Practice Free PMP Exam Online Questions
An agile project has just started, and the backlog is being prioritized. The customer wants to prioritize business value over identified risks.
How should the customer’s request be managed?
- A . Accept risks as they decrease over a period of time.
- B . Create a risk value profile to track the relative importance of risks.
- C . Log and track risks separately as only business value is important.
- D . Assess risks together with business value during prioritization.
D
Explanation:
The customer’s request should be managed by assessing risks together with business value during prioritization because this is the best way to balance the customer’s expectations and the project’s feasibility. Agile projects are characterized by frequent delivery of value to the customer, but also by uncertainty and change. Therefore, risks should not be ignored or deferred, but rather integrated into the decision-making process. By assessing risks together with business value, the customer and the project team can identify the most valuable and viable features to deliver in each iteration, and also plan for risk responses and contingencies. The other options are not the best choices because they do not consider the impact of risks on the project’s success. Accepting risks as they decrease over a period of time (option A) may expose the project to unnecessary threats or missed opportunities, and may also violate the agile principle of responding to change. Creating a risk value profile to track the relative importance of risks (option B) may help to quantify and prioritize risks, but it does not address the customer’s request or the project’s value proposition. Logging and tracking risks separately as only business value is important (option C) may create a false sense of security and satisfaction, and may also neglect the agile principle of delivering working software.
Reference: PMBOK Guide, 6th edition, pages 18-19, 686-687. PMP Questions page 437. PMP Practice Exam 1.
A project manager is assigned to a new project to deliver a product at the end of the year. The project manager was informed by the vendor that a core component could not be shipped on time, which will impact the schedule.
What should project manager to do next to minimize the impact on the project?
- A . Schedule a meeting with all stakeholders to extend the project deadline
- B . Replace the vendor with a new vendor who can offer the component on time
- C . Add an item to the next status review to make stakeholders aware of the vendor issue.
- D . Review and update the issue log and determine if any alternative components can be offered
D
Explanation:
According to the PMBOK Guide, an issue is a point or matter in question or in dispute, or a point or matter that is not settled and is under discussion or over which there are opposing views or disagreements1. Issues can arise from any aspect of the project, such as scope, schedule, cost, quality, resources, risks, or stakeholders. Issues can affect the performance of the project or the satisfaction of the stakeholders. Therefore, issues need to be identified, analyzed, and resolved in a timely and appropriate manner.
The project manager is responsible for managing issues throughout the project life cycle. One of the tools that the project manager can use to document and track issues is the issue log. The issue log is a project document that provides a structured way of recording and monitoring issues2. The issue log typically contains information such as the issue description, the issue owner, the issue priority, the issue status, the issue resolution, and the issue closure date3.
In this question, the project manager is faced with an issue that can affect the project schedule and the delivery of the product. The vendor’s inability to ship a core component on time is a matter that is not settled and is under discussion with the vendor. The project manager should review and update the issue log to record this issue and its details. The project manager should also determine if any alternative components can be offered by the vendor or another source that can meet the project requirements and minimize the schedule impact. This is part of the issue resolution process, which involves identifying and evaluating possible solutions, selecting the best option, and implementing the agreed-upon action4.
The other options are not the best actions to take next to minimize the impact on the project. Scheduling a meeting with all stakeholders to extend the project deadline is premature and may not be necessary if the issue can be resolved with an alternative component. Replacing the vendor with a new vendor who can offer the component on time is risky and may not be feasible or cost-effective. Adding an item to the next status review to make stakeholders aware of the vendor issue is important, but it does not address the issue resolution or the schedule impact.
Reference: 1: PMBOK Guide, 6th edition, p. 720 2: PMBOK Guide, 6th edition, p. 89 3: PMBOK Guide,
6th edition, p. 374 4: PMBOK Guide, 6th edition, p. 375
A Scrum team is analyzing the burndown chart on day four of a 15-day sprint.
The burndown chart is shown below.
What should the team do next?
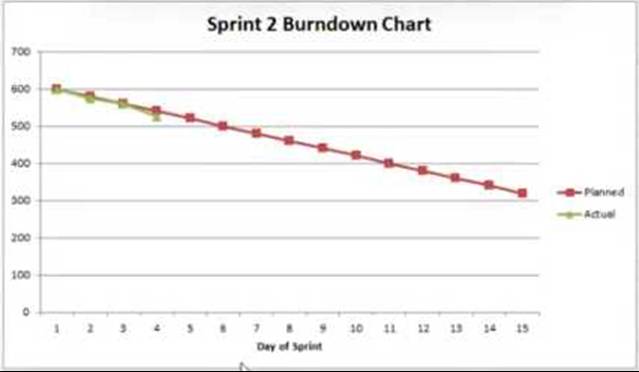
- A . Ask the product owner if some low-priority stories could be cut from the sprint.
- B . Continue with the sprint as the progress shows buffers for potential interruptions.
- C . Ask the project team to select any additional stories as they have additional capacity than planned.
- D . Continue with the sprint work as planned and keep monitoring.
D
Explanation:
On day four of a 15-day sprint, the team should continue with the sprint work as planned and keep monitoring the burndown chart. The burndown chart is a visual representation of the work left versus the time remaining in the sprint. If the “Actual” line closely follows the “Planned” line, it indicates that the team is on track. Making adjustments or changing the sprint scope at this stage is premature unless there are significant deviations or impediments1. The team should maintain their current pace and monitor progress, making adjustments only if necessary as the sprint progresses2.
Reference: “Burndown Chart:
What it is, How to Use it, Example [2024]” by Asana; “Scrum Sprint Burndown Chart [Everything you Need to Know]” by KnowledgeHut12.
A project manager for a factory construction project in a small town is evaluating the necessary actions to engage stakeholders. The local community is speculating the impact of the facility. There are rumors of job opportunities and environmental impacts which are listed on the project risk matrix
What should the project manager do with regard to community engagement in this situation”
- A . Include the local union representative in the high-power, high-impact stakeholder group
- B . Focus on the sideward stakeholders only and let the organization manage the community.
- C . Build channels to extend communication efforts to the local community
- D . Use the city administration to address communication with the community
C
Explanation:
According to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for the success of a project. In this scenario, the local community is a key stakeholder group due to the potential impact of the factory construction project. Therefore, the project manager should build channels to extend communication efforts to the local community. This could involve holding community meetings, distributing newsletters, or setting up a project website where updates and information can be shared. This approach ensures that the community is informed and has the opportunity to provide input, which can help to mitigate potential risks and address concerns.
Reference: PMBOK Guide, 6th Edition, Section 13: Stakeholder Management.
A project manager prepared a project benefits management plan.
Which of the following should be included in this document?
- A . Project requirements, target benefits, issue log, metrics
- B . Target benefits, strategic alignment, time frame for realizing benefits
- C . Strategic alignment, benefits owner, risk register
- D . Target benefits, benefits owner, lessons learned
B
Explanation:
A project benefits management plan should include the target benefits, which are the expected tangible and intangible outcomes that provide value to stakeholders. It should also detail the strategic alignment, showing how the project aligns with the organization’s objectives and strategy. Additionally, the plan should outline the time frame for realizing the benefits, indicating when and how the benefits will be delivered123.
Reference: Project Benefits Management Plan: PMP Exam Master Tips1
Benefits Management for Projects: Making a Benefits Management Plan2 Benefits Management Plan – Project Management Knowledge3
A project manager has just been assigned to a team that is developing a new design product. The work breakdown structure (VW/BS) has been created and the activities have been assigned to the team members. The project manager finds that there are activities that could be completed sooner by other team members. If the current assignments are left as is, the project could be delayed 2 weeks.
What should the project manager do in this situation?
- A . Review the work allocation and reassign some tasks to shorten the critical path.
- B . Maintain the task assignments as planned and compress the other tasks to keep the project on schedule.
- C . Ask the team members to work overtime to finish the tasks on time according to the schedule.
- D . Keep the task assignments unchanged since the project management plan has been approved.
A
Explanation:
The project manager should always monitor and control the project schedule and make adjustments as needed to ensure timely completion of the project. If the project manager identifies that some activities can be done faster by other resources, they should review the work allocation and reassign some tasks to shorten the critical path. The critical path is the longest sequence of activities that determines the project duration. By reducing the duration of the critical path activities, the project manager can avoid delays and meet the project deadline. This is also consistent with the principle of optimizing resources and minimizing waste, which is part of the PMI Talent Triangle®.
Reference: PMBOK Guide 7th Edition, page 131
Agile Practice Guide, page 50
PMI Talent Triangle® 1
A project manager scheduled a session to identify risks on the current project. Most of the stakeholders did not attend the meeting, although they previously confirmed their attendance.
How should the project manager proceed in order to complete the risk register?
- A . Cancel the meeting and create the risk register using the project documents.
- B . Continue the meeting and send the updated risk register to all stakeholders.
- C . Run the meeting and follow up with each one of the absent stakeholders to get their input.
- D . Escalate the issue of stakeholders not attending the meeting to the project sponsor.
C
Explanation:
A risk register is a tool to identify, document, monitor and resolve project risks. It is an essential part of the risk management process and should involve the participation of relevant stakeholders.
Stakeholder engagement is a process of identifying, understanding and involving people who have a stake in the outcome of the project. Effective stakeholder engagement requires ongoing communication, consultation, and collaboration. Therefore, the best option for the project manager is to run the meeting with the available stakeholders and then follow up with each one of the absent stakeholders to get their input. This way, the project manager can ensure that the risk register is comprehensive, accurate and reflects the views and concerns of all stakeholders. Canceling the meeting and creating the risk register using the project documents (option A) is not a good option because it does not involve the stakeholders and may miss some important risks or perspectives.
Continuing the meeting and sending the updated risk register to all stakeholders (option B) is also not a good option because it does not allow the absent stakeholders to provide their input or feedback on the risk register. Escalating the issue of stakeholders not attending the meeting to the project sponsor (option D) is not a good option either because it does not address the root cause of the problem and may create unnecessary conflict or resentment among the stakeholders.
Reference: 1: Risk Register: A Project Manager’s Guide with Examples [2023] • Asana
2: 10 Principles Of Stakeholder Engagement | APM
3: What is Stakeholder Engagement, and Why is it Important for Strategic Planning?
On a project with multiple international locations, a trend for delays has been flagged. When looking into the issue, the project manager realized that some of the key activities were scheduled over the holiday periods in the overseas offices.
What should the project manager do next?
- A . Update the schedule to reflect the holidays and share the workload among offices to mitigate schedule slippage.
- B . Hire additional personnel on a temporary basis to cover the extra workload during the holiday seasons.
- C . Request that the offices in overseas locations work overtime to mitigate schedule slippages.
- D . Update the schedule to reflect the holidays and notify the project sponsor of the delayed completion.
A
Explanation:
According to the PMBOK® Guide, a project manager should be able to plan and manage the project schedule, taking into account the availability and capacity of resources, as well as the project constraints and assumptions. When a project involves multiple international locations, the project manager should also consider the cultural and environmental factors that may affect the project performance, such as holidays, working hours, communication pReference, and legal requirements. In this scenario, the project manager realized that some of the key activities were scheduled over the holiday periods in the overseas offices, which caused delays in the project. The project manager should update the schedule to reflect the holidays and share the workload among offices to mitigate schedule slippage. This option demonstrates the project manager’s ability to adjust the schedule based on the actual resource availability and to balance the resource allocation across different locations. Updating the schedule and sharing the workload may also help to maintain the team’s morale and productivity, as well as the stakeholder’s satisfaction. Hiring additional personnel on a temporary basis, requesting that the offices in overseas locations work overtime, or notifying the project sponsor of the delayed completion are not effective or appropriate actions to take in this situation. These options may incur additional costs, risks, or conflicts, and may not address the root cause of the problem. They may also indicate a lack of planning, communication, or collaboration skills on the part of the project manager.
Reference: PMBOK® Guide, 6th edition, pages 191-192, 267-268, 349-350.
we architects are unable to agree on how to approach certain components of the development that will be included In the upcoming sprint. After a one-on-one discussion, the architects have decided to each own a particular module of the system, and the team supports the decision.
What should the project manager do?
- A . Discuss the issue with the team to resolve the disagreement.
- B . Ensure that there is consensus among the project stakeholders.
- C . Discuss the issue during the next sprint planning meeting.
- D . Support the outcome of the architects’ agreement.
D
Explanation:
In this scenario, the architects have resolved their disagreement by deciding to each own a particular module of the system. The team supports this decision. As a project manager, it is important to support the outcome of the architects’ agreement1. This approach aligns with the principles of effective project management, which emphasize the importance of communication, risk management, and proactive problem-solving2.
Reference: TeamGantt Blog, ArchDaily, Indeed.com Career development
At the end of a project with multiple suppliers, the project manager is reviewing the closing process and finds that an unexpected financial balance is remaining.
What will help the project manager understand why this has occurred?
- A . Project audit
- B . Lessons learned
- C . Organizational process assets
- D . Procurement audit
D
Explanation:
A procurement audit is a structured review of the procurement process and the contracts that were established with the suppliers. It evaluates the performance of the suppliers, the compliance with the contract terms and conditions, the quality of the deliverables, and the effectiveness of the procurement management. A procurement audit can help the project manager understand why there is an unexpected financial balance remaining at the end of the project, by identifying any errors, discrepancies, overpayments, or underpayments that occurred during the procurement process. A procurement audit can also provide recommendations for future improvements and lessons learned. The other options are not the best ways to understand why there is an unexpected financial balance remaining, because they may not focus on the procurement aspect of the project, or they may not provide enough detail or analysis to explain the cause of the issue.
Reference: Project Procurement Management – PMBOK Guide, Procurement Audit – Project Management Knowledge
