Practice Free NSE8_812 Exam Online Questions
You deployed a fully loaded FG-7121F in the data center and enabled sslvpn-load-balance.
Based on the behavior of this feature which statement is correct?
- A . You can use src-ip or dst-ip-dport on dp-load-distribution-method to make SSL VPN load balancing work as expected.
- B . If an FPM goes down, SSL VPN IP pool IP addresses will be re-allocated to the remaining FPMs.
- C . To have better traffic distribution you should use IP pools that increment in multiples of 12.
- D . Enabling SSL VPN load balancing will clear the session table.
An HA topology is using the following configuration:
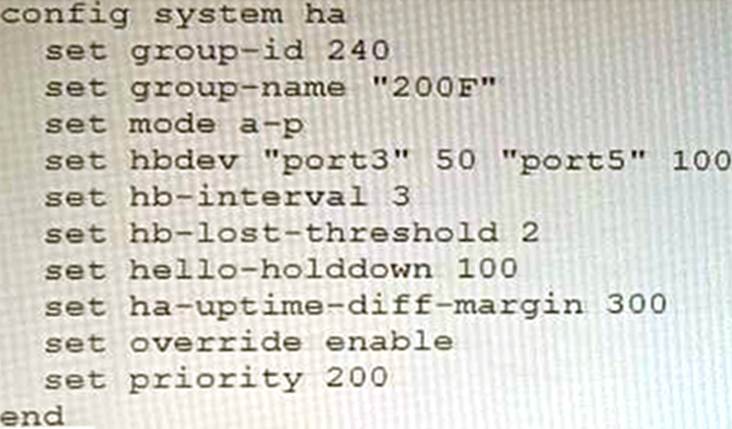
Based on this configuration, how long will it take for a failover to be detected by the secondary cluster member?
- A . 600ms
- B . 200ms
- C . 300ms
- D . 100ms
A
Explanation:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.4.0/administration-guide/489324/failover-protection
Refer to the exhibit.
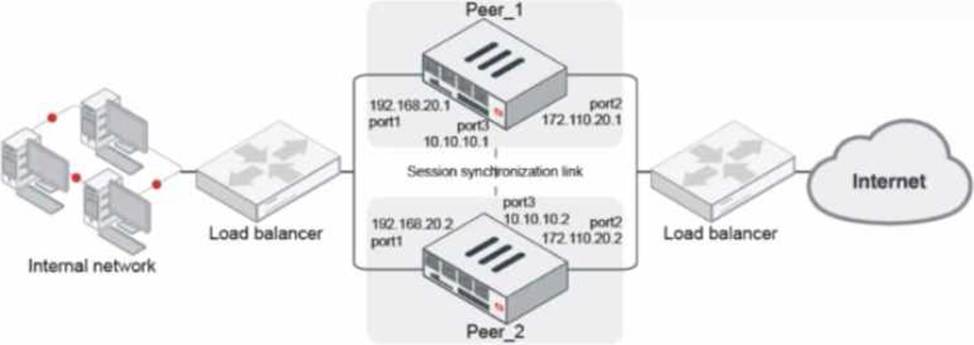
Given the exhibit, which two statements about FortiGate FGSP HA cluster behavior are correct? (Choose two.)
- A . You can run FortiGate Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) high availability in addition to FGSP simultaneously.
- B . Session synchronization occurs over Layer 3 by default, and if unavailable it will then try Layer 2.
- C . You can selectively synchronize only specific sessions between FGSP cluster members.
- D . Cluster members will upgrade one at a time and failover during firmware upgrades.
A customer with a FortiDDoS 200F protecting their fibre optic internet connection from incoming traffic sees that all the traffic was dropped by the device even though they were not under a DoS attack. The traffic flow was restored after it was rebooted using the GUI.
Which two options will prevent this situation in the future? (Choose two)
- A . Change the Adaptive Mode.
- B . Create an HA setup with a second FortiDDoS 200F
- C . Move the internet connection from the SFP interfaces to the LC interfaces
- D . Replace with a FortiDDoS 1500F
BD
Explanation:
B is correct because creating an HA setup with a second FortiDDoS 200F will provide redundancy in case one of the devices fails. This will prevent all traffic from being dropped in the event of a failure. D is correct because the FortiDDoS 1500F has a larger throughput capacity than the FortiDDoS 200F. This means that it will be less likely to drop traffic even under heavy load.
The other options are incorrect.
Option A is incorrect because changing the Adaptive Mode will not prevent the device from dropping traffic.
Option C is incorrect because moving the internet connection from the SFP interfaces to the LC interfaces will not change the throughput capacity of the device.
Reference: FortiDDoS 200F Datasheet | Fortinet Document Library
FortiDDoS 1500F Datasheet | Fortinet Document Library
High Availability (HA) on FortiDDoS | FortiDDoS / FortiOS 7.0.0 – Fortinet Document Library
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit A
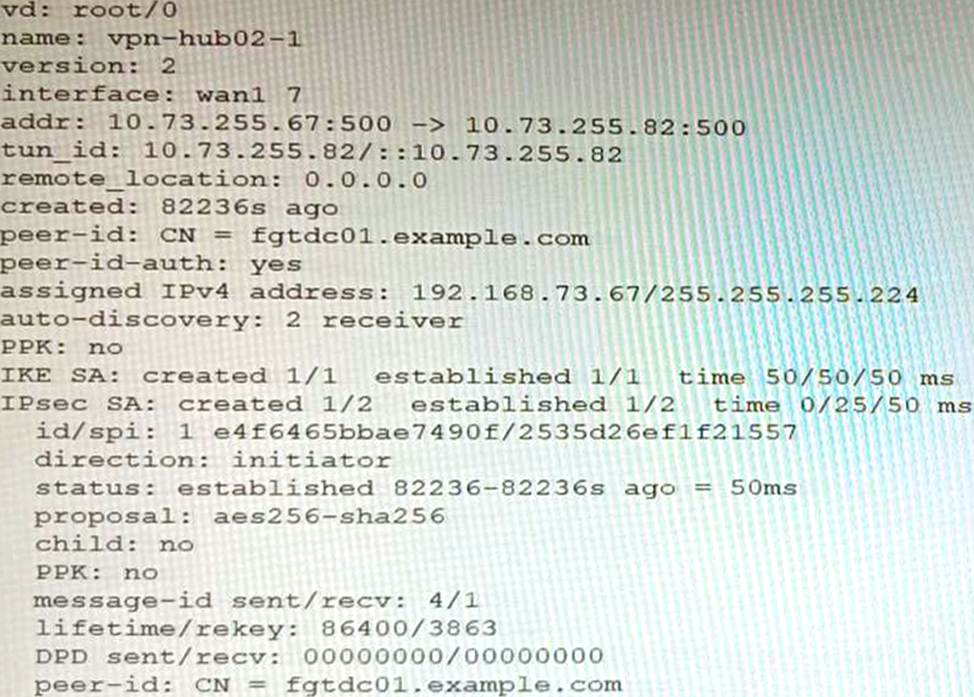
Exhibit B

Exhibit C
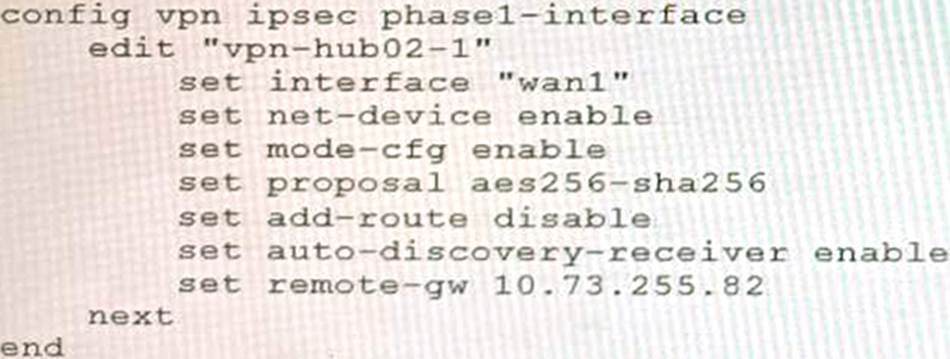
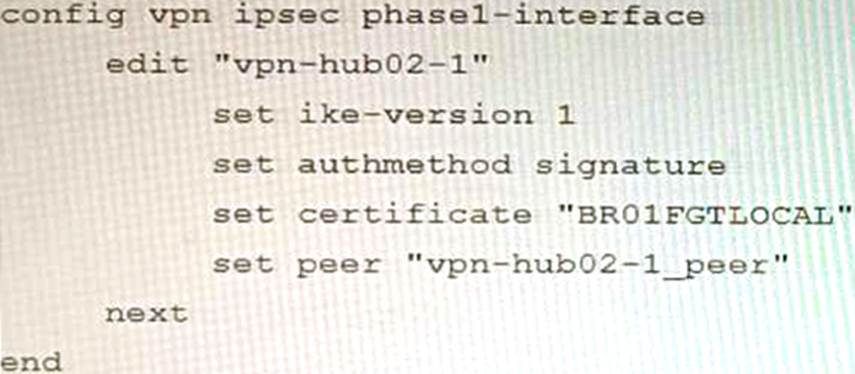
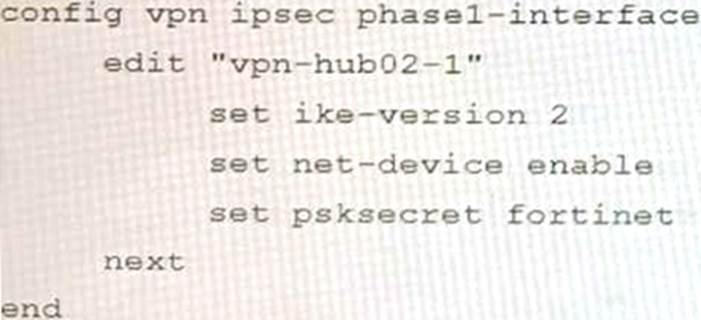
A customer is trying to set up a VPN with a FortiGate, but they do not have a backup of the configuration. Output during a troubleshooting session is shown in the exhibits A and B and a baseline VPN configuration is shown in Exhibit C Referring to the exhibits, which configuration will restore VPN connectivity?
A)
B)
C)

D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
C
Explanation:
The output in Exhibit A shows that the VPN tunnel is not established because the peer IP address is incorrect. The output in Exhibit B shows that the peer IP address is 192.168.1.100, but the baseline VPN configuration in Exhibit C shows that the peer IP address should be 192.168.1.101.
To restore VPN connectivity, you need to change the peer IP address in the VPN tunnel configuration to 192.168.1.101. The correct configuration is shown below: config vpn ipsec phase1-interface edit "wan"
set peer-ip 192.168.1.101
set peer-id 192.168.1.101
set dhgrp 1
set auth-mode psk
set psk SECRET_PSK
next
end
Option A is incorrect because it does not change the peer IP address.
Option B is incorrect because it changes the peer IP address to 192.168.1.100, which is the incorrect IP address.
Option D is incorrect because it does not include the necessary configuration for the VPN tunnel.
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit A

Exhibit B

Exhibit C

A customer is trying to set up a VPN with a FortiGate, but they do not have a backup of the configuration. Output during a troubleshooting session is shown in the exhibits A and B and a baseline VPN configuration is shown in Exhibit C Referring to the exhibits, which configuration will restore VPN connectivity?
A)

B)

C)

D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
C
Explanation:
The output in Exhibit A shows that the VPN tunnel is not established because the peer IP address is incorrect. The output in Exhibit B shows that the peer IP address is 192.168.1.100, but the baseline VPN configuration in Exhibit C shows that the peer IP address should be 192.168.1.101.
To restore VPN connectivity, you need to change the peer IP address in the VPN tunnel configuration to 192.168.1.101. The correct configuration is shown below: config vpn ipsec phase1-interface edit "wan"
set peer-ip 192.168.1.101
set peer-id 192.168.1.101
set dhgrp 1
set auth-mode psk
set psk SECRET_PSK
next
end
Option A is incorrect because it does not change the peer IP address.
Option B is incorrect because it changes the peer IP address to 192.168.1.100, which is the incorrect IP address.
Option D is incorrect because it does not include the necessary configuration for the VPN tunnel.
On a FortiGate Configured in Transparent mode, which configuration option allows you to control Multicast traffic passing through the?

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
A
Explanation:
When multicast-skip-policy is enabled, no check is performed based on multicast policy. A multicast packet received on an interface is flooded unconditionally to all interfaces (except the incoming interface) belonging to the same forwarding domain. Multicast packets are forwarded even when there is no multicast policy or the multicast policy is set to deny. To forward multicast traffic based on multicast policy, multicast-skip-policy must be disabled. In transparent mode, there is a per-VDOM configuration to skip policy check and forward all multicast traffic. This command is only available in transparent mode, and is disabled by default.
Refer to the exhibit showing an SD-WAN configuration.
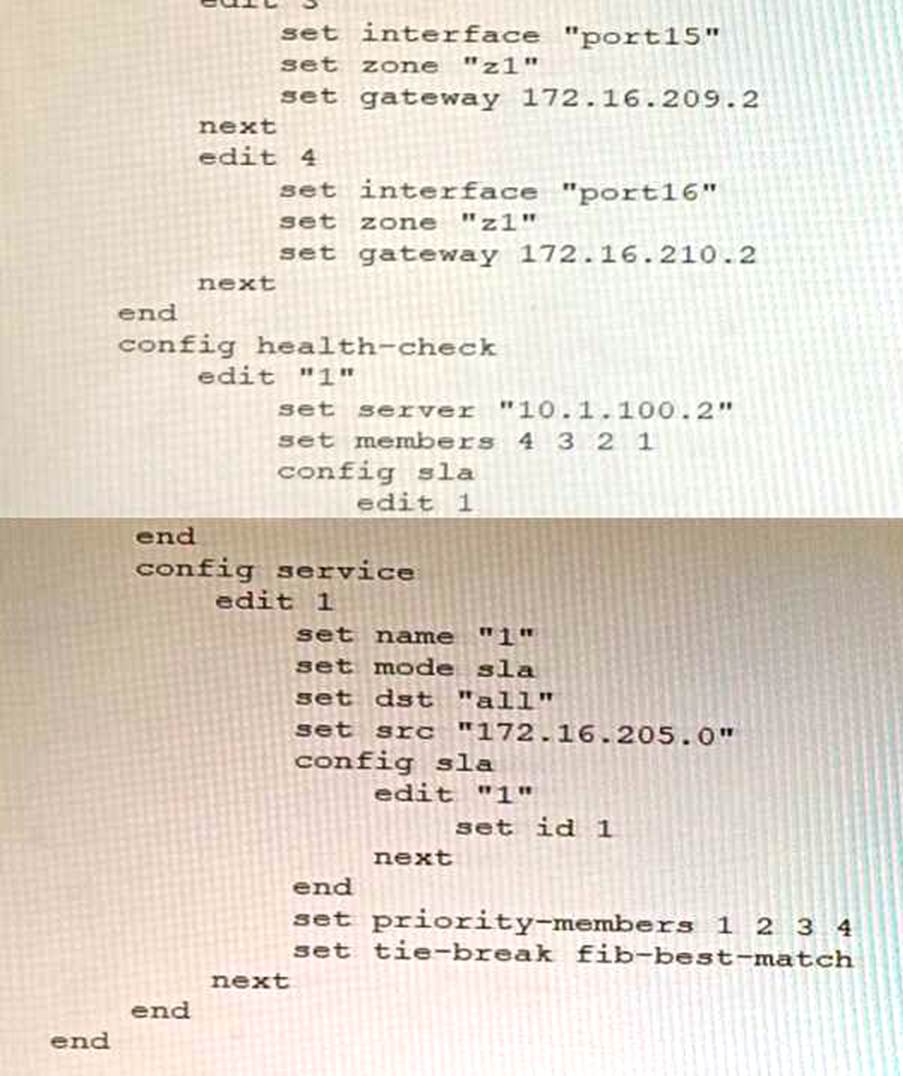
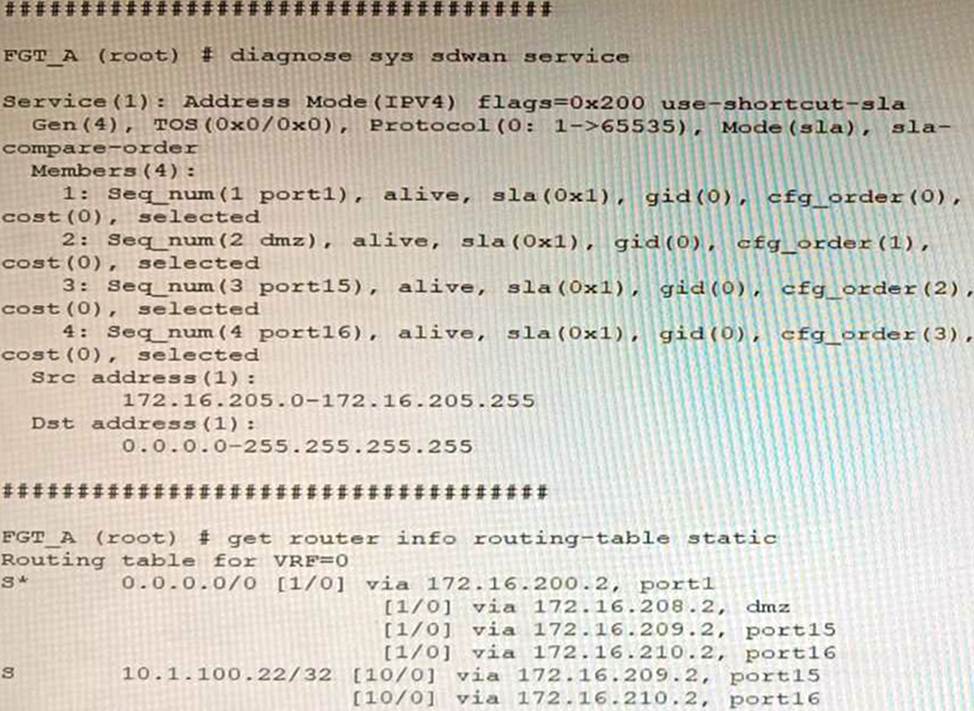
According to the exhibit, if an internal user pings 10.1.100.2 and 10.1.100.22 from subnet 172.16.205.0/24, which outgoing interfaces will be used?
- A . port16 and port1
- B . port1 and port1
- C . port16 and port15
- D . port1 and port15
D
Explanation:
According to the exhibit, the SD-WAN configuration has two rules: one for traffic to 10.1.100.0/24 subnet, and one for traffic to 10.1.100.16/28 subnet. The first rule uses the best quality strategy, which selects the SD-WAN member with the best measured quality based on performance SLA metrics. The second rule uses the manual strategy, which specifies port1 as the SD-WAN member to select. Therefore, if an internal user pings 10.1.100.2 and 10.1.100.22 from subnet 172.16.205.0/24, the outgoing interfaces will be port16 and port1 respectively, assuming that port16 has the best quality among the SD-WAN members.
Reference:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/6.2.14/cookbook/218559/configuring-the-sd-wan-interface
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.2.8/administration-guide/686587/ecmp-support-for-the-longest-match-in-sd-wan-rule-matching
Refer to the exhibit showing an SD-WAN configuration.


According to the exhibit, if an internal user pings 10.1.100.2 and 10.1.100.22 from subnet 172.16.205.0/24, which outgoing interfaces will be used?
- A . port16 and port1
- B . port1 and port1
- C . port16 and port15
- D . port1 and port15
D
Explanation:
According to the exhibit, the SD-WAN configuration has two rules: one for traffic to 10.1.100.0/24 subnet, and one for traffic to 10.1.100.16/28 subnet. The first rule uses the best quality strategy, which selects the SD-WAN member with the best measured quality based on performance SLA metrics. The second rule uses the manual strategy, which specifies port1 as the SD-WAN member to select. Therefore, if an internal user pings 10.1.100.2 and 10.1.100.22 from subnet 172.16.205.0/24, the outgoing interfaces will be port16 and port1 respectively, assuming that port16 has the best quality among the SD-WAN members.
Reference:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/6.2.14/cookbook/218559/configuring-the-sd-wan-interface
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.2.8/administration-guide/686587/ecmp-support-for-the-longest-match-in-sd-wan-rule-matching
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the high availability configuration for the FortiAuthenticator (FAC1).

Based on this information, which statement is true about the next FortiAuthenticator (FAC2) member that will join an HA cluster with this FortiAuthenticator (FAC1)?
- A . FAC2 can only process requests when FAC1 fails.
- B . FAC2 can have its HA interface on a different network than FAC1.
- C . The FortiToken license will need to be installed on the FAC2.
- D . FSSO sessions from FAC1 will be synchronized to FAC2.
B
Explanation:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.5.3/administration-guide/122076/high-availability
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.5.3/administration-guide/122076/high-availability#Standalo
