Practice Free XK0-005 Exam Online Questions
A systems administrator needs to verify whether the built container has the app.go file in its root directory.
Which of the following can the administrator use to verify the root directory has this file?
- A . docker image inspect
- B . docker container inspect
- C . docker exec <container_name> ls
- D . docker ps <container_name>
C
Explanation:
The docker exec <container_name> ls command can be used to verify whether the built container has the app.go file in its root directory. This command will run the ls command inside the specified container and list the files and directories in its root directory. If the app.go file is present, it will be displayed in the output. The docker image inspect command will display information about an image, not a container, and it will not list the files inside the image. The docker container inspect
command will display information about a container, not its files. The docker ps <container_name> command is invalid, as ps does not accept a container name as an argument. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 16: Virtualization and Cloud Technologies, page 499.
A Linux systems administrator receives a report that a user is unable to start an application.
The administrator reviews the following error:
yaml
CopyEdit
Killed process 1141 (application) … total-vm:5622584kB … oom_score_adj:0 oom_reaper: reaped process 1141 …
Which of the following describes the situation?
- A . The system does not have adequate CPU capacity to allocate to the application.
- B . The application is trying to connect to multiple remote systems without having an adequate number of connections available.
- C . The application is trying to open more files than the available disk can accommodate.
- D . The application is trying to allocate more memory than the available system and swap space can support.
D
Explanation:
The logs clearly indicate the Out of Memory (OOM) killer terminated the process (Killed process… oom_score…).
D is correct: The application attempted to allocate more memory than was available (RAM + swap), triggering the OOM killer.
Incorrect Options:
A: No CPU-related error or throttling is shown.
B: No network error or socket limitation messages are shown.
C: No error related to open file handles or disk usage.
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ XK0-005 Study Guide, Chapter 9 man dmesg, man proc
A cloud engineer needs to check the link status of a network interface named eth1 in a Linux server.
Which of the following commands can help to achieve the goal?
- A . ifconfig hw eth1
- B . netstat -r eth1
- C . ss -ti eth1
- D . ip link show eth1
D
Explanation:
The ip link show eth1 command can be used to check the link status of a network interface named eth1 in a Linux server. It will display information such as the MAC address, MTU, state, and flags of the interface. The ifconfig hw eth1 command is invalid, as hw is not a valid option for ifconfig. The netstat -r eth1 command would display the routing table for eth1, not the link status. The ss -ti eth1 command would display TCP information for sockets associated with eth1, not the link status. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 13: Networking Fundamentals, page 436.
A systems administrator is creating new user accounts on several Linux machines and wants to automate the process from a Linux system used for operations. In this operations system, the list of servers is located in the /home/user/serverslist file and the list of user accounts is located in the /home/user/userslist file.
Which of the following scripts will help accomplish this task?
- A . bashfor server in $(cat /home/user/serverslist) do for user in $(cat /home/user/userslist) do sudo useradd $user done done
- B . bashfor server in $(cat /home/user/serverslist) do ssh -i user@$server "for user in $(cat /home/user/userslist) do sudo useradd $user done; exit" done
- C . bashfor server in $(cat /home/user/serverslist) do scp /home/user/userslist user@$server:/tmp ssh -i user@$server "for user in $(cat /tmp/userslist) do sudo useradd $user done; exit" done
- D . bashssh user@$(cat /home/user/serverslist) "sudo useradd $(cat /home/user/userslist); exit"
B
Explanation:
The script in option B performs the task by SSH-ing into each server listed in serverslist and then adding each user listed in userslist. This is an effective way to remotely create user accounts without manually logging into each server. The ssh command allows the execution of the useradd commands on the remote machines.
Users are reporting that a Linux server is responding slowly. A systems administrator troubleshooting the server issue sees the following iostat output, with %iowait at 50.38.
Which of the following is most likely the issue?
- A . The CPU is mostly waiting for I/O operations.
- B . / filesystem does not have enough storage allocated.
- C . /var filesystem is almost full.
- D . The CPU capacity is inadequate.
A
Explanation:
The %iowait value represents the percentage of time the CPU is waiting for I/O operations to complete. A high %iowait value suggests the system is bottlenecked by disk I/O, which could lead to slow response times. Addressing disk I/O bottlenecks would improve performance.
Reference: Linux Performance Monitoring with iostat
A Linux administrator needs to create a symlink for /usr/local/bin/app-a, which was installed in /usr/local/share/app-a.
Which of the following commands should the administrator use?
- A . In -s /usr/local/bin/app-a /usr/local/share/app-a
- B . mv -f /usr/local/share/app-a /usr/local/bin/app-a
- C . cp -f /usr/local/share/app-a /usr/local/bin/app-a
- D . rsync -a /usr/local/share/app-a /usr/local/bin/app-a
A
Explanation:
To create a symlink for /usr/local/bin/app-a, which was installed in /usr/local/share/app-a, the administrator can use the command ln -s /usr/local/share/app-a /usr/local/bin/app-a (A). This will create a symbolic link named /usr/local/bin/app-a that points to the original file /usr/local/share/app-a. The other commands will not create a symlink, but either move, copy, or synchronize the file.
[CompTIA Linux+ Study Guide], Chapter 3: Working with Files, Section: Creating Links [How to Create Symbolic Links in Linux]
Users have been unable to reach www.comptia.org from a Linux server.
A systems administrator is troubleshooting the issue and does the following:
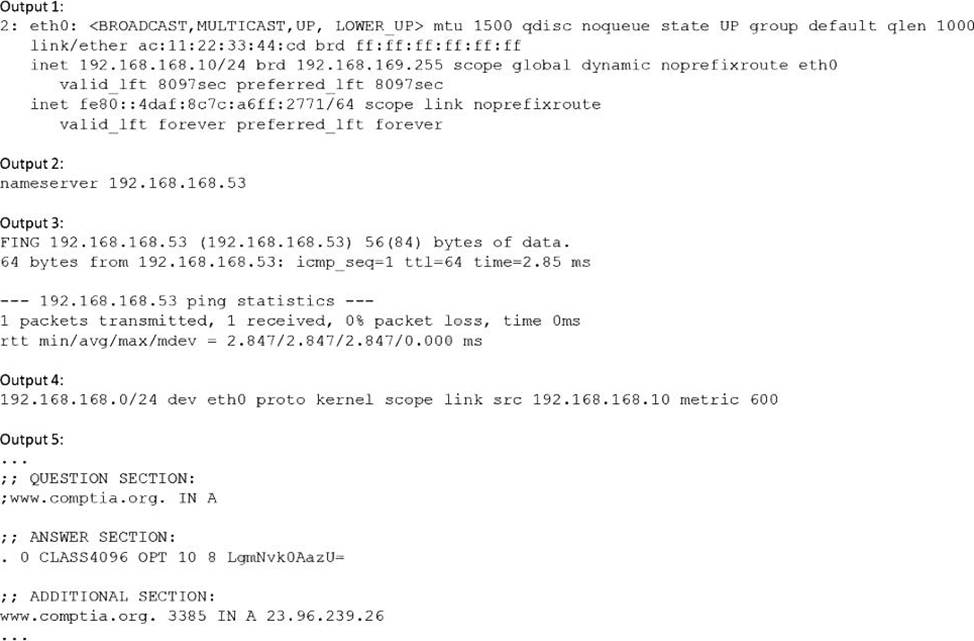
Based on the information above, which of the following is causing the issue?
- A . The name www.comptia.org does not point to a valid IP address.
- B . The server 192.168.168.53 is unreachable.
- C . No default route is set on the server.
- D . The network interface eth0 is disconnected.
B
Explanation:
The issue is caused by the server 192.168.168.53 being unreachable. This server is the DNS server configured in the /etc/resolv.conf file, which is used to resolve domain names to IP addresses. The ping command shows that the server cannot be reached, and the nslookup command shows that the name www.comptia.org cannot be resolved using this server.
The other options are incorrect because:
The name www.comptia.org does point to a valid IP address, as shown by the nslookup command using another DNS server (8.8.8.8).
The default route is set on the server, as shown by the ip route command, which shows a default gateway of 192.168.168.1.
The network interface eth0 is connected, as shown by the ip link command, which shows a state of UP for eth0.
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ Study Guide, Fourth Edition, page 457-458, 461-462.
A Linux administrator is changing the default system umask. The newly created files should have the -rw-r—– permission, and the newly created directories should have the drwxr—– permission.
Which of the following commands should the administrator use?
- A . umask 0035
- B . umask 0036
- C . umask 0037
- D . umask 0038
C
Explanation:
umask subtracts permissions from default (666 for files, 777 for dirs).
To achieve 640 for files → umask = 137
To achieve 750 for dirs → umask = 027
The closest match to both for stricter permissions is umask 0037.
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ XK0-005 Study Guide, Chapter 11
man umask
A Linux administrator rebooted a server. Users then reported some of their files were missing. After doing some troubleshooting, the administrator found one of the filesystems was missing. The filesystem was not listed in /etc/f stab and might have been mounted manually by someone prior to reboot.
Which of the following would prevent this issue from reoccurring in the future?
- A . Sync the mount units.
- B . Mount the filesystem manually.
- C . Create a mount unit and enable it to be started at boot.
- D . Remount all the missing filesystems
C
Explanation:
The best way to prevent this issue from reoccurring in the future is to create a mount unit and enable it to be started at boot. A mount unit is a systemd unit that defines how and where a filesystem should be mounted. By creating a mount unit for the missing filesystem and enabling it with systemct1 enable, the administrator can ensure that the filesystem will be automatically mounted at boot time, regardless of whether it is listed in /etc/fstab or not. Syncing the mount units will not prevent the issue, as it will only synchronize the state of existing mount units with /etc/fstab, not create new ones. Mounting the filesystem manually will not prevent the issue, as it will only mount the filesystem temporarily, not permanently. Remounting all the missing filesystems will not prevent the issue, as it will only mount the filesystems until the next reboot, not after. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 14: Managing Disk Storage, page 457.
A systems administrator is tasked with setting up key-based SSH authentication. In which of the following locations should the administrator place the public keys for the server?
- A . ~/.sshd/authkeys
- B . ~/.ssh/keys
- C . ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
- D . ~/.ssh/keyauth
C
Explanation:
The administrator should place the public keys for the server in the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file. The SSH (Secure Shell) protocol is a method for establishing secure and encrypted connections between remote systems. The SSH protocol supports two types of authentication: password-based and key-based. Password-based authentication requires the user to enter the password of the remote system every time they connect. Key-based authentication requires the user to generate a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is stored on the remote system, while the private key is kept on the local system. The public key and the private key are mathematically related, but not identical. The SSH protocol uses the keys to verify the identity of the user and establish a secure connection without requiring a password. The ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file is a file that contains the public keys of the users who are allowed to connect to the remote system using key-based authentication. The administrator should place the public keys for the server in this file, one per line, and set the appropriate permissions for the file. The administrator should also configure the SSH server to enable key-based authentication by editing the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file and setting the option PasswordAuthentication to no. The administrator should place the public keys for the server in the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file. This is the correct answer to the question. The other options are incorrect because they are not the standard locations for the public keys for the server (~/.sshd/authkeys, ~/.ssh/keys, or ~/.ssh/keyauth). CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 17: Implementing Basic Security, page 513.
