Practice Free XK0-005 Exam Online Questions
HOTSPOT
A new drive was recently added to a Linux system.
Using the environment and tokens provided, complete the following tasks:
• Create an appropriate device label.
• Format and create an ext4 file system on the new partition.
The current working directory is /.
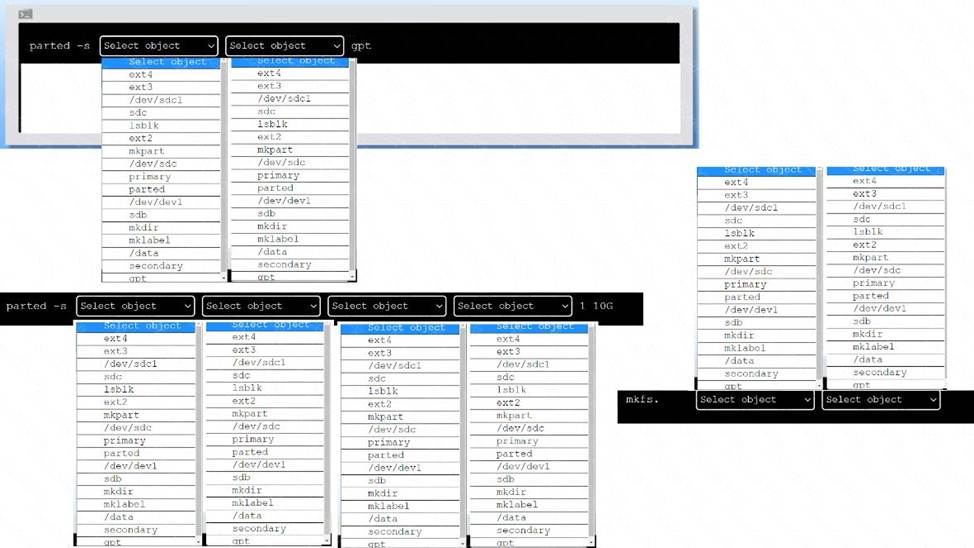
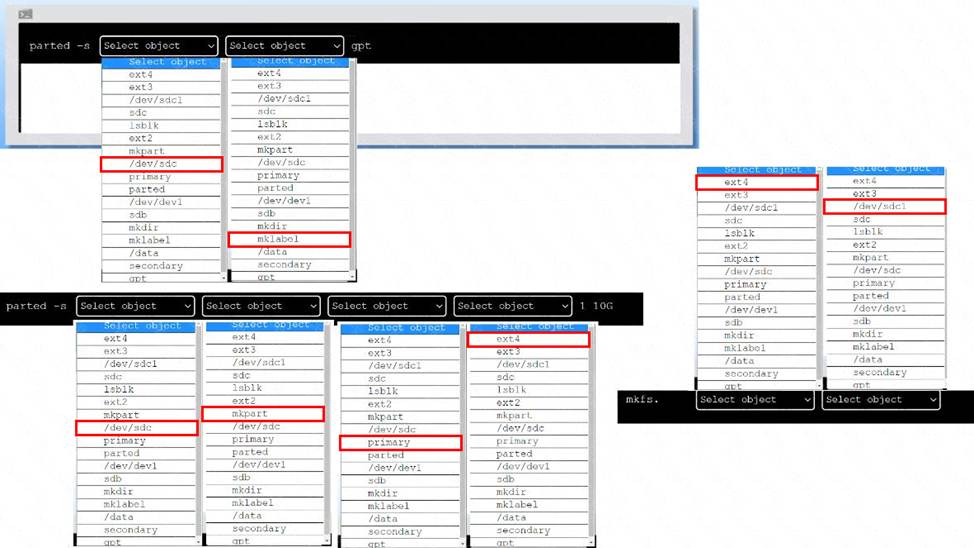
Explanation:
To create an appropriate device label, format and create an ext4 file system on the new partition, you can use the following commands:
To create a GPT (GUID Partition Table) label on the new drive /dev/sdc, you can use the parted
command with the -s option (for script mode), the device name (/dev/sdc), the mklabel command,
and the label type (gpt).
The command is:
parted -s /dev/sdc mklabel gpt
To create a primary partition of 10 GB on the new drive /dev/sdc, you can use the parted command with the -s option, the device name (/dev/sdc), the mkpart command, the partition type (primary),
the file system type (ext4), and the start and end points of the partition (1 and 10G). The command is:
parted -s /dev/sdc mkpart primary ext4 1 10G
To format and create an ext4 file system on the new partition /dev/sdc1, you can use the mkfs command with the file system type (ext4) and the device name (/dev/sdc1). The command is: mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdc1
You can verify that the new partition and file system have been created by using the lsblk command, which will list all block devices and their properties.
A Linux administrator is implementing a CI/CD process for the company’s internal accounting web application.
Which of the following best defines the purpose of this process?
- A . To automate the process of building, testing, and deploying application components
- B . To perform security penetration tests on deployed applications to identify vulnerabilities
- C . To formalize the approval process of application releases and configuration changes
- D . To leverage code to document the infrastructure, configurations, and dependencies
A
Explanation:
CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) is a practice that automates the process of building, testing, and deploying applications. This approach reduces manual intervention, ensuring code changes are integrated and tested frequently, leading to faster and more reliable application deployment.
A user is cleaning up a directory because it has more than 100,000 files that were generated from an experiment.
When the user tries to remove the unneeded experiment files, the user receives an error:
arduino cannot execute [Argument list too long]
Which of the following should the user execute to remove these files?
- A . find. -name "experiment*.txt" -exec rm "{}" ;
- B . rm -rf experiment*.txt
- C . rm –force experiment*.txt
- D . for i in experiment*.txt; do find. -name $i -exec rmdir "{}" ; done
A
Explanation:
The "Argument list too long" error occurs when the number of files exceeds the command-line argument limit. The find command with -exec is a workaround, as it processes files one by one, avoiding the argument limit. This method is efficient for handling large numbers of files.
A systems administrator wants to upgrade /bin/ someapp to a new version, but the administrator
does not know the package name.
Which of the following will show the RPM package name that provides that binary file?
- A . rpm ―qf /bin/ someapp
- B . rpm ―Vv / bin/ someapp
- C . rpm – P / bin/ some app
- D . rpm ―i / bin/ someapp
A
Explanation:
The rpm command is used to manage RPM packages on Linux systems. The -qf option queries the package name that provides a given file. Therefore, the command rpm -qf /bin/someapp will show the RPM package name that provides the binary file /bin/someapp. The statements B, C, and D are incorrect because they do not query the package name, but rather verify, remove, or install a package. [How to Use RPM Command in Linux with Examples]
A network administrator issues the dig www.comptia.org command and receives an NXDOMAIN response.
Which of the following files should the administrator check first?
- A . /etc/resolv.conf
- B . /etc/hosts
- C . /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts
- D . /etc/nsswitch.conf
A
Explanation:
The dig command uses the DNS servers listed in the /etc/resolv.conf file to resolve domain names. If
the dig command returns an NXDOMAIN response, it means the domain does not exist according to the DNS servers used. Therefore, the administrator should check the /etc/resolv.conf file first34. :3(https://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/linux-newbie-8/help-me-dig-status-nxdomain-4175684441/)4(https://serverfault.com/questions/729025/what-are-all-the-flags-in-a-dig-response)
A Linux administrator has logged in to a server for the first time and needs to know which services are allowed through the firewall.
Which of the following options will return the results for which the administrator is looking?
- A . firewall-cmd ―get-services
- B . firewall-cmd ―check-config
- C . firewall-cmd ―list-services
- D . systemct1 status firewalld
C
Explanation:
The firewall-cmd –list-services command will return the results for which the administrator is looking. This command will list all services that are allowed through the firewall in the default zone or a specified zone. A service is a predefined set of ports and protocols that can be enabled or disabled by firewalld. The firewall-cmd –get-services command will list all available services that are supported by firewalld, not only those that are allowed through the firewall. The firewall-cmd — check-config command will check if firewalld configuration files are valid, not list services. The systemct1 status firewalld command will display information about the firewalld service unit, such as its state, PID, memory usage, and logs, not list services. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 18: Securing Linux Systems, page 543.
A Linux systems administrator is resolving a privileged access issue for users who are members of an admin group.
Which of the following configuration files should the administrator update so the users in the admin group will have root privileged access to the Linux system?
- A . /etc/sudoers
- B . /etc/login.defs
- C . /etc/group
- D . /etc/shadow
A
Explanation:
To grant sudo/root privileges to a group (like admin), the correct file to edit is:
bash
/etc/sudoers
This is where privilege escalation rules are defined.
A line such as:
bash
%admin ALL=(ALL) ALL
will grant all users in the admin group root privileges.
/etc/login.defs controls general login settings.
/etc/group defines group membership but does not assign privileges.
/etc/shadow holds encrypted passwords and is not relevant here.
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ XK0-005 Official Study Guide, Domain 6.0 C User and Group Management
“To allow members of a group to execute commands with root privileges, update the /etc/sudoers file using visudo.”
Which of the following data structures is written in JSON?
A)

B)

C)
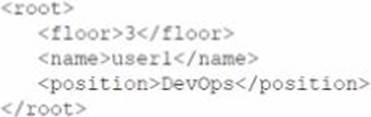
D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
C
Explanation:
Option C is the only data structure that is written in JSON format. JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation, and it is a lightweight and human-readable data interchange format. JSON uses curly braces to enclose objects, which consist of key-value pairs separated by commas. JSON uses square brackets to enclose arrays, which consist of values separated by commas. JSON supports six data types: strings, numbers, booleans, null, objects, and arrays. Option C follows these rules and syntax of JSON, while the other options do not. Option A is written in XML format, which uses tags to enclose elements and attributes. Option B is written in YAML format, which uses indentation and colons to define key-value pairs. Option D is written in INI format, which uses sections and equal signs to define key-value pairs. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 21: Automating Tasks with Ansible, page 591.
A systems administrator is installing various software packages using a pack-age manager.
Which of the following commands would the administrator use on the Linux server to install the package?
- A . winget
- B . softwareupdate
- C . yum-config
- D . apt
A Linux administrator is working on a system and notices that some of the packages are not at the latest version.
Which of the following commands should the administrator use to correct this issue?
- A . rpm –update
- B . apt update
- C . dnt update
- D . dpkg –update
B
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
The apt update command updates the package lists for repositories but does not upgrade installed packages.
After apt update, the administrator should run apt upgrade to install the latest versions of all packages.
rpm –update is incorrect because RPM does not have an –update option for updating repositories.
RPM package management requires yum or dnf on RHEL-based systems.
dnt update is not a valid command (probably a typo for dnf update, which would be used on Fedora/RHEL systems).
dpkg –update is incorrect because dpkg is used for managing individual .deb packages and does not update repositories.
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ Official Study Guide, Chapter on Package Management
