Practice Free XK0-005 Exam Online Questions
A systems administrator is deploying three identical, cloud-based servers.
The administrator is using the following code to complete the task:

Which of the following technologies is the administrator using?
- A . Ansible
- B . Puppet
- C . Chef
- D . Terraform
D
Explanation:
The code snippet is written in Terraform language, which is a tool for building, changing, and versioning infrastructure as code. Terraform uses a declarative syntax to describe the desired state of the infrastructure and applies the changes accordingly. The code defines a resource of type aws_instance, which creates an AWS EC2 instance, and sets the attributes such as the AMI ID, instance type, security group IDs, and key name. The code also uses a count parameter to create three identical instances and assigns them different names using the count.index variable. This is the correct technology that the administrator is using. The other options are incorrect because they use different languages and syntaxes for infrastructure as code. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 19: Managing Cloud and Virtualization Technologies, page 559.
A systems technician is working on deploying several microservices to various RPM-based systems, some of which could run up to two hours.
Which of the following commands will allow the technician to execute those services and continue deploying other microservices within the same terminal section?
- A . gedit & disown
- B . kill 9 %1
- C . fg %1
- D . bg %1 job name
D
Explanation:
The command that will allow the technician to execute the services and continue deploying other microservices within the same terminal session is bg %1 job name. This command will send the job with ID 1 and name job name to the background, where it will run without occupying the terminal.
The other options are incorrect because:
gedit & disown will launch a graphical text editor in the background and detach it from the terminal, but it will not execute any service.
kill 9 %1 will terminate the job with ID 1 using a SIGKILL signal, which cannot be ignored or handled by the process.
fg %1 will bring the job with ID 1 to the foreground, where it will occupy the terminal until it finishes or is stopped. CompTIA Linux+ Study Guide, Fourth Edition, page 181-182.
Which of the following is a way to enable a production web server’s communications with strong encryption and identity verification?
- A . Creating a key pair using ssh-keygen and using the generated key pair to secure the HTTPS communication
- B . Creating a private key locally using openssl, creating a certificate request, sending the request to an external certification provider, and using the provided certificate for HTTPS communication
- C . Creating a 4096-bytes or longer self-signed certificate using openssl and using it to secure HTTPS
communication - D . Creating a secret file using /dev/random as a source and using the generated file for HTTPS communication
B
Explanation:
Production web servers should use certificates issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). B is correct: This describes the proper process―generate a private key, create a CSR (Certificate Signing Request), send it to a CA, and use the returned signed certificate for HTTPS.
Incorrect Options:
A: SSH keys are for SSH, not HTTPS/TLS.
C: Self-signed certs are insecure in production.
D: Irrelevant to HTTPS; /dev/random is used for entropy generation.
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ XK0-005 Study Guide, Chapter 11 man openssl
A cloud engineer is asked to copy the file deployment.yaml from a container to the host where the container is running.
Which of the following commands can accomplish this task?
- A . docker cp container_id/deployment.yaml deployment.yaml
- B . docker cp container_id:/deployment.yaml deployment.yaml
- C . docker cp deployment.yaml local://deployment.yaml
- D . docker cp container_id/deployment.yaml local://deployment.yaml
B
Explanation:
The command docker cp container_id:/deployment.yaml deployment.yaml can accomplish the task of copying the file deployment.yaml from a container to the host. The docker command is a tool for managing Docker containers and images. The cp option copies files or directories between a container and the local filesystem. The container_id is the identifier of the container, which can be obtained by using the docker ps command. The /deployment.yaml is the path of the file in the container, which must be preceded by a slash. The deployment.yaml is the path of the file on the host, which can be relative or absolute. The command docker cp container_id:/deployment.yaml deployment.yaml will copy the file deployment.yaml from the container to the current working directory on the host. This is the correct command to use to accomplish the task. The other options are incorrect because they either use the wrong syntax (docker cp container_id/deployment.yaml deployment.yaml or docker cp container_id/deployment.yaml local://deployment.yaml) or do not exist (docker cp deployment.yaml local://deployment.yaml). CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005)
Certification Study Guide, Chapter 19: Managing Cloud and Virtualization Technologies, page 567.
A Linux administrator reviews a set of log output files and needs to identify files that contain any occurrence of the word denied. All log files containing entries in uppercase or lowercase letters should be included in the list.
Which of the following commands should the administrator use to accomplish this task?
- A . find. -type f -print | xrags grep -ln denied
- B . find. -type f -print | xrags grep -nv denied
- C . find. -type f -print | xrags grep -wL denied
- D . find. -type f -print | xrags grep -li denied
D
Explanation:
The command find. -type f -print | xargs grep -li denied will accomplish the task of identifying files that contain any occurrence of the word denied. The find command is a tool for searching for files and directories on Linux systems. The. is the starting point of the search, which means the current directory. The -type f option specifies the type of the file, which means regular file. The -print option prints the full file name on the standard output. The | is a pipe symbol that redirects the output of one command to the input of another command. The xargs command is a tool for building and executing commands from standard input. The grep command is a tool for searching for patterns in files or input. The -li option specifies the flags that the grep command should apply. The -l flag shows only the file names that match the pattern, instead of the matching lines. The -i flag ignores the case of the pattern, which means it matches both uppercase and lowercase letters. The denied is the pattern that the grep command should search for. The command find. -type f -print | xargs grep -li denied will find all the regular files in the current directory and its subdirectories, and then search for any occurrence of the word denied in those files, ignoring the case, and print only the file names that match the pattern. This will allow the administrator to identify files that contain any occurrence of the word denied. This is the correct command to use to accomplish the task. The other options are incorrect because they either do not ignore the case of the pattern (find. -type f -print | xargs grep – ln denied or find. -type f -print | xargs grep -wL denied) or do not show the file names that match the pattern (find. -type f -print | xargs grep -nv denied).
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 16: Managing Logging and Monitoring, page 489.
A developer is unable to access a Linux server via SSH.
Given the following output:
SSH server configuration (/etc/ssh/sshd_config):
PermitRootLogin no
PubkeyAuthentication yes
PasswordAuthentication yes
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
X11Forwarding no
User Information (/etc/passwd):
developer:x:1000:1000:comptia:/home/developer:/bin/bash
User Shadow File (/etc/shadow):
developer:!!::0:99999:7:::
Which of the following explains why the developer is unable to log in to the server?
- A . The developer’s private key has been deleted from the server.
- B . The developer’s account has been locked out.
- C . The developer’s public key is in the wrong location.
- D . SSH has been disabled for user log-in.
B
Explanation:
The reason the developer cannot log in is because their account is locked.
This is indicated by the "!!" in the /etc/shadow file:
developer:!!::0:99999:7:::
The "!!" in the password field means the account is locked, and the user cannot authenticate using a password.
To unlock the account, the administrator must reset the password:
passwd developer
OR, if SSH key authentication is used, the administrator can remove the lock without setting a password:
usermod -U developer
Why the other options are incorrect?
A Linux administrator has set up a new DNS forwarder and is configuring all internal servers to use the new forwarder to look up external DNS requests. The administrator needs to modify the firewall on the server for the DNS forwarder to allow the internal servers to communicate to it and make the changes persistent between server reboots.
Which of the following commands should be run on the DNS forwarder server to accomplish this task?
- A . ufw allow out dns
- B . systemct1 reload firewalld
- C . iptables -A OUTPUT -p udp -ra udp -dport 53 -j ACCEPT
- D . flrewall-cmd –zone-public –add-port-53/udp –permanent
D
Explanation:
The command that should be run on the DNS forwarder server to accomplish the task is firewall-cmd –zone=public –add-port=53/udp –permanent. The firewall-cmd command is a tool for managing firewalld, which is a firewall service that provides dynamic and persistent network security on Linux systems. The firewalld uses zones and services to define the rules and policies for the network traffic. The zones are logical groups of network interfaces and sources that have the same level of trust and security. The services are predefined sets of ports and protocols that are associated with certain applications or functions. The –zone=public option specifies the zone name that the rule applies to. The public zone is the default zone that represents the untrusted network, such as the internet. The – -add-port=53/udp option adds a port and protocol to the zone. The 53 is the port number that is used by the DNS service. The udp is the protocol that is used by the DNS service. The — permanent option makes the change persistent across reboots. The command firewall-cmd — zone=public –add-port=53/udp –permanent will modify the firewall on the server for the DNS forwarder to allow the internal servers to communicate to it and make the changes persistent between server reboots. This is the correct command to use to accomplish the task. The other options are incorrect because they either do not modify the firewall on the server for the DNS forwarder (ufw allow out dns or systemct1 reload firewalld) or do not use the correct syntax for the command (iptables -A OUTPUT -p udp -ra udp -dport 53 -j ACCEPT instead of iptables -A OUTPUT -p udp -ra udp –dport 53 -j ACCEPT). CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Managing Network Connections, page 392.
A Linux systems administrator is setting up a new web server and getting 404 – NOT FOUND errors while trying to access the web server pages from the browser.
While working on the diagnosis of this issue, the Linux systems administrator executes the following commands:

Which of the following commands will BEST resolve this issue?
- A . sed -i ‘s/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/’ /etc/selinux/config
- B . restorecon -R -v /var/www/html
- C . setenforce 0
- D . setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect_db on
B
Explanation:
The command restorecon -R -v /var/www/html will best resolve the issue. The issue is caused by the incorrect SELinux context of the web server files under the /var/www/html directory. The output of ls -Z /var/www/html shows that the files have the type user_home_t, which is not allowed for web content. The command restorecon restores the default SELinux context of files based on the policy rules. The options -R and -v are used to apply the command recursively and verbosely. This command will change the type of the files to httpd_sys_content_t, which is the correct type for web content. This will allow the web server to access the files and serve the pages to the browser. The other options are incorrect because they either disable SELinux entirely (sed -i ‘s/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/’ /etc/selinux/config or setenforce 0), which is not a good security practice, or enable an unnecessary boolean (setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect_db on), which is not related to the issue. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 18: Securing Linux Systems, page 535.
A Linux administrator discovers that a configured schedule is not running properly and needs to re-create the schedule. The task should run every Monday at 13:30 but only during the months of February, May, August, and November.
Which of the following options should the administrator use?
- A . OnCalendar=Mon -2,5,8,11-13:30:00
- B . OnCalendar=-FEB,-MAY,-AUG,-NOV Mon 13:30:00
- C . OnCalendar=*-2,5,8,11 13:30:00 Mon
- D . OnCalendar=Mon *-FEB *-MAY *-AUG *-NOV 13:30:00
C
Explanation:
The correct systemd.timer syntax is:
bash
OnCalendar=Mon *-2,5,8,11 13:30:00
This runs every Monday at 13:30 in the specified months.
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ XK0-005 Study Guide, Domain 4.4 C Scheduled Tasks
“Systemd timers use OnCalendar=DAY MONTH TIME syntax for scheduled tasks.”
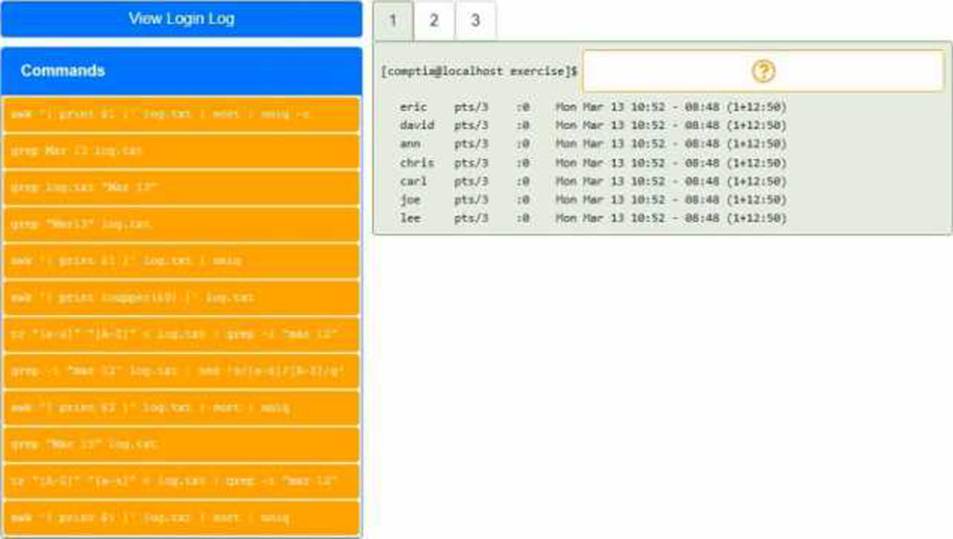
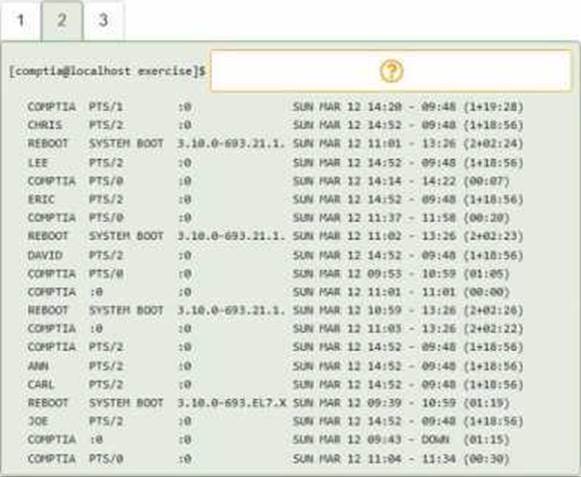
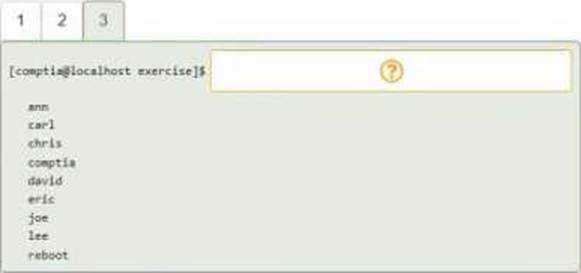
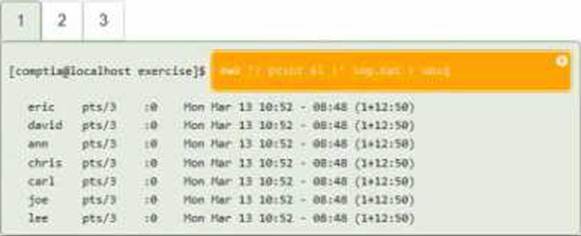
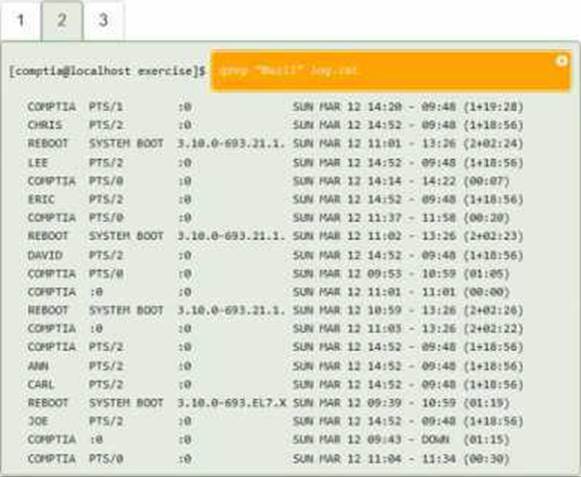
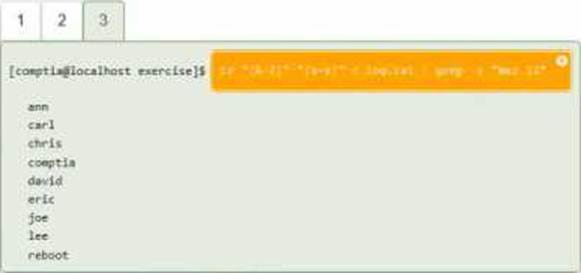
DRAG DROP
You have been asked to parse a log file of logins to determine various information about who is
logging in and when.
INSTRUCTIONS
Open and inspect the Login log file.
Drag and drop the correct commands onto the output that was generated from that command.
Tokens can be used only once and not all will be used.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.