Practice Free NSE8_812 Exam Online Questions
You are deploying a FortiExtender (FEX) on a FortiGate-60F. The FEX will be managed by the FortiGate. You anticipate high utilization. The requirement is to minimize the overhead on the device for WAN traffic.
Which action achieves the requirement in this scenario?
- A . Add a switch between the FortiGate and FEX.
- B . Enable CAPWAP connectivity between the FortiGate and the FortiExtender.
- C . Change connectivity between the FortiGate and the FortiExtender to use VLAN Mode
- D . Add a VLAN under the FEX-WAN interface on the FortiGate.
C
Explanation:
VLAN Mode is a more efficient way to connect a FortiExtender to a FortiGate than CAPWAP Mode. This is because VLAN Mode does not require the FortiExtender to send additional control traffic to the FortiGate.
The other options are not correct.
You have configured a Site-to-Site IPsec VPN tunnel between a FortiGate and a third-party device but notice that one of the error counters on the tunnel interface keeps increasing.

Which two configuration options can resolve this problem? (Choose two.)
- A . Enable Forward Error Correction (FEC) on the VPN interface for egress traffic.
- B . Adjust the MTU of the physical interface to which the IPsec tunnel is bound.
- C . Enable DF-bit honoring in the global settings.
- D . Adjust the MTU of the IPsec interface.
Refer to the exhibit showing the history logs from a FortiMail device.
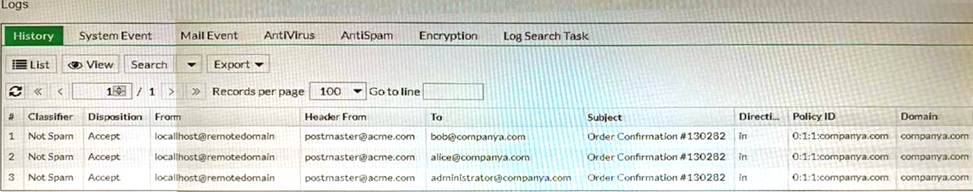
Which FortiMail email security feature can an administrator enable to treat these emails as spam?
- A . DKIM validation in a session profile
- B . Sender domain validation in a session profile
- C . Impersonation analysis in an antispam profile
- D . Soft fail SPF validation in an antispam profile
C
Explanation:
Impersonation analysis is a feature that detects emails that attempt to impersonate a trusted sender, such as a company executive or a well-known brand, by using spoofed or look-alike email addresses. This feature can help prevent phishing and business email compromise (BEC) attacks. Impersonation analysis can be enabled in an antispam profile and applied to a firewall policy.
Reference:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortimail/6.4.0/administration-guide/103663/impersonation-analysis
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortimail/7.2.0/cookbook/221814/protecting-against-email-impersonation-in-fortimail
You are designing a setup where the FortiGate device is connected to two upstream ISPs using BGP. Part of the requirement is that you must be able to refresh the route advertisements manually without disconnecting the BGP neighborships.
Which feature must you enable on the BGP neighbors to accomplish this goal?
- A . Synchronization
- B . Deterministic-med
- C . Graceful-restart
- D . Soft-reconfiguration
D
Explanation:
The soft reconfigure is correct by elimination (FGTs all support BGP Refresh, so question is not worded correctly – to refresh routes in advertisements, there is no need to do manually anything, after the change is committed to config FGT will send BGP Refresh message to the peers to notify them of it. The same is true for Cisco and Juniper routers. The question should ask "when routing policy was changed" – then yes, reconfiguraiton is the way to notify BGP peers that BGP policy was changed.
A FortiGate running FortiOS 7.2.0 GA is configured in multi-vdom mode with a vdom set to vdom type Admin and another vdom set to vdom type Traffic.
Which two GUI sections are available on both VDOM types? (Choose two.)
- A . Interface configuration
- B . Packet capture
- C . Security Fabric topology and external connectors
- D . Certificates
- E . FortiClient configuration
Refer to the CLI output:
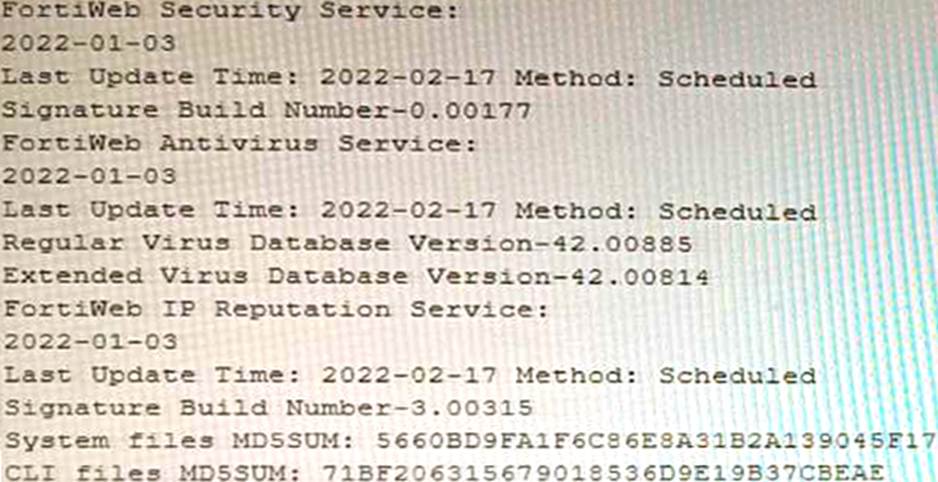
Given the information shown in the output, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
- A . Geographical IP policies are enabled and evaluated after local techniques.
- B . Attackers can be blocked before they target the servers behind the FortiWeb.
- C . The IP Reputation feature has been manually updated
- D . An IP address that was previously used by an attacker will always be blocked
- E . Reputation from blacklisted IP addresses from DHCP or PPPoE pools can be restored
BE
Explanation:
The CLI output shown in the exhibit indicates that FortiWeb has enabled IP Reputation feature with local techniques enabled and geographical IP policies enabled after local techniques (set geoip-policy-order after-local). IP Reputation feature is a feature that allows FortiWeb to block or allow traffic based on the reputation score of IP addresses, which reflects their past malicious activities or behaviors. Local techniques are methods that FortiWeb uses to dynamically update its own blacklist based on its own detection of attacks or violations from IP addresses (such as signature matches, rate limiting, etc.). Geographical IP policies are rules that FortiWeb uses to block or allow traffic based on the geographical location of IP addresses (such as country, region, city, etc.). Therefore, based on the output, one correct statement is that attackers can be blocked before they target the servers behind the FortiWeb. This is because FortiWeb can use IP Reputation feature to block traffic from IP addresses that have a low reputation score or belong to a blacklisted location, which prevents them from reaching the servers and launching attacks. Another correct statement is that reputation from blacklisted IP addresses from DHCP or PPPoE pools can be restored. This is because FortiWeb can use local techniques to remove IP addresses from its own blacklist if they stop sending malicious traffic for a certain period of time (set local-techniques-expire-time), which allows them to regain their reputation and access the servers. This is useful for IP addresses that are dynamically assigned by DHCP or PPPoE and may change frequently.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiweb/6.4.0/administration-guide/19662/ip-reputation
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiweb/6.4.0/administration-guide/19662/geographical-ip-policies
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiweb/7.4.2/administration-guide/608374/ip-reputation-blocklisting-source-ips-with-poor-reputation Fortinet compiles a reputation for each public IP address. Clients will have poor reputations if they have been participating in attacks, willingly or otherwise. Because blacklisting innocent clients is equally undesirable, Fortinet also restores the reputations of clients that improve their behavior. This is crucial when an infected computer is cleaned, or in DHCP or PPPoE pools where an innocent client receives an IP address that was previously leased by an attacker.
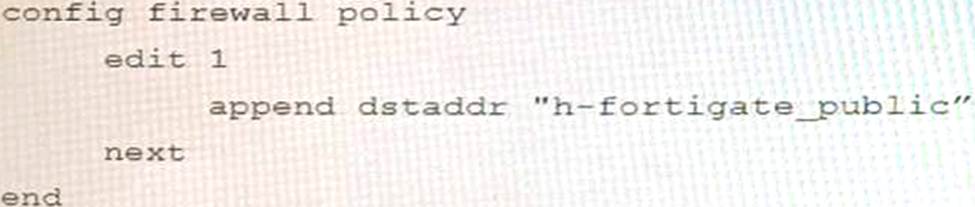
Refer to the exhibit containing the configuration snippets from the FortiGate.
Customer requirements:
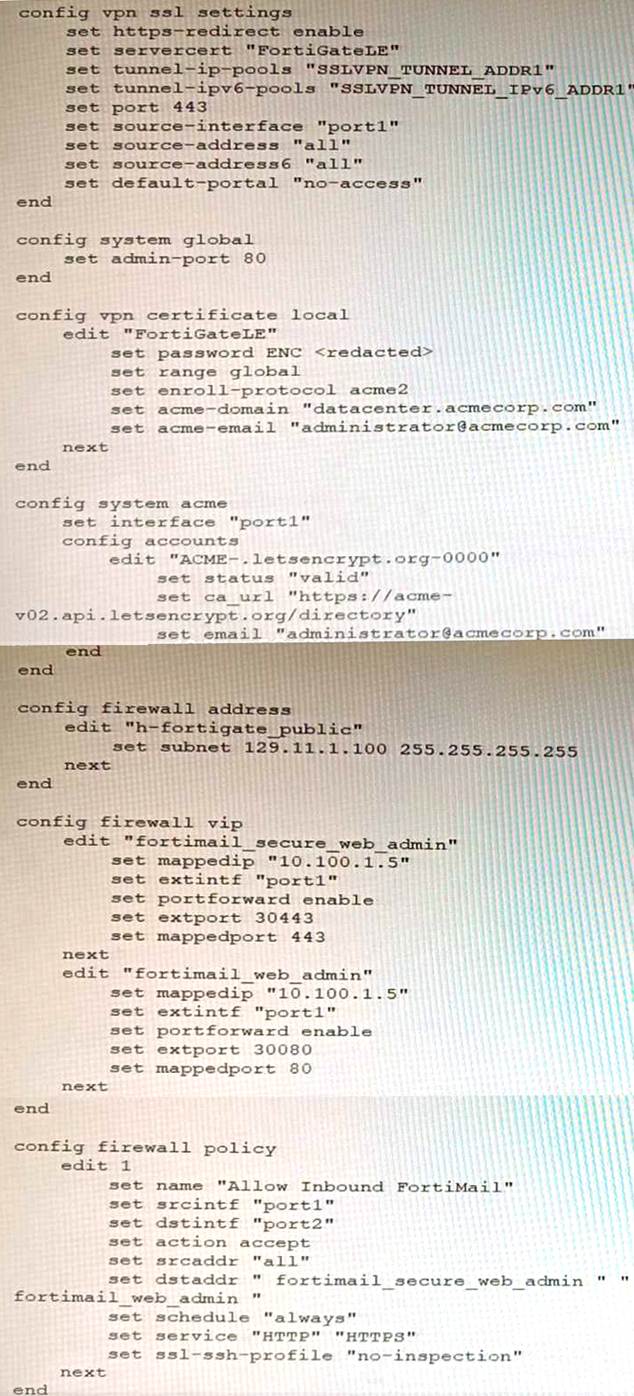
• SSLVPN Portal must be accessible on standard HTTPS port (TCP/443)
• Public IP address (129.11.1.100) is assigned to portl
• Datacenter.acmecorp.com resolves to the public IP address assigned to portl
The customer has a Let’s Encrypt certificate that is going to expire soon and it reports that subsequent attempts to renew that certificate are failing.
Reviewing the requirement and the exhibit, which configuration change below will resolve this issue?
A)
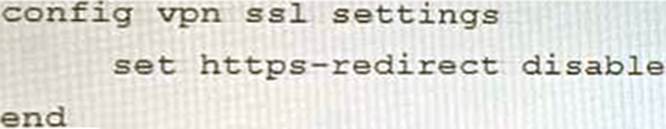
B)

C)
D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
A
Explanation:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.4.1/administration-guide/822087/automatically-provision-a-certificate
Refer to the exhibits.

A customer is trying to restore a VPN connection configured on a FortiGate. Exhibits show output during a troubleshooting session when the VPN was working and the current baseline VPN configuration.

Which configuration parameters will restore VPN connectivity based on the diagnostic output?
A)

B)

C)

D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
You must analyze an event that happened at 20:37 UTC.
One log relevant to the event is extracted from FortiGate logs:
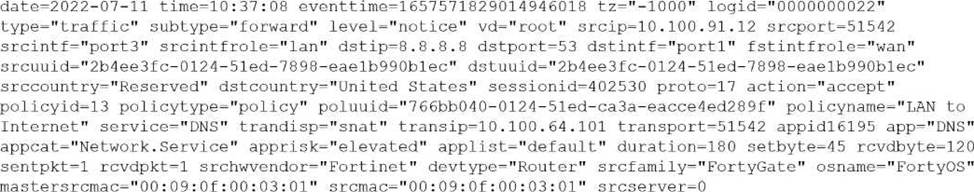
The devices and the administrator are all located in different time zones Daylight savings time (DST) is disabled
• The FortiGate is at GMT-1000.
• The FortiAnalyzer is at GMT-0800
• Your browser local time zone is at GMT-03.00
You want to review this log on FortiAnalyzer GUI, what time should you use as a filter?
- A . 20:37:08
- B . 10:37:08
- C . 17:37:08
- D . 12.37:08
D
Explanation:
https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiAnalyzer/Technical-Note-Understanding-FortiAnalyzer-time-related-fields/ta-p/197569
A Hub FortiGate is connecting multiple branch FortiGate devices separating the traffic centrally in unique VRFs. Routing information is exchanged using BGP between the Hub and the Branch FortiGate devices.
You want to efficiently enable route leaking of specific routes between the VRFs.
Which two steps are required to achieve this requirement? (Choose two.)
- A . Create a vdom link between VRF10 and VRF12
- B . Enable Multi-VDOM mode on the Hub FortiGate and add a VDOM to connect VRF10 and VRF12
- C . Enable BGP recursive routing on the HUB FortiGate
- D . Configure route-maps to leak the selected routes using BGP
AD
Explanation:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.0.1/administration-guide/834664/route-leaking-between-vrfs-with-bgp
