Practice Free PT0-003 Exam Online Questions
A penetration tester identifies the following open ports during a network enumeration scan:
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
111/tcp open rpcbind
443/tcp open https
27017/tcp open mongodb
50123/tcp open ms-rpc
Which of the following commands did the tester use to get this output?
- A . nmap -Pn -A 10.10.10.10
- B . nmap -sV 10.10.10.10
- C . nmap -Pn -w 10.10.10.10
- D . nmap -sV -Pn -p- 10.10.10.10
D
Explanation:
To detect all open ports and enumerate services, the tester needs to:
Use -sV (Service Version Detection)
Use -Pn (Disables ICMP ping to bypass firewalls)
Use -p- (Scans all 65,535 TCP ports)
nmap -sV -Pn -p- 10.10.10.10 (Option D):
This command performs full-port scanning, including high-numbered ports like 50123/tcp (ms-rpc).
Without -p-, high ports would be missed.
Reference: CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide – "Nmap Scanning Techniques"
Incorrect options:
Option A (-A): Includes OS detection but does not guarantee scanning all ports.
Option B (-sV without -p-): Scans default ports only, missing 50123/tcp.
Option C (-w): Invalid Nmap flag.
A tester completed a report for a new client. Prior to sharing the report with the client, which of the following should the tester request to complete a review?
- A . A generative AI assistant
- B . The customer’s designated contact
- C . A cybersecurity industry peer
- D . A team member
B
Explanation:
Before sharing a report with a client, it is crucial to have it reviewed to ensure accuracy, clarity, and completeness. The best choice for this review is a team member.
Here’s why:
Internal Peer Review:
Familiarity with the Project: A team member who worked on the project or is familiar with the methodologies used can provide a detailed and context-aware review.
Quality Assurance: This review helps catch any errors, omissions, or inconsistencies in the report before it reaches the client.
Alternative Review Options:
A Generative AI Assistant: While useful for drafting and checking for language issues, it may not fully understand the context and technical details of the penetration test.
The Customer’s Designated Contact: Typically, the client reviews the report after the internal review to provide their perspective and request clarifications or additional details.
A Cybersecurity Industry Peer: Although valuable, this option might not be practical due to confidentiality concerns and the peer’s lack of specific context regarding the engagement.
In summary, an internal team member is the most suitable choice for a thorough and contextually accurate review before sharing the report with the client.
During an assessment, a penetration tester gains access to one of the internal hosts.
Given the following command:
schtasks /create /sc onlogon /tn "Windows Update" /tr "cmd.exe /c reverse_shell.exe"
Which of the following is the penetration tester trying to do with this code?
- A . Enumerate the scheduled tasks
- B . Establish persistence
- C . Deactivate the Windows Update functionality
- D . Create a binary application for Windows System Updates
B
Explanation:
The command creates a scheduled task that executes a reverse shell payload at logon, ensuring persistence.
Option A (Enumerate tasks) ❌ : This command creates a task, not lists tasks (schtasks /query is used for enumeration).
Option B (Establish persistence) ✅ : Correct.
The attacker ensures a reverse shell opens every time a user logs in.
Option C (Deactivate Windows Update) ❌ : The task is named "Windows Update" but does not disable updates.
Option D (Create a Windows Update binary) ❌ : This executes a reverse shell, not a system update.
Reference: CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Guide C Windows Persistence Techniques
During an assessment, a penetration tester plans to gather metadata from various online files, including pictures.
Which of the following standards outlines the formats for pictures, audio, and additional tags that facilitate this type of reconnaissance?
- A . EXIF
- B . GIF
- C . COFF
- D . ELF
A
Explanation:
Metadata extraction allows attackers to collect sensitive information from digital files.
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) (Option A):
EXIF metadata contains camera details, GPS coordinates, timestamps, and software versions used to edit the file.
Attackers use tools like ExifTool to extract metadata for reconnaissance.
Reference: CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide – "Metadata Analysis in Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT)"
Incorrect options:
Option B (GIF): A file format for images, but not a metadata standard.
Option C (COFF): Common Object File Format, related to executable files, not images.
Option D (ELF): Executable and Linkable Format, used for Linux binaries, not metadata analysis.
A penetration tester assesses a complex web application and wants to explore potential security weaknesses by searching for subdomains that might have existed in the past.
Which of the following tools should the penetration tester use?
- A . Censys.io
- B . Shodan
- C . Wayback Machine
- D . SpiderFoot
C
Explanation:
The Wayback Machine is an online tool that archives web pages over time, allowing users to see how a website looked at various points in its history. This can be extremely useful for penetration testers looking to explore potential security weaknesses by searching for subdomains that might have existed in the past.
Accessing the Wayback Machine:
Go to the Wayback Machine website: archive.org/web.
Enter the URL of the target website you want to explore.
Navigating Archived Pages:
The Wayback Machine provides a timeline and calendar interface to browse through different snapshots taken over time.
Select a snapshot to view the archived version of the site. Look for links, subdomains, and resources that may no longer be available in the current version of the website.
Identifying Subdomains:
Examine the archived pages for references to subdomains, which might be visible in links, scripts, or embedded content.
Use the information gathered to identify potential entry points or older versions of web applications that might still be exploitable.
Tool Integration:
Tools like Burp Suite or SpiderFoot can integrate with the Wayback Machine to automate the
discovery process of archived subdomains and resources.
Real-World Example:
During a penetration test, a tester might find references to oldadmin.targetsite.com in an archived page from several years ago. This subdomain might no longer be listed in DNS but could still be accessible, leading to potential security vulnerabilities.
Reference from Pentesting Literature:
In various penetration testing guides and HTB write-ups, using the Wayback Machine is a common technique for passive reconnaissance, providing historical context and revealing past configurations that might still be exploitable.
Step-by-Step ExplanationReference: HTB Official Writeups
Which of the following activities should be performed to prevent uploaded web shells from being exploited by others?
- A . Remove the persistence mechanisms.
- B . Spin down the infrastructure.
- C . Preserve artifacts.
- D . Perform secure data destruction.
A
Explanation:
Web shells provide remote access and persistence for attackers. The best mitigation is to remove persistence mechanisms.
Remove the persistence mechanisms (Option A):
Attackers often modify startup scripts, cron jobs, or registry keys to maintain access.
If persistence is not removed, even after the web shell is deleted, attackers can reinstall or reaccess it.
Reference: CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide – "Removing Persistent Web Shells"
Incorrect options:
Option B (Spin down the infrastructure): Shutting down servers does not remove the persistence.
Option C (Preserve artifacts): Important for forensics but does not prevent exploitation.
Option D (Perform secure data destruction): Secure wipe is useful but not always feasible for a production system.
A penetration tester is conducting an assessment of a web application’s login page. The tester needs to determine whether there are any hidden form fields of interest.
Which of the following is the most effective technique?
- A . XSS
- B . On-path attack
- C . SQL injection
- D . HTML scraping
D
Explanation:
Hidden form fields in web applications can store user roles, session tokens, and security parameters that attackers may exploit.
HTML scraping (Option D):
Involves analyzing HTML source code to find hidden fields like:
<input type="hidden" name="admin_access" value="true">
Attackers use tools like Burp Suite, ZAP, or browser developer tools (Ctrl+U or Inspect Element) to
locate hidden fields.
Reference: CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide – "Web Application Testing and Form Field Analysis"
Incorrect options:
Option A (XSS): Exploits JavaScript injection, not for finding hidden fields.
Option B (On-path attack): Involves MITM interception, not directly analyzing form fields.
Option C (SQL injection): Targets databases, not HTML forms
The following file was obtained during reconnaissance:
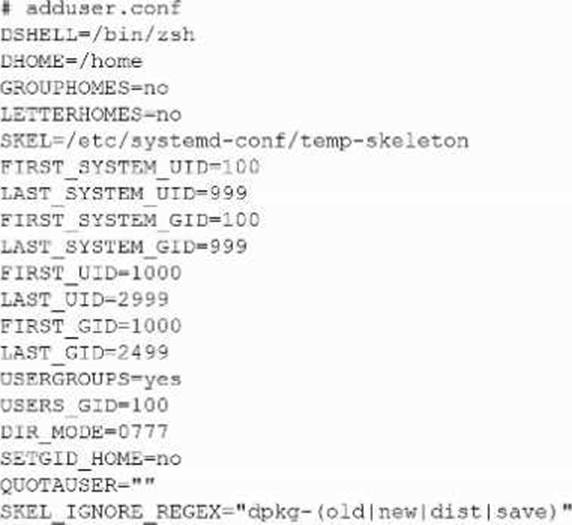
Which of the following is most likely to be successful if a penetration tester achieves non-privileged user access?
- A . Exposure of other users’ sensitive data
- B . Unauthorized access to execute binaries via sudo
- C . Hijacking the default user login shells
- D . Corrupting the skeleton configuration file
A
Explanation:
DIR_MODE=0777 configures new home directories to be created world-readable, world-writable, and world-executable (rwxrwxrwx). With such permissive permissions, any unprivileged local user can traverse into other users’ home directories, list files, read them, and even modify or replace them. That makes exposure of other users’ sensitive data the most likely and immediate outcome once the tester has any local user account.
Why the other options are less likely:
B. Unauthorized sudo execution: Requires membership in sudo/wheel or explicit entries in /etc/sudoers. Nothing in the snippet indicates that, and file mode on home dirs doesn’t grant sudo.
C. Hijacking default login shells: DSHELL=/bin/zsh only sets the default shell for new users. Replacing /bin/zsh or altering /etc/passwd would require root.
D. Corrupting the skeleton configuration: SKEL=/etc/systemd-conf/temp-skeleton is under /etc/…, which is root-owned on standard systems. A normal user cannot write there, so “corrupting the skeleton” is unlikely without privilege escalation.
Practical exploitation as a non-privileged user (illustrative):
# Find world-writable homes
find /home -maxdepth 1 -type d -perm -0002 -ls
# Read another user’s files
cd /home/targetuser && ls -la && cat Documents/tax_return.pdf
(Depending on per-file permissions.)
CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Objective Mapping (for study):
Domain 3.0 Attacks and Exploits
A penetration tester writes a Bash script to automate the execution of a ping command on a Class C network:
bash
for var in ―MISSING TEXT―
do
ping -c 1 192.168.10.$var
done
Which of the following pieces of code should the penetration tester use in place of the ―MISSING TEXT― placeholder?
- A . crunch 1 254 loop
- B . seq 1 254
- C . echo 1-254
- D . {1.-254}
B
Explanation:
Correct Syntax for a Range Loop in Bash:
The seq command generates a sequence of numbers in a specified range, which is ideal for iterating over IP addresses in a Class C subnet (1C254).
Example: seq 1 254 will output numbers 1, 2, …, 254 sequentially.
Explanation of Other Options:
A (crunch): The crunch command is used for wordlist generation and is unrelated to looping in Bash.
C (echo 1-254): This would output "1-254" as a string instead of generating a numeric range.
D ({1.-254}): This is incorrect Bash syntax and would result in a script error.
Final Script:
bash
for var in $(seq 1 254)
do
ping -c 1 192.168.10.$var
done
CompTIA Pentest+
Reference: Domain 4.0 (Penetration Testing Tools)
Bash Scripting and Automation
A penetration tester runs a network scan but has some issues accurately enumerating the vulnerabilities due to the following error:
OS identification failed
Which of the following is most likely causing this error?
- A . The scan did not reach the target because of a firewall block rule.
- B . The scanner database is out of date.
- C . The scan is reporting a false positive.
- D . The scan cannot gather one or more fingerprints from the target.
D
Explanation:
OS identification in tools like Nmap relies on fingerprinting techniques, which analyze response characteristics (e.g., TCP/IP stack behavior).
The scan cannot gather one or more fingerprints from the target (Option D):
If the system is configured to block ICMP responses, or if certain ports are closed, fingerprinting fails.
Some modern firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) interfere with OS fingerprinting by modifying packet responses.
Reference: CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide – "Network Scanning and Fingerprinting Challenges"
Incorrect options:
Option A (Firewall block rule): A firewall may block the scan, but typically it would result in no response rather than an "OS identification failed" message.
Option B (Outdated scanner database): While an outdated database might miss vulnerabilities, it does not directly cause OS detection failure.
Option C (False positive): A false positive refers to incorrect detection, but this is an OS detection failure, not a misidentified OS.
