Practice Free PEGACPDC25V1 Exam Online Questions
As a Customer Service Representative, you present an offer to a customer who called to learn more about a new product. The customer rejects the offer.
What is the next step that Pega Customer Decision Hub takes?
- A . Stops presenting offers to the customer
- B . Adds the customer to the potential churn list
- C . Reevaluates the Next-Best-Action
- D . Sends a detailed email about the offer
C
Explanation:
Pega Customer Decision Hub is a dynamic and adaptive system that constantly reevaluates the Next-Best-Action for each customer based on their interactions and feedback. If a customer rejects an offer, the system will update the customer profile and the offer performance, and then reapply the Next-Best-Action strategy to select and prioritize another offer that is more relevant and valuable for the customer. Verified [Pega Decisioning Consultant | Pega Academy]
What does a dotted line from a "Group By" component to a "Filter" component mean?
- A . There is a one-to-one relationship between the "Group By" and the "Filter" components.
- B . To evaluate the "Group By" component, the "Filter" component is evaluated first.
- C . A property from the "Group By" is referenced by the “Filter" component.
- D . Information from the "Group By" is copied over to the "Filter" component.
C
Explanation:
A dotted line from a “Group By” component to a “Filter” component means that a property from the “Group By” is referenced by the “Filter” component. For example, if you group customers by age and then filter them by average spending, you need to reference a property from the “Group By” component, such as .pxSegment, in the “Filter” component. A dotted line does not indicate a one-to-one relationship, an evaluation order, or a copying of information between components
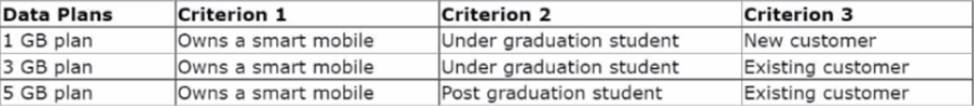
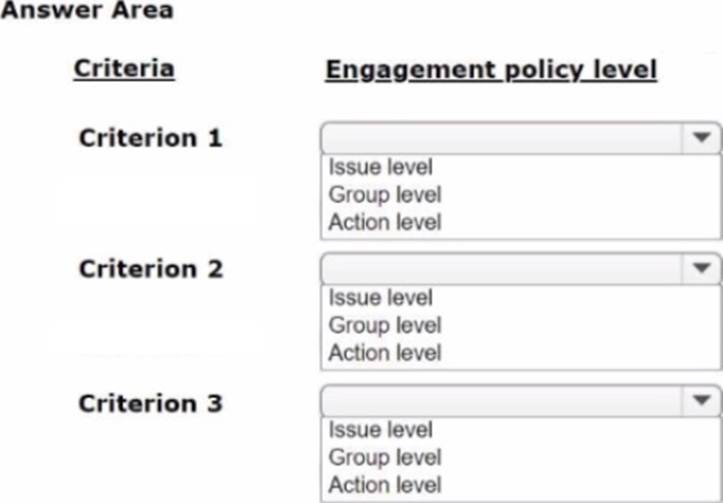
HOTSPOT
As a decisioning architect, you are setting up the action hierarchy for MyCo. Select the correct action hierarchy level for each of the hierarchy items identified.


MyCo, a telecom company, wants to introduce a new group of offers called Tablets for all customers.
As a decisioning architect, which two valid actions do you create? (Choose Two)
- A . 5% discount on the price
- B . Tablet operating system
- C . Tablet serial number
- D . Netflix subscription for 12 months
U+ Bank is facing an unforeseen technical issue with its customer care system. As a result, the bank wants to share the new temporary contact details with all customers over an SMS.
Which type of outbound interaction do you configure to implement this requirement?
- A . Priority communication
- B . Customer event
- C . Security event
- D . Scheduled update
U+ Bank implemented a customer journey for its customers. The journey consists of three stages. The first stage raises awareness about available products, the second stage presents available offers, and in the last stage, customers can talk to an advisor to get a personalized quote. The bank wants to actively increase offers promotion over time.
What action does the bank need to take to achieve this business requirement?
- A . Enable increasing stage upweighting for the second stage of the journey.
- B . Upweight the propensity by adding more predictors that fit the target customers and repeat this process over time.
- C . Enable increasing stage upweighting for the first stage of the journey.
- D . Enable constant stage upweighting for the second stage of the journey.
A
Explanation:
Increasing stage upweighting is a feature that allows you to gradually increase the weight of a stage over time, making the offers in that stage more likely to be selected. This is useful for promoting offers that are time-sensitive or have a limited availability. In this case, the bank wants to actively increase offers promotion over time, so enabling increasing stage upweighting for the second stage of the journey, where the offers are presented, is the best option. Verified [Pega Decisioning Consultant | Pega Academy]
U+- Bank has recently implemented Pega Customer Decision Hub™. As a first step, the bank went live with the contact center to improve customer engagement. Now, U+ Bank wants to extend its customer engagement through the web channel. As a decisioning architect, you have created the new set of actions, the corresponding treatments, enabled the web channel, and defined a new real-time container trigger in the Next-Best-Action Designer
What else do you configure for the new treatments to be present in the next-best-action recommendations?
- A . Change the generated decision strategy.
- B . Create a channel strategy specifically for web.
- C . No need to do anything. The strategy is auto-generated.
- D . Modify the Next-Best-Action Framework strategy to cater to the new web channel.
HOTSPOT
MyCo, a telecom company, developed a new data plan group to suit the needs of its customers. The following table lists the three data plan actions and the criteria that customers must satisfy to qualify for the offer:
What does business agility in a customer engagement project typically focus on?
- A . Optimizing outbound marketing campaigns
- B . Increasing dependency on manual decision-making
- C . Rapidly adapting strategies to meet changing customer needs
- D . Automating customer service workflows
You are the decisioning architect on an Al-powered one-to-one customer engagement implementation project. You are asked to design the next-best-action prioritization expression that balances the customer needs with the business objectives.
What factor do you consider in the prioritization expression?
- A . Predicted customer behavior
- B . Offer eligibility
- C . Customer contact policy
- D . Offer relevancy
A
Explanation:
The prioritization expression is a formula that calculates the priority score of each offer for each customer, based on various factors that reflect the customer needs and the business objectives. One of the most important factors is the predicted customer behavior, which is measured by the propensity. The propensity is a value that indicates how likely a customer is to accept an offer, based on their attributes and behaviors. The propensity is calculated by using predictive analytics models that learn from historical data and feedback. The higher the propensity, the higher the priority score, making the offer more relevant and valuable for the customer. Verified [Pega Decisioning Consultant | Pega Academy]
