Practice Free NSE7_SSE_AD-25 Exam Online Questions
For monitoring potentially unwanted applications on endpoints, which information is available on the FortiSASE software installations page? (Choose two answers)
- A . The endpoint the software is installed on1
- B . The license status of the software2
- C . The vendor of the software3
- D . The usage frequency of the software
A, C
Explanation:
In FortiSASE, the Software Installations page (located under Network > Managed Endpoints) provides a centralized view of all software inventory reported by the FortiClient agents. This feature is essential for administrators to maintain visibility into the environment and identify potentially unwanted applications (PUA) or unauthorized software installed on remote devices.
Software Inventory Reporting: FortiClient sends the endpoint’s software inventory to FortiSASE upon initial registration and updates the portal whenever a change―such as an installation, update, or removal―occurs on the endpoint.
Available Information (Vendor): When viewing the global list of applications, the portal displays detailed metadata for each software entry. This includes the Vendor of the software and its specific version, allowing administrators to differentiate between reputable enterprise applications and suspicious third-party utilities.
Available Information (Endpoint Association): The interface includes an Endpoint Count field that indicates how many devices have a specific application installed. By selecting a specific application and using the View Endpoints action, the administrator can see a list of every individual endpoint where that software is currently active.
Incorrect Options: While license management is a general feature of the ecosystem, the Software Installations page itself does not track the license status of individual third-party applications (Option B). Similarly, while FortiSASE monitors traffic, the Software Installations inventory page does not
report on the usage frequency (how often a user opens or uses the app) of the installed binaries (Option D).
By leveraging this inventory, administrators can proactively manage risk by identifying endpoints that possess high-risk software and taking remediation steps or applying ZTNA posture tags based on the presence of specific unauthorized software.
How does FortiSASE Secure Private Access (SPA) facilitate connectivity to private resources in a hub-and-spoke network? (Choose one answer)
- A . SPA establishes direct links to spokes without IPsec or BGP and uses an easy configuration key to
secure web traffic for remote users. - B . SPA applies source network address translation (SNAT) for remote user traffic and uses IKEv1 for IPsec tunnels to connect to standalone hubs without BGP support.
- C . SPA connects to private resources using HTTP and HTTPS protocols and relies on FortiClient for agentless access to SD-WAN deployments.
- D . SPA connects a FortiSASE POP to a FortiGate hub or SD-WAN deployment using IPsec and BGP for dynamic route exchange with an easy configuration key for simplified setup on FortiOS.1
D
Explanation:
FortiSASE Secure Private Access (SPA) is designed to provide remote users with seamless and secure access to private applications hosted behind an organization’s FortiGate Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) or SD-WAN hubs.2
Hub-and-Spoke Architecture: In this deployment model, the organization’s FortiGate (either a standalone NGFW or an SD-WAN hub) acts as the hub, while the global FortiSASE Security Points of Presence (PoPs) act as spokes.3
IPsec and BGP Integration: The connectivity between the FortiSASE PoPs and the corporate hub is established via IPsec VPN tunnels. To manage routing and ensure that remote users can reach the correct internal subnets, Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is used for dynamic route exchange.4 This allows the hub to advertise internal prefixes to FortiSASE, enabling the PoPs to route user traffic effectively without requiring complex static route management.
Simplified Configuration: To reduce administrative overhead and prevent manual configuration errors on the FortiOS side, Fortinet introduced the SPA easy configuration key (also known as an invitation code or simplified SPA setup). An administrator generates this key in the FortiSASE portal and enters it on the FortiGate hub. This triggers the Fabric Overlay Orchestrator to automatically provision the necessary IPsec tunnels, BGP peerings, and firewall policies required for SPA connectivity.
According to the FortiSASE 25 Architecture Guide, this method is preferred over legacy VPNs because it supports both TCP and UDP traffic, integrates natively with existing SD-WAN deployments, and automatically finds the shortest path to applications using ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) shortcuts where applicable.
Which FortiSASE feature ensures least-privileged user access to all applications?
- A . secure web gateway (SWG)
- B . SD-WAN
- C . zero trust network access (ZTNA)
- D . thin branch SASE extension
C
Explanation:
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is the FortiSASE feature that ensures least-privileged user access to all applications. ZTNA operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," providing secure access based on the identity of users and devices, regardless of their location.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA):
ZTNA ensures that only authenticated and authorized users and devices can access applications.
It applies the principle of least privilege by granting access only to the resources required by the user, minimizing the potential for unauthorized access.
Implementation:
ZTNA continuously verifies user and device trustworthiness and enforces granular access control policies.
This approach enhances security by reducing the attack surface and limiting lateral movement within the network.
Reference: FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide: Provides detailed information on ZTNA and its role in ensuring least-privileged access.
FortiSASE 23.2 Documentation: Explains the implementation and benefits of ZTNA within the FortiSASE environment.
What is the maximum number of Secure Private Access (SPA) service connections (SPA hubs) supported in the SPA use case? (Choose one answer)
- A . 8
- B . 12
- C . 4
- D . 16
B
Explanation:
In recent versions of FortiSASE (starting from version 24.4 and later), the platform has increased its scalability to support larger enterprise environments.
Maximum Hub Support: According to the FortiSASE Mature Administration Guide and the FortiSASE 25.3.148 Feature Release Notes, administrators can now configure a maximum of 12 SPA Service Connections (SPA hubs). Previously, this limit was restricted to 4 hubs.
Scalability for Large Enterprises: This enhancement allows organizations with complex, geographically dispersed networks―such as those with multiple regional datacenters or cloud hubs―to integrate up to 12 distinct FortiGate SD-WAN hubs into their SASE infrastructure.
Service Connection Licensing: Each SPA hub requires a dedicated FortiGate SPA Service Connection license. In MSSP environments using FortiCloud Organizations, a single FortiSASE instance can inherit these licenses from a root OU, supporting up to the same cumulative maximum of 12 service connections.
Routing and Performance: These 12 hubs form the "Private Access" backbone, where FortiSASE security PoPs act as spokes. The use of BGP (either per-overlay or on loopback) ensures that traffic is dynamically routed to the optimal hub based on the destination network and defined SLA priorities.
Refer to the exhibits.
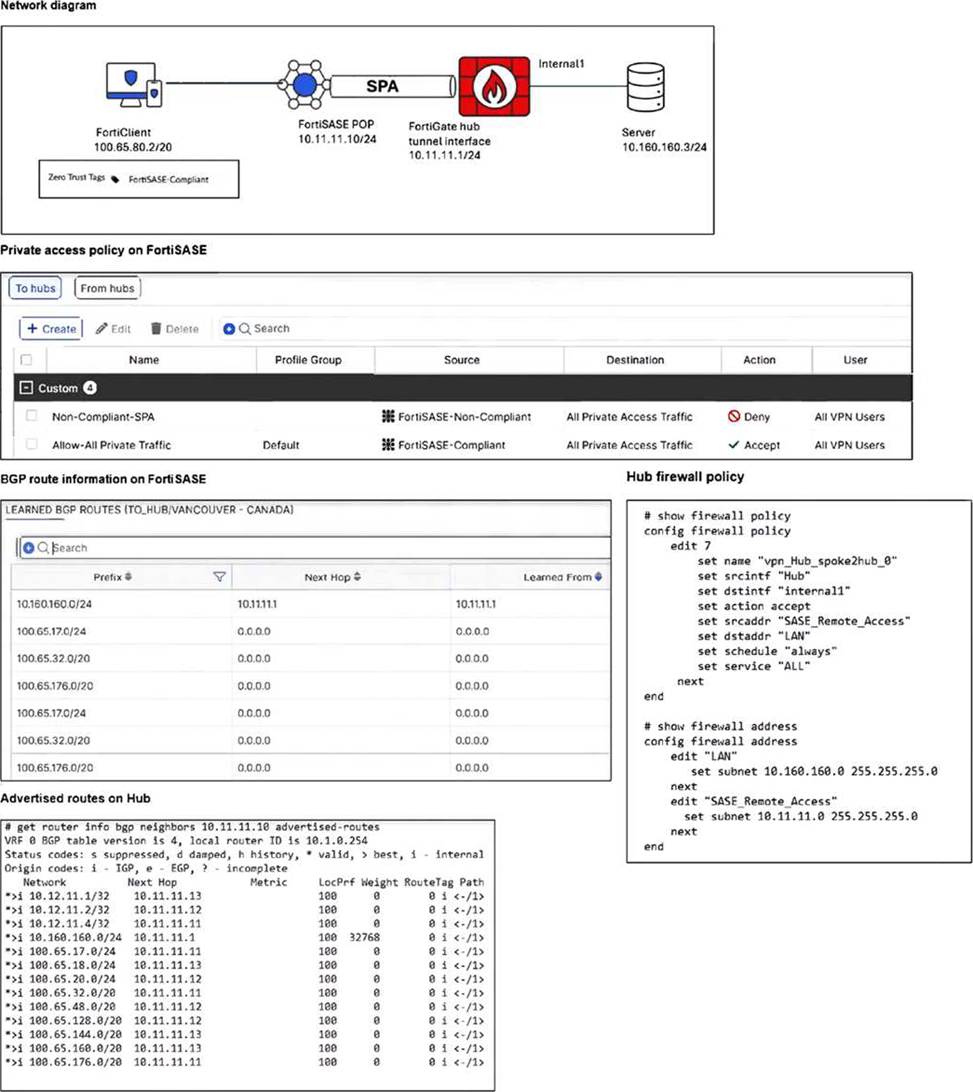
A FortiSASE administrator has configured FortiSASE as a spoke to a FortiGate hub. The tunnel is up to the FortiGate hub. However, the remote FortiClient is not able to access the web server hosted behind the FortiGate hub.
What is the reason for the access failure? (Choose one answer)
- A . The hub is not advertising the required routes.
- B . A private access policy has denied the traffic because of failed compliance.
- C . The hub firewall policy does not include the FortiClient address range.
- D . The server subnet BGP route was not received on FortiSASE.
C
Explanation:
Based on the detailed analysis of the provided exhibits (image_65feb6.jpg), the connectivity failure is caused by a mismatch in the Hub firewall policy configuration.
Endpoint Analysis: The Network Diagram shows the FortiClient endpoint has an IP address of 100.65.80.2/20 and currently carries the FortiSASE-Compliant ZTNA tag.
FortiSASE Policy Validation: The Private access policy on FortiSASE shows an "Accept" rule for traffic originating from "FortiSASE-Compliant" sources destined for "All Private Access Traffic". This confirms the traffic is successfully leaving the FortiSASE PoP.
Routing Validation: The Learned BGP Routes on FortiSASE table shows the prefix 10.160.160.0/24 (the Server subnet) is correctly received via Next Hop 10.11.11.1. Routing is correctly established.
Hub Firewall Policy Error: Examining the Hub firewall policy (edit 7), the srcaddr is set to
"SASE_Remote_Access". Looking at the address object definition for "SASE_Remote_Access," it is configured with the subnet 10.11.11.0 255.255.255.0.
The Conflict: The FortiClient’s actual IP address (100.65.80.2) does not fall within the 10.11.11.0/24 range defined in the policy’s source address. On a FortiGate hub, for traffic to be permitted through the tunnel to the internal server, the firewall policy must include the specific subnet assigned to the remote clients, not just the tunnel interface subnet. Because the FortiClient address range is missing from the hub’s policy, the traffic is dropped at the hub.
An organization needs to resolve internal hostnames using its internal rather than public DNS servers for remotely connected endpoints.
Which two components must be configured on FortiSASE to achieve this? (Choose two.)
- A . SSL deep inspection
- B . Split DNS rules
- C . Split tunnelling destinations
- D . DNS filter
BC
Explanation:
To resolve internal hostnames using internal DNS servers for remotely connected endpoints, the following two components must be configured on FortiSASE:
Split DNS Rules:
Split DNS allows the configuration of specific DNS queries to be directed to internal DNS servers instead of public DNS servers.
This ensures that internal hostnames are resolved using the organization’s internal DNS infrastructure, maintaining privacy and accuracy for internal network resources.
Split Tunneling Destinations:
Split tunneling allows specific traffic (such as DNS queries for internal domains) to be routed through the VPN tunnel while other traffic is sent directly to the internet.
By configuring split tunneling destinations, you can ensure that DNS queries for internal hostnames are directed through the VPN to the internal DNS servers.
Reference: FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide: Provides details on configuring split DNS and split tunneling for VPN clients.
FortiSASE 23.2 Documentation: Explains the implementation and configuration of split DNS and split
tunneling for securely resolving internal hostnames.
Refer to the exhibits.
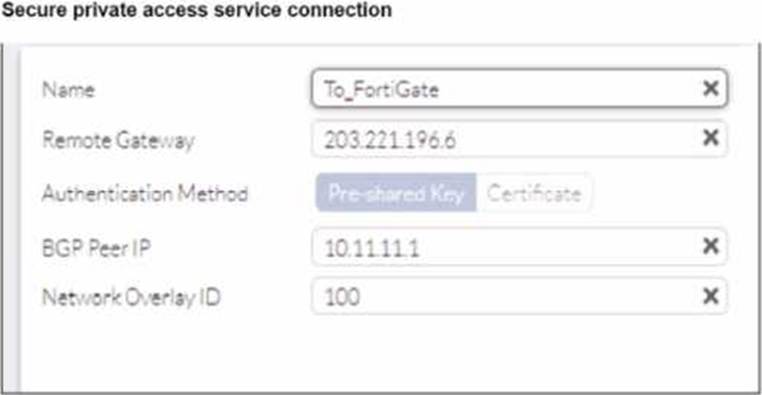
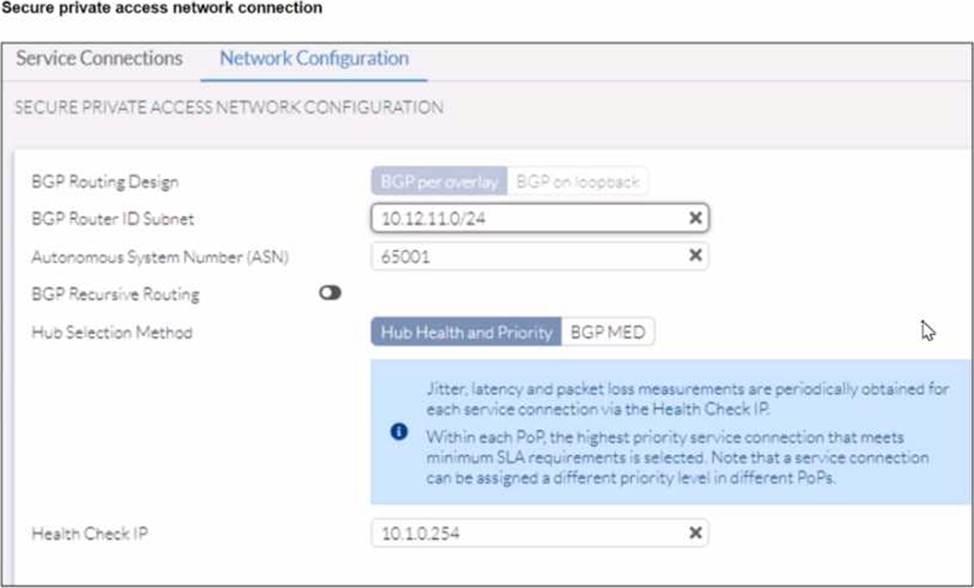

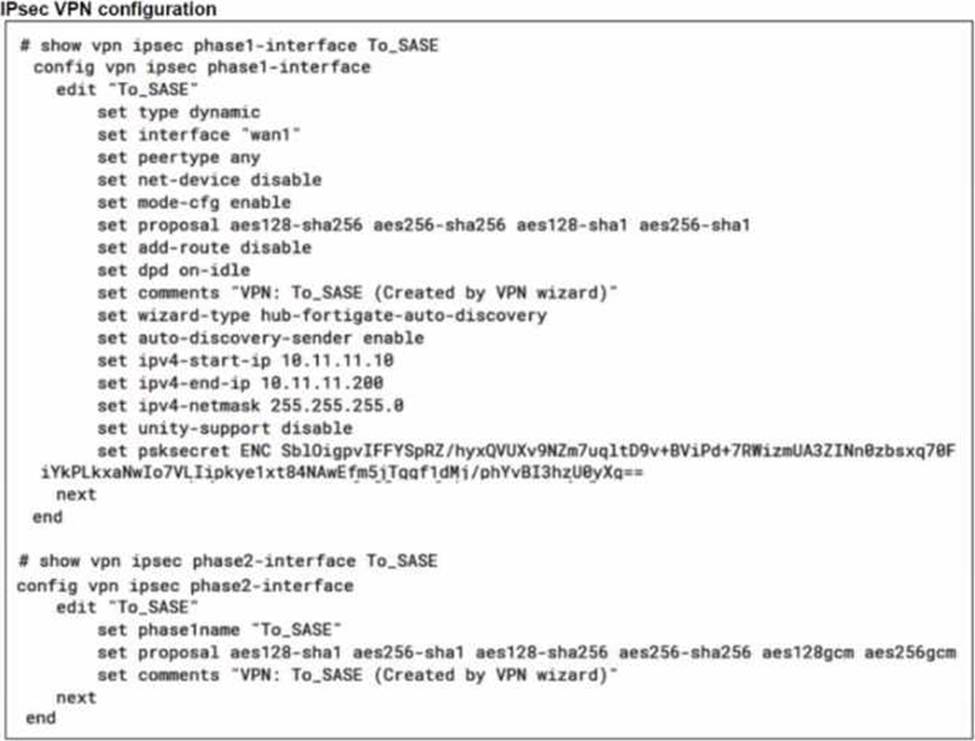

A FortiSASE administrator is trying to configure FortiSASE as a spoke to a FortiGate hub. The VPN tunnel does not establish
Based on the provided configuration, what configuration needs to be modified to bring the tunnel up?
- A . NAT needs to be enabled in the Spoke-to-Hub firewall policy.
- B . The BGP router ID needs to match on the hub and FortiSASE.
- C . FortiSASE spoke devices do not support mode config.
- D . The hub needs IKEv2 enabled in the IPsec phase 1 settings.
C
Explanation:
The VPN tunnel between the FortiSASE spoke and the FortiGate hub is not establishing due to the configuration of mode config, which is not supported by FortiSASE spoke devices. Mode config is used to assign IP addresses to VPN clients dynamically, but this feature is not applicable to FortiSASE spokes.
Mode Config in IPsec:
The configuration snippet shows that mode config is enabled in the IPsec phase 1 settings.
Mode config is typically used for VPN clients to dynamically receive an IP address from the VPN server, but it is not suitable for site-to-site VPN configurations involving FortiSASE spokes.
Configuration Adjustment:
To establish the VPN tunnel, you need to disable mode config in the IPsec phase 1 settings.
This adjustment will allow the FortiSASE spoke to properly establish the VPN tunnel with the FortiGate hub.
Steps to Disable Mode Config:
Access the VPN configuration on the FortiSASE spoke.
Edit the IPsec phase 1 settings to disable mode config.
Ensure other settings such as pre-shared key, remote gateway, and BGP configurations are correct and consistent with the FortiGate hub.
Reference: FortiOS 7.6 Administration Guide: Provides details on configuring IPsec VPNs and mode config settings.
FortiSASE 23.2 Documentation: Explains the supported configurations for FortiSASE spoke devices and VPN setups.
A FortiSASE administrator is receiving reports that some users have travelled overseas and cannot establish their agent-based VPN tunnels, although they can authenticate with their SSO credentials to access O365 and SFDC directly. The administrator reviewed the firewall policies and ZTNA tags of some users and could not find anything unusual.
Which action can the administrator take to resolve
this problem? (Choose one answer)
- A . Create a dedicated firewall policy for the users.
- B . Instruct the users to restart their laptops and log in again.
- C . Ensure that the countries the users are visiting are not listed under the Deny list in the Geofencing settings.
- D . Instruct the users to install the updated version of the agent-based client.
C
Explanation:
In a FortiSASE environment, the ability of a remote user to establish a VPN tunnel is governed not only by their credentials and firewall policies but also by geographic access controls.
Geofencing Mechanism: FortiSASE includes a Geofencing feature (found under Configuration > Restrictions or Configuration > Geofencing in newer versions) that allows administrators to restrict or allow access to SASE services based on the geographic location of the endpoint’s public IP address.
Connection Failure vs. SSO Success: The scenario describes a situation where users can successfully authenticate via SSO to reach third-party SaaS apps like Office 365 (O365) or Salesforce (SFDC) but cannot connect to the SASE VPN. This occurs because the SSO authentication is handled directly by the Identity Provider (IdP) (e.g., Microsoft Entra ID), which may not have the same geographic restrictions. However, when the FortiClient attempts to establish the tunnel to the FortiSASE Point of Presence (PoP), the SASE gateway checks the Geofencing list. If the country the user is visiting is on the Deny list (or not on the Allow list), the connection is dropped at the "local-in" policy level on the SASE backend, preventing the tunnel from forming.
Verification and Resolution: To resolve this, the administrator must verify the Geofencing settings and ensure that the countries where the traveling users are located are permitted to connect. If the feature is enabled with a "Deny" list, the specific country must be removed from that list; if it uses an "Allow" list, the country must be added.
Analysis of Other Options:
Option A: Firewall policies govern traffic after the tunnel is established; they cannot resolve a failure to connect the tunnel itself.
Option B: Restarting the device is a general troubleshooting step but will not bypass a server-side geographic block.
Option D: While keeping clients updated is a best practice, the issue described (specific to overseas travel while other functions work) points to a configuration restriction rather than a software bug.
A customer needs to implement device posture checks for their remote endpoints while accessing the protected server. They also want the TCP traffic between the remote endpoints and the protected servers to be processed by FortiGate.
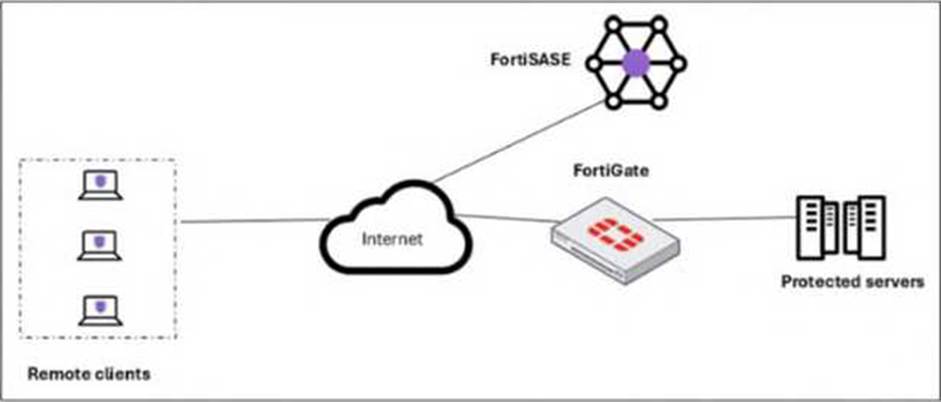
In this scenario, which two setups will achieve these requirements? (Choose two answers)
- A . Configure ZTNA tags on FortiGate.
- B . Configure FortiGate as a zero trust network access (ZTNA) access proxy.
- C . Configure ZTNA servers and ZTNA policies on FortiGate.
- D . Configure private access policies on FortiSASE with ZTNA.
B, C
Explanation:
To implement Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) where a FortiGate hub enforces device posture and processes traffic directly, specific architectural and configuration steps are required on the FortiGate appliance.
ZTNA Access Proxy (B): The FortiGate must be configured as a ZTNA access proxy. In this role, the FortiGate acts as a secure gateway that mediates connections between remote users and internal applications. This setup ensures that all TCP traffic is intercepted and processed by the FortiGate, providing a direct, shortest-path connection that bypasses the FortiSASE cloud PoPs for the data plane.
ZTNA Servers and Policies (C): Within the FortiGate configuration, administrators must define ZTNA servers (which identify the protected applications or resources) and ZTNA policies. ZTNA policies are the enforcement rules that check for valid client certificates and specific ZTNA tags (synchronized from FortiSASE) before allowing access to a resource. This configuration allows the FortiGate to perform continuous posture checks on every session.
Posture Check Mechanism: While ZTNA tags are used, they are generally synchronized from the FortiSASE Endpoint Management Service (EMS) rather than manually configured on the FortiGate itself. This synchronization ensures the FortiGate has real-time visibility into the security posture (e.g., AV compliance, OS version) of the endpoints as reported by FortiClient.
Analysis of Incorrect Options:
Option A: Creating ZTNA tags manually on a FortiGate is technically possible but is not the recommended "setup" in a FortiSASE deployment, as tags are meant to be dynamically assigned by EMS and synced to the fabric.
Option D: "Private access policies on FortiSASE" refers to the SD-WAN Secure Private Access (SPA) use case. In the SD-WAN SPA model, traffic is steered through the FortiSASE PoP first, whereas the requirement specifically asks for TCP traffic to be processed by the FortiGate using ZTNA.
Refer to the exhibit.
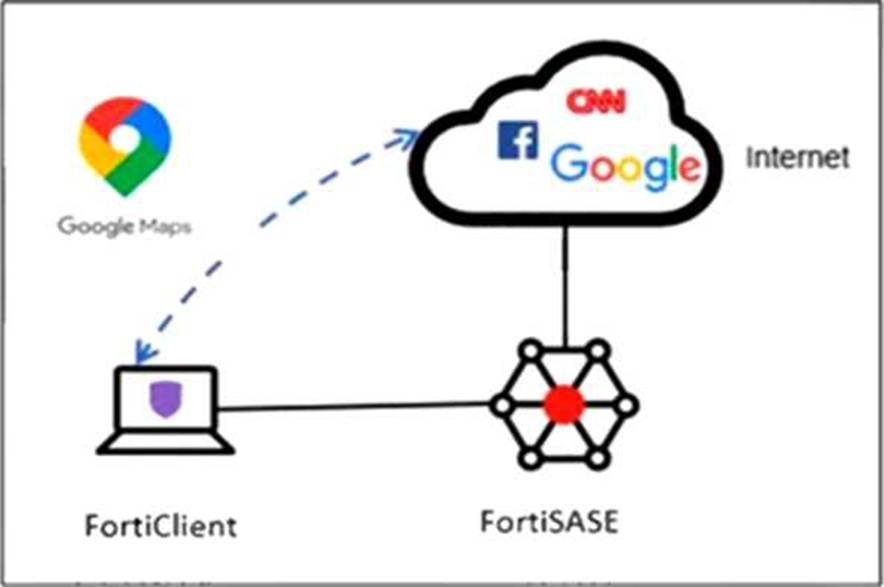
An organization must inspect all the endpoint internet traffic on FortiSASE, and exclude Google Maps traffic from the FortiSASE tunnel and redirect it to the endpoint physical interface.
Which configuration must you apply to achieve this requirement? (Choose one answer)
- A . Add the Google Maps URL in the zero trust network access (ZTNA) TCP access proxy forwarding rule.
- B . Configure a steering bypass tunnel firewall policy using Google Maps FQDN to exclude and redirect the traffic.
- C . Exempt Google Maps in URL filtering in the web filter profile.
- D . Add the Google Maps URL as a steering bypass destination in the endpoint profile.
D
Explanation:
In FortiSASE, the requirement to redirect specific traffic away from the secure tunnel and through the local physical interface is achieved through Steering Bypass (commonly referred to as split tunneling).
Steering Bypass Destinations: This feature is configured within the Endpoint Profile settings. When an administrator adds a destination (such as the Google Maps URL or FQDN) to the Steering Bypass table, the FortiClient agent updates the local routing table on the endpoint.
Traffic Redirection: Traffic matching these bypass rules is explicitly excluded from the FortiSASE VPN tunnel and instead sent directly out of the device’s local internet gateway (physical interface). This is ideal for optimizing bandwidth and reducing latency for trusted, high-volume applications like mapping services or video conferencing.
Analysis of Other Options:
Option A: ZTNA TCP access proxy rules are designed for secure access to private applications, not for managing how internet-bound traffic is routed.
Option B: While it uses the term "steering bypass," there is no "tunnel firewall policy" configuration for this purpose; the configuration is done at the endpoint profile level.
Option C: Exempting a URL in the Web Filter profile only instructs FortiSASE to skip security scanning (AV, DLP, etc.) for that traffic. The traffic would still be encapsulated in the tunnel and sent to FortiSASE, which does not meet the requirement to redirect it to the physical interface.
By configuring the Google Maps URL as a steering bypass destination, the organization ensures the traffic never enters the SASE tunnel, fulfilling the requirement for both traffic inspection (for all other traffic) and local redirection (for Google Maps).
