Practice Free XK0-005 Exam Online Questions
A systems administrator is reconfiguring existing user accounts in a Linux system.
Which of the following commands should the administrator use to include "myuser" in the finance group?
- A . groupadd finance myuser
- B . groupmod finance myuser
- C . useradd -g finance myuser
- D . usermod -aG finance myuser
A systems administrator wants to leverage their password-protected SSH key to connect to multiple servers without entering their password every time.
Which of the following commands should the administrator use?
- A . ssh-copy-id
- B . ssh-agent
- C . ssh-add
- D . ssh-keygen
C
Explanation:
ssh-add adds the private key to the SSH authentication agent, allowing the user to enter the passphrase once per session.
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ XK0-005 Study Guide, Domain 3.0 C Secure Shell
“Use ssh-add to add the SSH private key to memory, enabling passwordless logins during the session.”
A DevOps engineer needs to allow incoming traffic to ports in the range of 4000 to 5000 on a Linux server.
Which of the following commands will enforce this rule?
- A . iptables -f filter -I INPUT -p tcp –dport 4000:5000 -A ACCEPT
- B . iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp –dport 4000:5000 -j ACCEPT
- C . iptables filter -A INPUT -p tcp –dport 4000:5000 -D ACCEPT
- D . iptables filter -S INPUT -p tcp –dport 4000:5000 -A ACCEPT
B
Explanation:
The command iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp –dport 4000:5000 -j ACCEPT will enforce the rule of allowing incoming traffic to ports in the range of 4000 to 5000 on a Linux server.
The iptables command is a tool for managing firewall rules on Linux systems. The -t option specifies the table to operate on, in this case filter, which is the default table that contains the rules for filtering packets. The -A option appends a new rule to the end of a chain, in this case INPUT, which is the chain that processes the packets that are destined for the local system. The -p option specifies the protocol to match, in this case tcp, which is the transmission control protocol. The –dport option specifies the destination port or port range to match, in this case 4000:5000, which is the range of ports from 4000 to 5000. The -j option specifies the target to jump to if the rule matches, in this case ACCEPT, which is the target that allows the packet to pass through. The command iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp –dport 4000:5000 -j ACCEPT will add a new rule to the end of the INPUT chain that will accept the incoming TCP packets that have a destination port between 4000 and 5000. This command will enforce the rule and allow the traffic to the specified ports. This is the correct command to use to accomplish the task. The other options are incorrect because they either use the wrong options (-f instead of -t or -D instead of -A) or do not exist (iptables filter -A INPUT -p tcp — dport 4000:5000 -D ACCEPT or iptables filter -S INPUT -p tcp –dport 4000:5000 -A ACCEPT).
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 18: Securing Linux Systems, page 543.Topic 2, Exam Pool B
A Linux administrator needs to harden a system and guarantee that the Postfix service will not run,
even after a restart or system upgrade.
Which of the following commands allows the administrator to fulfill the requirement?
- A . systemctl mask postfix.service
- B . systemctl disable postfix.service
- C . systemctl stop postfix.service
- D . systemctl -n restart postfix.service
A
Explanation:
The systemctl mask postfix.service command prevents the Postfix service from being started manually or automatically by symlinking its service file to /dev/null. This ensures that even if a system restart or upgrade occurs, the service will remain disabled and will not start.
Which of the following commands is used to configure the default permissions for new files?
- A . setenforce
- B . sudo
- C . umask
- D . chmod
C
Explanation:
The command that is used to configure the default permissions for new files is umask.
The umask command is a tool for setting the default permissions for new files and directories on Linux systems. The umask value is a four-digit octal number that represents the permissions that are subtracted from the default permissions. The default permissions for files are 666, which means read and write for owner, group, and others. The default permissions for directories are 777, which means read, write, and execute for owner, group, and others. The umask value consists of four digits: the first digit is for special permissions, such as setuid, setgid, and sticky bit; the second digit is for the owner permissions; the third digit is for the group permissions; and the fourth digit is for the others permissions. The umask value can be calculated by subtracting the desired permissions from the default permissions. For example, if the desired permissions for files are 664, which means read and write for owner and group, and read for others, then the umask value is 002, which is 666 – 664. The command umask 002 will set the umask value to 002, which will ensure that only file owners and group members can modify new files by default. The command that is used to configure the default permissions for new files is umask. This is the correct answer to the question. The other options are incorrect because they either do not set the default permissions for new files (setenforce, sudo, or chmod) or do not exist (kill -HUP or kill -TERM). CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study
Guide, Chapter 11: Managing File Permissions and Ownership, page 349.
A Linux administrator is scheduling a system job that runs a script to check available disk space every hour. The Linux administrator does not want users to be able to start the job.
Given the following:
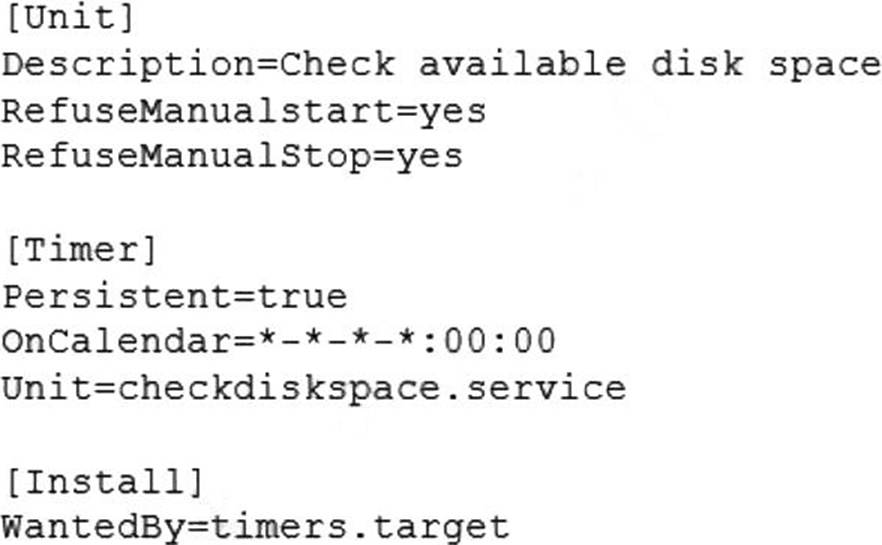
The Linux administrator attempts to start the timer service but receives the following error message:
![]()
Which of the following is MOST likely the reason the timer will not start?
- A . The checkdiskspace.timer unit should be enabled via systemct1.
- B . The timers.target should be reloaded to get the new configuration.
- C . The checkdiskspace.timer should be configured to allow manual starts.
- D . The checkdiskspace.timer should be started using the sudo command.
C
Explanation:
The most likely reason the timer will not start is that the checkdiskspace.timer should be configured to allow manual starts. By default, systemd timers do not allow manual activation via systemct1 start, unless they have RefuseManualStart=no in their [Unit] section. This option prevents users from accidentally starting timers that are meant to be controlled by other mechanisms, such as calendar events or dependencies. To enable manual starts for checkdiskspace.timer, the administrator should add RefuseManualStart=no to its [Unit] section and reload systemd.
The other options are not correct reasons for the timer not starting. The checkdiskspace.timer unit does not need to be enabled via systemct1 enable, because enabling a timer only makes it start automatically at boot time or after a system reload, but does not affect manual activation. The timers.target does not need to be reloaded to get the new configuration, because reloading a target only affects units that have a dependency on it, but does not affect manual activation. The checkdiskspace.timer does not need to be started using the sudo command, because the administrator is already running systemct1 as root, as indicated by the # prompt. : systemd.timer(5) – Linux manual page; systemct1(1) – Linux manual page
A new hard drive /dev/sdd was added to a server.
Which of the following commands will create a partition table with a single partition /dev/sdd1 that consumes the entire disk?
- A . echo ‘type=83’ | sudo sfdisk /dev/sdd
- B . sudo sfdisk /dev/sdd -t=83
- C . echo ‘auto’ | sudo fdisk /dev/sdd
- D . sudo fdisk /dev/sdd -1 -t=83
A
Explanation:
Step-by-Step Comprehensive Detailed
Command The sfdisk tool is used to manipulate partition tables in Linux. Option A creates a single partition on /dev/sdd of type 83 (Linux filesystem). type=83 specifies the partition type for Linux.
The command pipes this configuration to sfdisk to apply it directly to /dev/sdd.
Why Other Options are Incorrect:
B: Incorrect syntax; -t is not a valid option for sfdisk.
C: The fdisk command does not accept this syntax for automatic partition creation.
D: There is no -1 or -t=83 option in fdisk.
CompTIA Linux+ Certification Exam Objectives man sfdisk
A Linux administrator needs to transfer a local file named accounts. pdf to a remote / tmp directory of a server with the IP address 10.10.10.80.
Which of the following commands needs to be executed to transfer this file?
- A . rsync [email protected]: /tmp accounts.pdf
- B . scp accounts.pdf [email protected]:/tmp
- C . cp [email protected]. 80: /tmp accounts.pdf
- D . ssh accounts.pdf [email protected]: /tmp
B
Explanation:
The best command to use to transfer the local file accounts.pdf to the remote /tmp directory of the server with the IP address 10.10.10.80 is B. scp accounts.pdf [email protected]:/tmp. This command will use the secure copy protocol (scp) to copy the file from the local machine to the remote server over SSH. The command requires the username and password of the user on the remote server, as well as the full path of the destination directory.
The other commands are either incorrect or not suitable for this task.
For example:
A Linux administrator copied a Git repository locally, created a feature branch, and committed some changes to the feature branch.
Which of the following Git actions should the Linux administrator use to publish the changes to the main branch of the remote repository?
- A . rebase
- B . tag
- C . commit
- D . push
D
Explanation:
The push action is used to publish the changes made in a local branch to a remote branch of a Git repository. This action will update the remote branch with the commits made in the local branch and synchronize the two branches. The rebase action is used to reapply commits from one branch onto another branch, creating a linear history of commits. This action does not publish any changes to a remote repository. The tag action is used to create an annotated reference to a specific commit in a Git repository. This action does not publish any changes to a remote repository. The commit action is used to record changes made in the local repository and create a new snapshot of the project state. This action does not publish any changes to a remote repository. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 20: Writing and Executing Bash Shell Scripts, page 579.
A systems administrator is receiving tickets from users who cannot reach the application app that should be listening on port 9443/tcp on a Linux server.
To troubleshoot the issue, the systems administrator runs netstat and receives the following output:
![]()
Based on the information above, which of the following is causing the issue?
- A . The IP address 0.0.0.0 is not valid.
- B . The application is listening on the loopback interface.
- C . The application is listening on port 1234.
- D . The application is not running.
B
Explanation:
The server is in a "Listen" state on port 9943 using its loopback address. The "1234" is a process-id
The cause of the issue is that the application is listening on the loopback interface. The loopback interface is a virtual network interface that is used for internal communication within the system. The loopback interface has the IP address 127.0.0.1, which is also known as localhost. The netstat output shows that the application is listening on port 9443 using the IP address 127.0.0.1. This means that the application can only accept connections from the same system, not from other systems on the network. This can prevent the users from reaching the application and cause the issue. The administrator should configure the application to listen on the IP address 0.0.0.0, which means all available interfaces, or on the specific IP address of the system that is reachable from the network. This will allow the application to accept connections from other systems and resolve the issue. The cause of the issue is that the application is listening on the loopback interface. This is the correct answer to the question. The other options are incorrect because they are not supported by the outputs. The IP address 0.0.0.0 is valid and means all interfaces, the application is not listening on port 1234, and the application is running as shown by the process ID 1234. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Managing Network Connections, page 383.
