CLI and GUI on a Linux server
How to PROPERLY boot into single user mode in RHEL/CentOS 7/8 Changing Systemd Boot Target in Linux
Exit Desktop to Terminal in Ubuntu 19.10
Which of the following is a benefit of a service mesh?
- A . Encrypted communication between two services in a Kubernetes environment
- B . Direct access to the Kubernetes API services through the use of tokens
- C . Elevated privileges in a Kubernetes pod to allow root access in a hardened cluster
- D . Creating PVCs in a Kubernetes cluster to store and manage persistent data
A
Explanation:
A service mesh provides secure, encrypted communication between microservices in a Kubernetes environment. It also provides features like traffic management, observability, and load balancing at the network layer. The most popular service mesh implementations, such as Istio, handle security by enforcing mutual TLS (mTLS) encryption between services, ensuring data privacy and integrity.
Which of the following describes how a user’s public key is used during SSH authentication?
- A . The user’s public key is used to hash the password during SSH authentication.
- B . The user’s public key is verified against a list of authorized keys. If it is found, the user is allowed to log in.
- C . The user’s public key is used instead of a password to allow server access.
- D . The user’s public key is used to encrypt the communication between the client and the server.
A systems administrator is customizing a new Linux server.
Which of the following settings for umask would ensure that new files have the default permissions of -rw-r–r–?
- A . 0017
- B . 0027
- C . 0038
- D . 0640
B
Explanation:
The umask determines the default permission for new files. To get -rw-r–r– (644), the umask should be set to 0027. This sets the permissions to allow read and write for the owner, read-only for the group, and no permissions for others.
A Linux administrator cloned an existing Linux server and built a new server from that clone.
The administrator encountered the following error after booting the cloned server:
![]()
The administrator performed the commands listed below to further troubleshoot and mount the missing filesystem:
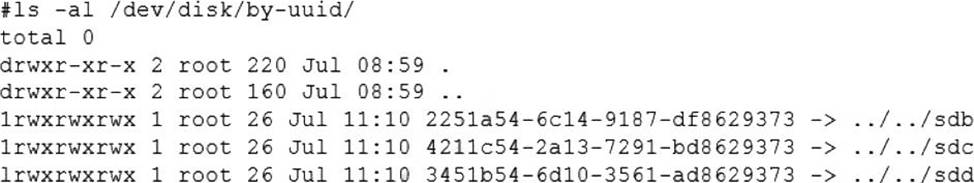
Which of the following should administrator use to resolve the device mismatch issue and mount the disk?
- A . mount disk by device-id
- B . fsck -A
- C . mount disk by-label
- D . mount disk by-blkid
A
Explanation:
The administrator should use the command mount disk by device-id to resolve the device mismatch issue and mount the disk. The issue is caused by the cloned server having a different device name for the disk than the original server. The output of blkid shows that the disk has the device name /dev/sdb1 on the cloned server, but the output of cat /etc/fstab shows that the disk is expected to have the device name /dev/sda1. The command mount disk by device-id will mount the disk by using its unique identifier (UUID) instead of its device name. The UUID can be obtained from the output of blkid or lsblk -f. The command will mount the disk to the specified mount point (/data) and resolve the issue. The other options are incorrect because they either do not mount the disk (fsck -A), do not use the correct identifier (mount disk by-label or mount disk by-blkid), or do not exist (mount disk by-blkid). CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 10: Managing Storage, pages 318-319.
After starting an Apache web server, the administrator receives the following error:
Apr 23 localhost.localdomain httpd 4618]: (98) Address already in use: AH00072: make_sock: could
not bind to address [: :]80
Which of the following commands should the administrator use to further trou-bleshoot this issue?
- A . Ss
- B . Ip
- C . Dig
- D . Nc
A
Explanation:
The ss command is used to display information about socket connections, such as the port number, state, and process ID. The error message indicates that the port 80 is already in use by another process, which prevents the Apache web server from binding to it. By using the ss command with the -l and -n options, the administrator can list all the listening sockets and their port numbers in numeric form, and identify which process is using the port 80. For example: ss -ln | grep :80. The ip, dig, and nc commands are not relevant for this issue, as they are used for different purposes, such as configuring network interfaces, querying DNS records, and testing network connectivity.
A Linux administrator would like to measure possible packet loss between a workstation and a remote web application that is running on port 443.
Which of the following would be the best command for the administrator to use to display this information?
- A . ping -c 50 <remote server IP>
- B . tcpdump -p 443 <remote server IP>
- C . mtr -T -P 443 <remote server IP>
- D . traceroute -p 443 <remote server IP>
C
Explanation:
mtr (My Traceroute) is a network diagnostic tool that combines the functionality of traceroute and ping. It shows real-time packet loss and latency on a hop-by-hop basis. The -T option uses TCP instead of ICMP, and the -P 443 option specifies the remote port. This provides the best method for checking packet loss on port 443.
