Practice Free PMP Exam Online Questions
After the second iteration of a component development project, the project team conducts a retrospective It shows that in the initial phase the project has failed to comply with a product functionality. The planning for this product has a predominantly predictive approach.
Which technique will help the project manager to accelerate the deliverable?
- A . Impact mapping
- B . Rolling wave planning
- C . Collective code ownership
- D . Scrum of Scrums
B
Explanation:
Rolling wave planning is a project planning technique that allows the project manager to plan and execute the project in short iterations, based on the available information and the level of detail required12. Rolling wave planning is suitable for projects that have a high degree of uncertainty, complexity, or change, such as a component development project13. Rolling wave planning can help the project manager to accelerate the deliverable by enabling the following benefits123:
It reduces the risk of rework and waste by allowing the project manager to adjust the plan as more information becomes available or as the requirements change.
It increases the flexibility and responsiveness of the project team by allowing them to focus on the most important and urgent tasks in each iteration, rather than following a rigid and detailed plan.
It improves the quality and customer satisfaction of the deliverable by allowing the project manager to incorporate feedback and lessons learned from each iteration into the next one, and by delivering incremental value to the customer.
It enhances the collaboration and communication among the project team and stakeholders by involving them in the planning and execution of each iteration, and by providing frequent and transparent updates on the project progress and status.
The other options are not the best techniques to accelerate the deliverable in this scenario. Impact mapping (A) is a strategic planning technique that helps the project manager to align the project deliverables with the organizational goals and the customer needs, by identifying the actors, impacts, and deliverables involved45. However, impact mapping does not address the issue of how to plan and execute the project in a fast and adaptive way, especially when the project has failed to comply with a product functionality. Collective code ownership © is a software development practice that encourages the entire team to share the responsibility and the authority to modify any code file as necessary, to improve the quality, the performance, and the functionality of the software product67. However, collective code ownership does not address the issue of how to plan and execute the project in a fast and adaptive way, especially when the project has a predominantly predictive approach. Scrum of Scrums (D) is a scaling technique that helps multiple Scrum teams to coordinate and collaborate on complex and interdependent projects, by having representatives from each team meet regularly to report on their progress, their impediments, and their dependencies89. However, Scrum of Scrums does not address the issue of how to plan and execute the project in a fast and adaptive way, especially when the project has a predominantly predictive approach.
Reference:
https://www.teamgantt.com/waterfall-agile-guide/hybrid-approach
https://www.float.com/resources/hybrid-project-management/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rolling-wave_planning
During a documentation audit of an international company it was identified that the last version of the project schedule was from one month ago even though the project manager knew it was recently updated.
How should the project manager have handled documentation for the project?
- A . Updated the project management plan regularly and had it securely shared with all stakeholders
- B . Assigned a project team member to ensure all project documentation was updated
- C . Reviewed the risk register to identify a response plan for the audit
- D . Kept documentation in the project management information system (PMIS), and shared it with appropriate stakeholders
D
Explanation:
According to the PMBOK Guide, a project management information system (PMIS) is an information
system consisting of the tools and techniques used to gather, integrate, and disseminate the outputs of project management processes. It is used to support all aspects of the project from initiating through closing, and can include both manual and automated systems. A PMIS can help the project manager to create, collect, store, manage, control, and distribute project information, such as the project schedule, to relevant stakeholders. Therefore, the project manager should have kept the documentation in the PMIS, and shared it with appropriate stakeholders, to ensure that the project schedule was updated and accessible. Updating the project management plan, assigning a project team member, or reviewing the risk register are not sufficient or relevant actions for handling the documentation for the project, as they do not address the issue of keeping the project schedule current and available.
Reference: PMBOK Guide, Sixth Edition, pages 89-90, 558; PMI-PBA Guide, First Edition, pages 83-84, 87.
In an attempt to streamline project communications, a project manager established a shared portal for all stakeholders to get project information. The sponsor complained about this system and says that it is ineffective.
What should the project manager have done to prevent this situation from occurring?
- A . Analyzed the sponsor’s communication requirements.
- B . Confirmed that the portal is providing adequate information.
- C . Verified that the project team is following the communications management plan.
- D . Ensured the sponsor had the necessary skills to use the portal.
A
Explanation:
According to the PMBOK Guide1, project communication management includes the processes of planning, managing, and monitoring project communications. The first process, plan communications management, involves determining the information and communication needs of the project stakeholders, such as the sponsor. The project manager should have analyzed the sponsor’s communication requirements, such as the type, format, frequency, and level of detail of the information they need, as well as their preferred communication channels and methods. By doing so, the project manager could have designed and implemented a communication system that meets the sponsor’s expectations and needs, and avoids any dissatisfaction or complaints. The other options are not the best preventive actions, as they are either reactive or irrelevant. Confirming that the portal is providing adequate information, verifying that the project team is following the communications management plan, and ensuring the sponsor had the necessary skills to use the portal are all actions that could be taken after the situation has occurred, but they do not address the root cause of the problem, which is the lack of alignment between the communication system and the sponsor’s requirements.
Reference: A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) C Sixth Edition Project Communication Management – Five Steps | PMI ProjectManagement.com – Project Communication Management
A technical team for a project is managed by the lead who was recently promoted to this role. Inside the team, a mature and experienced engineer is constantly questioning the actions of the team lead and is currently ignoring part of the team lead’s decisions. The team lead asks the project manager for help.
What should the project manager do?
- A . Suggest to the team lead how to deal with this team member and discuss the situation with the engineer.
- B . Organize a meeting with all of the project stakeholders and inform them about the new risk and its impact on the project.
- C . Organize a meeting with the project team and discuss the situation and its impact on project delivery.
- D . Suggest to the engineer how to work efficiently with the lead and discuss the situation with the lead’s functional manager.
C
Explanation:
When faced with internal team conflicts, especially between a team lead and an experienced engineer, it is important to address the issue collectively. Organizing a meeting with the project team allows for open communication and collaborative problem-solving. This aligns with the PMBOK® Guide’s principles of conflict resolution, which include promoting a team environment where issues can be discussed and resolved in a manner that respects all parties’ perspectives1. It also adheres to the Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) guidelines, which emphasize the importance of addressing conflicts directly and seeking a resolution that supports project delivery2.
Reference: PMBOK® Guide – Sixth Edition, Section 9.6 – Manage Team Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) Reference Materials
A project manager has been assigned to a high-visibility project that has been identified as having medium complexity, based on previous similar projects. The project needs to be delivered to the customer as a ready-to-use product.
Based on this scenario, what should the project manager focus on throughout the project life cycle?
- A . Resource management and lessons learned
- B . Time management and stakeholder engagement
- C . Cost management and risk management
- D . Stakeholder engagement and lessons learned
B
Explanation:
A high-visibility project with medium complexity requires careful time management to ensure that the project is delivered on schedule. The project manager should focus on planning, setting deadlines, and monitoring project progress1. Stakeholder engagement is also crucial in this scenario. The project manager needs to communicate effectively with all stakeholders to understand their expectations and keep them informed about the project’s progress23. This includes initiating regular status meetings and developing a clear communication protocol4.
Reference: Coursera,. The Digital Project Manager, Adobe, Project Central, Microsoft
A project in the execution phase is behind schedule and is missing some materials. The contractor submits an offer to supply the missing materials and reimburse the cost since the internal procurement process will cause more delay. The project manager does not agree with the costs submitted by the contractor for the missing materials.
What should the project manager do next?
- A . Ask the project sponsor to allocate more budget to cover the costs
- B . Update the procurement management plan and negotiate with the contractor.
- C . Ask the contractor to review the offer and reduce the costs.
- D . Update the procurement strategy and negotiate with the contractor
B D
Explanation:
According to the PMBOK Guide, 7th edition, one of the project manager’s responsibilities is to develop the project team, which includes enhancing their competencies and interactions1. This can be done through various methods, such as training, coaching, mentoring, knowledge sharing, and feedback1. In this scenario, the project manager notices that only one team member has a technical skill that is essential for the product quality and schedule. This creates a risk of dependency, delay, and error. To prevent the team from being unqualified, the project manager should take two actions: Encourage working in pairs and knowledge sharing: This is a form of informal training that allows the team members to learn from each other and transfer the technical skill. It also fosters collaboration, communication, and trust among the team members12.
Facilitate a training event with an external trainer: This is a form of formal training that provides the team members with a structured and standardized learning experience. It also ensures that the team members acquire the technical skill from a qualified and experienced source13.
These two actions will help the project manager develop the project team’s competencies and performance, as well as mitigate the risk of quality and schedule issues.
Reference: PMBOK Guide, 7th edition, Chapter 9: Team Development
PMP Exam Prep, 11th edition, by Rita Mulcahy, Chapter 9: Resource Management, page 357 Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) Handbook, page 23
According to the Project Management Professional (PMP)® Guide, the procurement management plan is a document that describes how the project will acquire goods and services from external sources. It includes the procurement strategy, the contract types, the procurement roles and responsibilities, the procurement documents, the procurement process, and the change control process. The procurement management plan should be updated whenever there are changes in the project scope, schedule, budget, quality, or risks that affect the procurement activities. In this case, the project manager should update the procurement management plan to reflect the current situation of the project and the contractor’s offer. Then, the project manager should negotiate with the contractor to reach a mutually acceptable agreement on the costs, terms, and conditions of the contract. Negotiation is a technique that involves communication, problem-solving, and decision-making to resolve conflicts and disputes between parties. Negotiation can help the project manager and the contractor to achieve a win-win outcome that satisfies both their interests and objectives. Negotiation can also help to maintain a positive and collaborative relationship between the project manager and the contractor, which is essential for the successful completion of the project.
Reference: 1: Project Procurement Management – PMI
2: Procurement Management Plan Template – Project Management Docs
3: Negotiation – PMI
[4]: Negotiation Skills for Project Managers – ProjectManager
A project manager is working with a Scrum team that is continually missing deadlines. The steering committee is concerned about the project as it is not clear that it will deliver the expected value After some analysis the project manager discovers there is a mismatch of competencies in one of the teams
What should the project manager do?
- A . Emphasize to the teams the importance of meeting the agreed deadlines
- B . Provide appropriate training to compensate for the mismatch.
- C . Update the project schedule to reflect the delay
- D . Accept the risk of the project missing deadlines due to the mismatch.
B
Explanation:
According to the PMBOK Guide, 7th edition, one of the principles of project management is to support team performance. This means that the project manager should foster a collaborative project team environment, build team competencies, and address and remove impediments, obstacles, and blockers for the team. In this scenario, the project manager should provide appropriate training to the team members who lack the necessary skills or knowledge to perform their tasks, rather than emphasizing deadlines, updating the schedule, or accepting the risk. Providing training will help the team improve their performance, deliver value, and meet the expectations of the steering committee and other stakeholders.
Reference: PMBOK Guide, 7th edition, page 9, Principle 8: Support team performance.
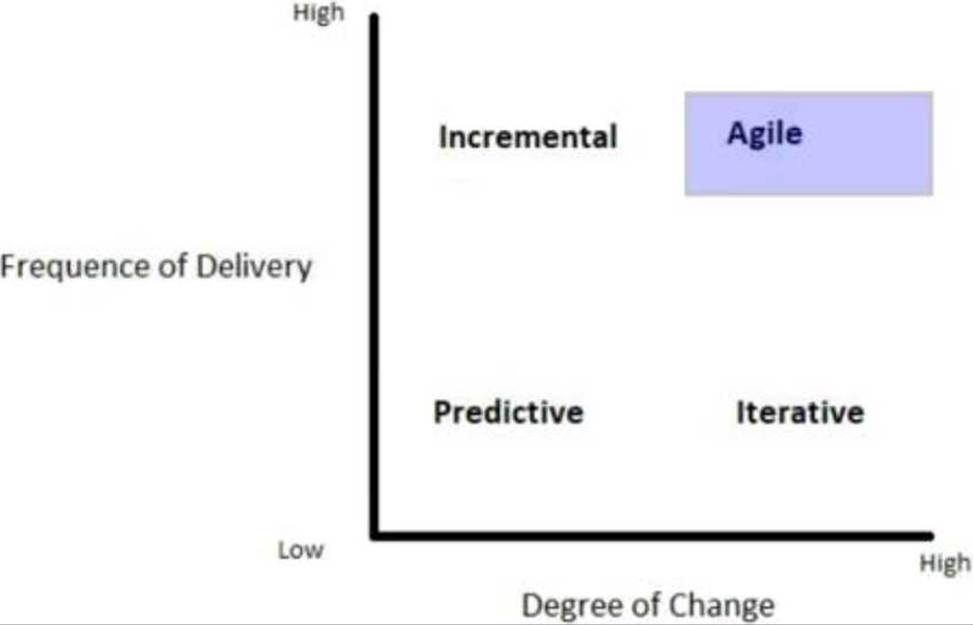
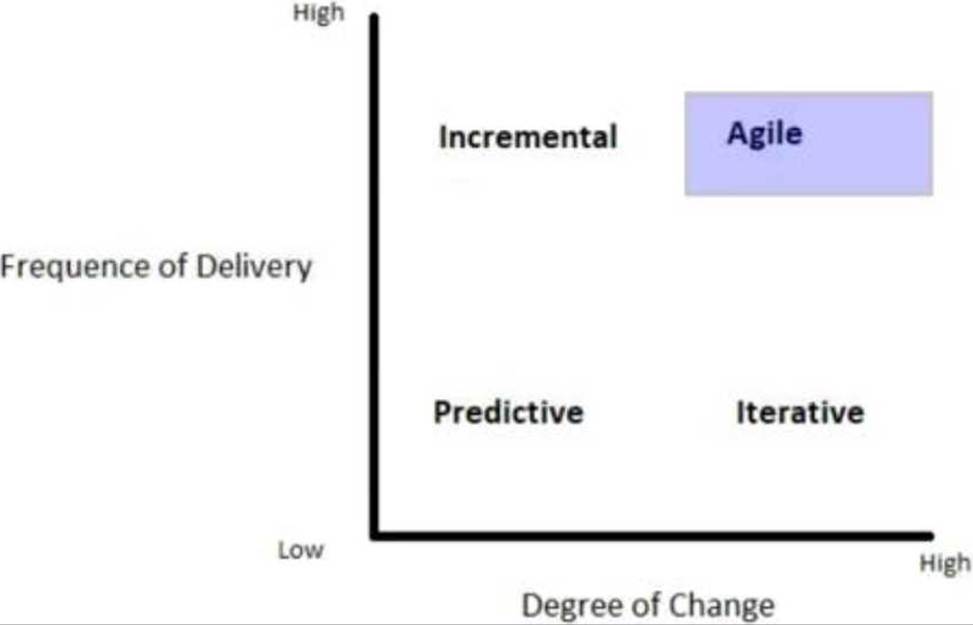
HOTSPOT
A retail company identifies that it is losing sales because customers are not promptly informed about promotions and sales points. The company needs to react quickly. A project charter is created along with requests to develop a mobile application for the customer. The marketing department has a long list of features to add to the application, but there are no specifications.
Considering the objective to deploy customer value, which project life cycle approach should be chosen?
An equipment vendor will implement a new production line for a client company. The year-long project will include 2- to 4-month long iterations; however, the client’s project manager has no agile experience.
How should the project manager ensure that the client is effectively represented in the daily meetings?
- A . Recommend agile training programs that best suit the client project manager’s schedule.
- B . Realign the project to a predictive approach to ensure optimal collaboration between the teams.
- C . Propose a session tor essential agile Knowledge transfer for the client team to align with the daily meeting goals
- D . Provide the client project manager with agile best practice documents and web resources.
C
Explanation:
The best way to ensure that the client is effectively represented in the daily meetings is to provide them with the necessary agile knowledge and skills to participate and collaborate with the vendor team. This can be done by proposing a session for essential agile knowledge transfer, where the vendor project manager can explain the agile principles, values, practices, and tools that will be used in the project. This will help the client team to understand the purpose and benefits of the daily meetings, as well as their roles and responsibilities in them. The other options are not as effective as they either do not address the root cause of the problem (lack of agile knowledge), or they introduce unnecessary changes or delays to the project (realigning the project or recommending training programs).
Reference: PMI Agile Practice Guide, page 14-15; PMBOK Guide, page 18-19
A project manager is asked to develop maintenance planning software for a power plant. A similar project was executed by another department in the organization that was later closed due to low performance. The project manager is concerned about the project’s performance and wants to take action in advance to ensure the project succeeds.
What should the project manager do?
- A . Evaluate the project risk and add external experts to address the potential risks.
- B . Inform the project sponsor about the risk and try to convince them to withdraw from the project.
- C . Continue executing the project as planned and add more resources if they are required.
- D . Review the lessons learned on similar projects so that they do not fall back into the same pattern.
D
Explanation:
According to the Project Management Professional (PMP) guidelines, learning from past experiences is a key aspect of project management. In this scenario, the project manager is aware of a similar project that was not successful. The best course of action is to review the lessons learned from that project and apply those insights to avoid repeating the same mistakes. This proactive approach can help improve the project’s chances of success.
Reference: PMBOK Guide, Project Management Knowledge Areas, Project Integration Management, Lessons Learned. Please refer to the specific sections in the PMBOK Guide and PMP study materials for more detailed information.
