Practice Free NSE7_EFW-7.2 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit, which shows an SSL certification inspection configuration.
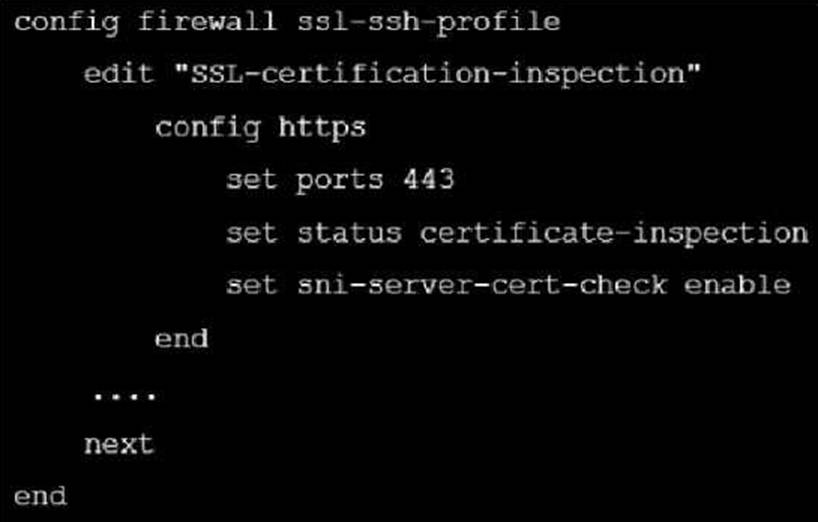
Which action does FortiGate take if the server name indication (SNI) does not match either the common name (CN) or any of the subject alternative names (SAN) in the server certificate?
- A . FortiGate uses the first entry listed in the SAN field in the server certificate
- B . FortiGate uses the CN information from the Subject field in the server certificate
- C . FortiGate uses the SNI from the user’s web browser.
- D . FortiGate closes the connection because this represents an invalid SSL/TLS configuration
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a network diagram.
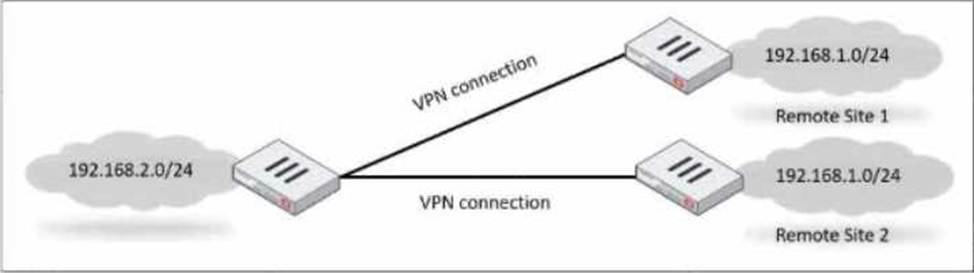
Which IPsec phase 2 configuration should you impalement so that only one remote site is connected at any time?
- A . Set route-overlap to allow.
- B . Set single-source to enable
- C . Set route-overlap to either use―new or use-old
- D . Set net-device to enable
C
Explanation:
To ensure that only one remote site is connected at any given time in an IPsec VPN scenario, you should use route-overlap with the option to either use-new or use-old. This setting dictates which routes are preferred and how overlaps in routes are handled, allowing for one connection to take precedence over the other (C).
Reference: FortiOS Handbook – IPsec VPN
You contoured an address object on the tool fortiGate in a Security Fabric. This object is not synchronized with a downstream device.
Which two reasons could be the cause? (Choose two)
- A . The address object on the tool FortiGate has fabric-object set to disable
- B . The root FortiGate has configuration-sync set to enable
- C . The downstream TortiGate has fabric-object-unification set to local
- D . The downstream FortiGate has configuration-sync set to local
A, C
Explanation:
Option A is correct because the address object on the tool FortiGate will not be synchronized with the downstream devices if it has fabric-object set to disable. This option controls whether the address object is shared with other FortiGate devices in the Security Fabric or not1.
Option C is correct because the downstream FortiGate will not receive the address object from the tool FortiGate if it has fabric-object-unification set to local. This option controls whether the downstream FortiGate uses the address objects from the root FortiGate or its own local address objects2.
Option B is incorrect because the root FortiGate has configuration-sync set to enable by default, which means that it will synchronize the address objects with the downstream devices unless they are disabled by the fabric-object option3.
Option D is incorrect because the downstream FortiGate has configuration-sync set to local by default, which means that it will receive the address objects from the root FortiGate unless they are overridden by the fabric-object-unification option4.
Reference: =
1: Group address objects synchronized from FortiManager5
2: Security Fabric address object unification6
3: Configuration synchronization7
4: Configuration synchronization7
: Security Fabric – Fortinet Documentation
Which two statements about IKE vision 2 are true? (Choose two.)
- A . Phase 1 includes main mode
- B . It supports the extensible authentication protocol (EAP)
- C . It supports the XAuth protocol.
- D . It exchanges a minimum of four messages to establish a secure tunnel
B, D
Explanation:
IKE version 2 supports the extensible authentication protocol (EAP), which allows for more flexible and secure authentication methods1. IKE version 2 also exchanges a minimum of four messages to establish a secure tunnel, which is more efficient than IKE version 12.
Reference: = IKE settings | FortiClient 7.2.2 – Fortinet Documentation, Technical Tip: How to configure IKE version 1 or 2 … – Fortinet Community
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a custom signature.
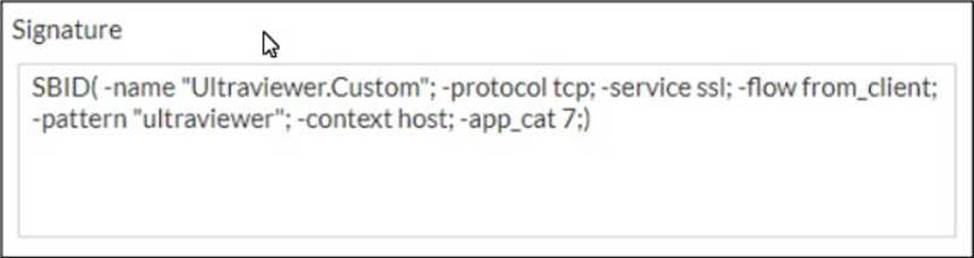
Which two modifications must you apply to the configuration of this custom signature so that you can save it on FortiGate? (Choose two.)
- A . Add severity.
- B . Add attack_id.
- C . Ensure that the header syntax is F-SBID.
- D . Start options with –.
AB
Explanation:
For a custom signature to be valid and savable on a FortiGate device, it must include certain mandatory fields. Severity is used to specify the level of threat that the signature represents, and attack_id is a unique identifier for the signature. Without these, the signature would not be complete and could not be correctly utilized by the FortiGate’s Intrusion Prevention System (IPS).
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a TCL script configuration on FortiManager.
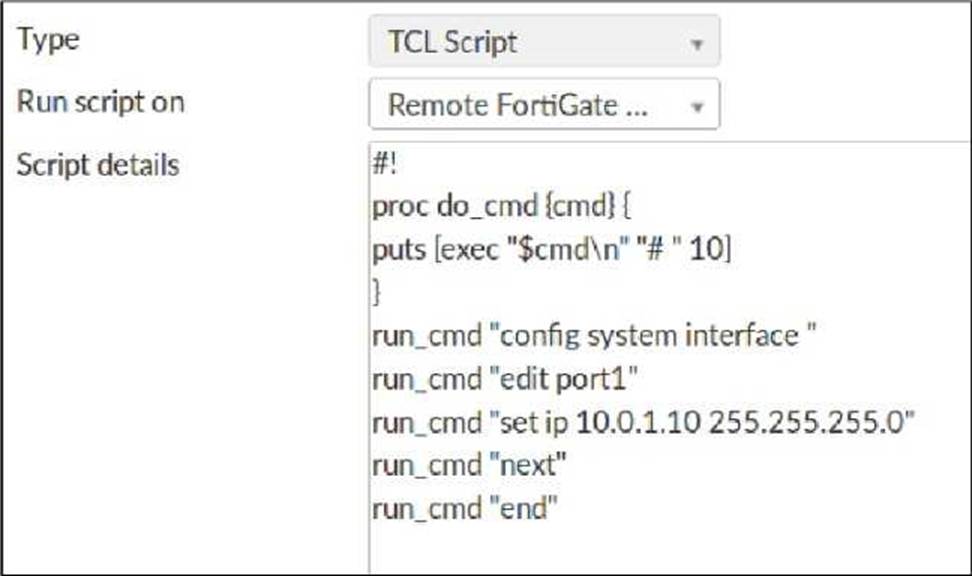
An administrator has configured the TCL script on FortiManager, but the TCL script failed to apply any changes to the managed device after being run.
Why did the TCL script fail to make any changes to the managed device?
- A . The TCL procedure run_cmd has not been created.
- B . The TCL script must start with #include.
- C . There is no corresponding #! to signify the end of the script.
- D . The TCL procedure lacks the required loop statements to iterate through the changes.
Refer to the exhibits, which contain the network topology and BGP configuration for a hub.
Exhibit A.
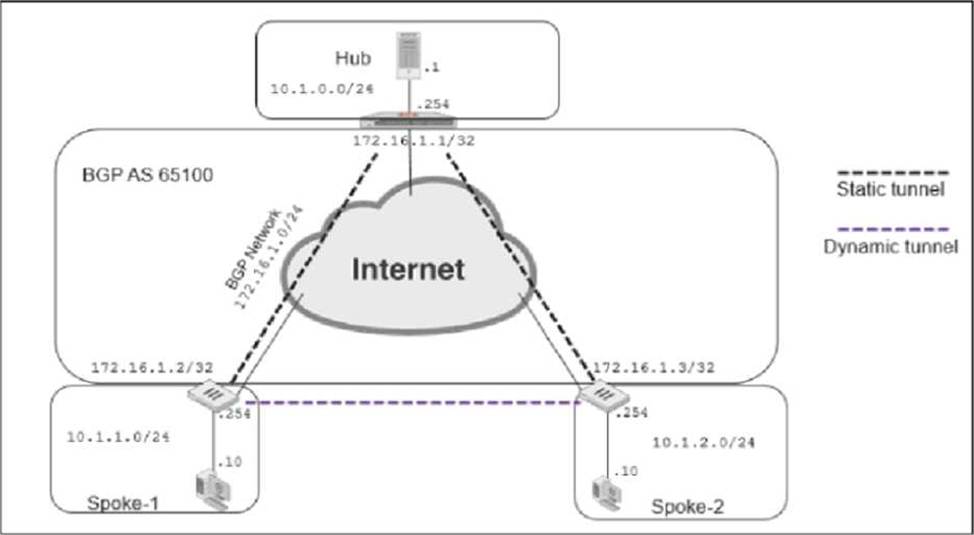
Exhibit B.
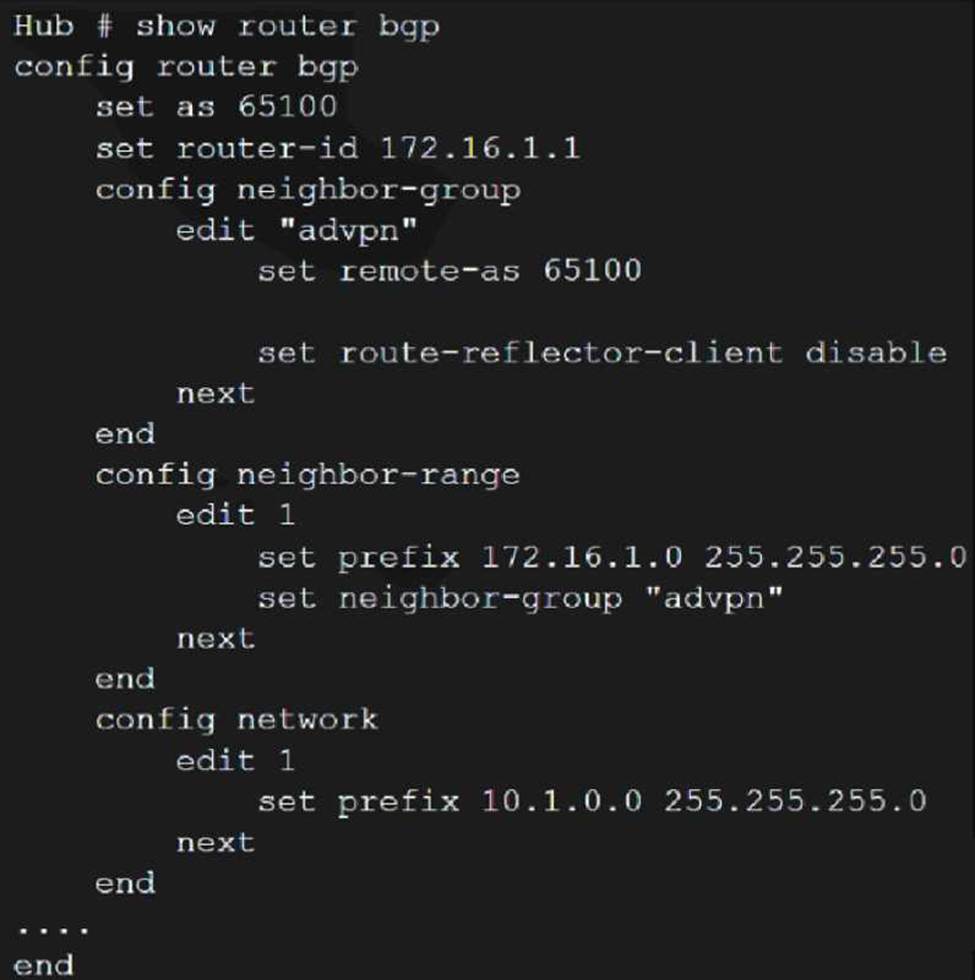
An administrator is trying to configure ADVPN with a hub and spoke VPN setup using iBGP. All the VPNs are up and connected to the hub. The hub is receiving route information from both spokes over iBGP; however the spokes are not receiving route information from each other.
What change must the administrator make to the hub BGP configuration so that the routes learned from one spoke are forwarded to the other spoke?
- A . Configure the hub as a route reflector
- B . Configure auto-discovery-sender on the hub
- C . Add a prefix list to the hub that permits routes to be shared between the spokes
- D . Enable route redistribution under config router bgp
Exhibit.
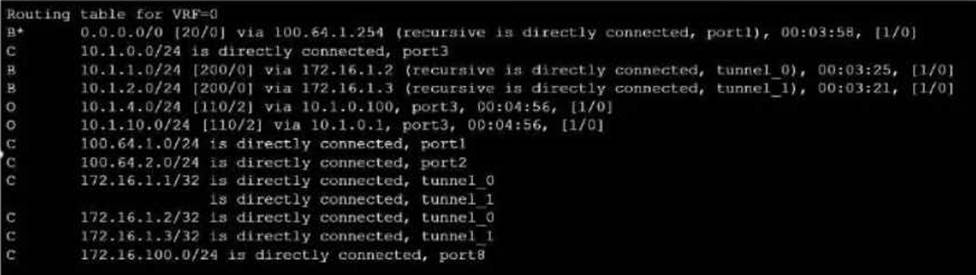
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a partial touting table
What two concisions can you draw from the corresponding FortiGate configuration? (Choose two.)
- A . IPSec Tunnel aggregation is configured
- B . net-device is enabled in the tunnel IPSec phase 1 configuration
- C . OSPI is configured to run over IPSec.
- D . add-route is disabled in the tunnel IPSec phase 1 configuration.
B, D
Explanation:
Option B is correct because the routing table shows that the tunnel interfaces have a netmask of 255.255.255.255, which indicates that net-device is enabled in the phase 1 configuration. This option allows the FortiGate to use the tunnel interface as a next-hop for routing, without adding a route to the phase 2 destination1.
Option D is correct because the routing table does not show any routes to the phase 2 destination networks, which indicates that add-route is disabled in the phase 1 configuration. This option controls whether the FortiGate adds a static route to the phase 2 destination network using the tunnel interface as the gateway2.
Option A is incorrect because IPSec tunnel aggregation is a feature that allows multiple phase 2 selectors to share a single phase 1 tunnel, reducing the number of tunnels and improving performance3. This feature is not related to the routing table or the phase 1 configuration.
Option C is incorrect because OSPF is a dynamic routing protocol that can run over IPSec tunnels, but it requires additional configuration on the FortiGate and the peer device4. This option is not related to the routing table or the phase 1 configuration.
Reference: =
1: Technical Tip: ‘set net-device’ new route-based IPsec logic2
2: Adding a static route5
3: IPSec VPN concepts6
4: Dynamic routing over IPsec VPN7
Exhibit.
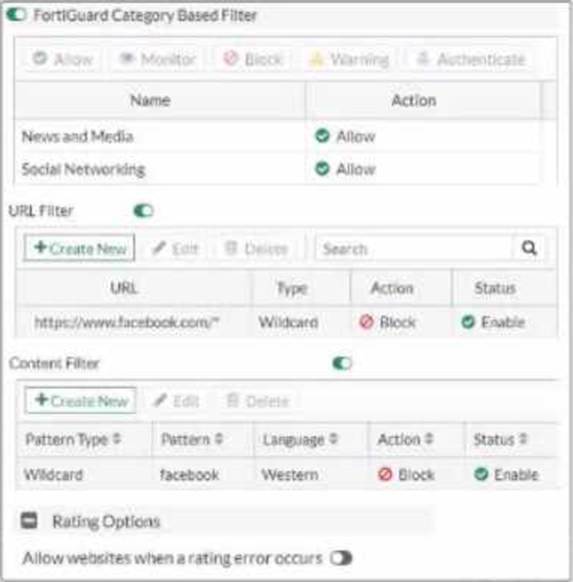
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a partial web filter profile conjuration
What can you cone udo from this configuration about access to www.facebook, com, which is categorized as Social Networking?
- A . The access is blocked based on the Content Filter configuration
- B . The access is allowed based on the FortiGuard Category Based Filter configuration
- C . The access is blocked based on the URL Filter configuration
- D . The access is hocked if the local or the public FortiGuard server does not reply
C
Explanation:
The access to www.facebook.com is blocked based on the URL Filter configuration. In the exhibit, it shows that the URL “www.facebook.com” is specifically set to “Block” under the URL Filter section1.
Reference: Fortigate: How to configure Web Filter function on Fortigate, Web filter | FortiGate / FortiOS 7.0.2 | Fortinet Document Library, FortiGate HTTPS web URL filtering … – Fortinet … – Fortinet Community
Exhibit.
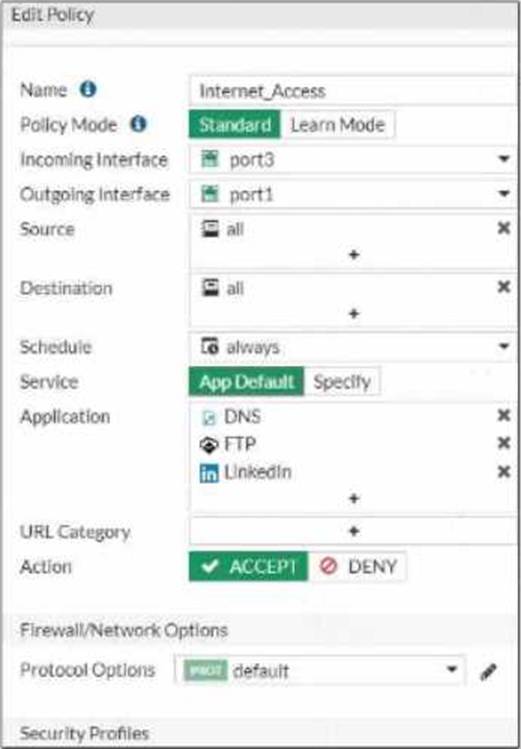
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a partial policy configuration.
Which setting must you configure to allow SSH?
- A . Specify SSH in the Service field
- B . Configure pot 22 in the Protocol Options field.
- C . Include SSH in the Application field
- D . Select an application control profile corresponding to SSH in the Security Profiles section
A
Explanation:
Option A is correct because to allow SSH, you need to specify SSH in the Service field of the policy configuration. This is because the Service field determines which types of traffic are allowed by the policy1. By default, the Service field is set to App Default, which means that the policy will use the default ports defined by the applications. However, SSH is not one of the default applications, so you need to specify it manually or create a custom service for it2.
Option B is incorrect because configuring port 22 in the Protocol Options field is not enough to allow SSH. The Protocol Options field allows you to customize the protocol inspection and anomaly protection settings for the policy3. However, this field does not override the Service field, which still needs to match the traffic type.
Option C is incorrect because including SSH in the Application field is not enough to allow SSH. The Application field allows you to filter the traffic based on the application signatures and categories4. However, this field does not override the Service field, which still needs to match the traffic type.
Option D is incorrect because selecting an application control profile corresponding to SSH in the Security Profiles section is not enough to allow SSH. The Security Profiles section allows you to apply various security features to the traffic, such as antivirus, web filtering, IPS, etc. However, this section does not override the Service field, which still needs to match the traffic type.
Reference: =
1: Firewall policies
2: Services
3: Protocol options profiles
4: Application control
