Practice Free NSE4_FGT_AD-7.6 Exam Online Questions
You have created a web filter profile named restrict media-profile with a daily category usage quota.
When you are adding the profile to the firewall policy, the restrict_media-profile is not listed in the available web profile drop down.
What could be the reason?
- A . The web filter profile is already referenced in another firewall policy.
- B . The firewall policy is in no-inspection mode instead of deep-inspection.
- C . The naming convention used in the web filter profile is restricting it in the firewall policy.
- D . The inspection mode in the firewall policy is not matching with web filter profile feature set.
D
Explanation:
In FortiOS 7.6, web filter profiles are inspection-mode dependent. Certain advanced web filtering features―such as daily category usage quota―are only supported when the firewall policy is operating in proxy-based inspection mode.
Why the profile is not visible
The profile restrict media-profile includes a daily category usage quota.
Daily quotas are a proxy-based web filtering feature.
If the firewall policy is configured with:
Inspection mode: Flow-based
Then FortiGate will not display proxy-only web filter profiles in the Web Filter drop-down list.
FortiGate automatically filters the available profiles based on feature compatibility with the policy’s inspection mode.
This behavior is explicitly documented in the FortiOS 7.6 Web Filtering and Inspection Mode Compatibility sections.
Why the other options are incorrect
Refer to the exhibit.

Based on this partial configuration, what are the two possible outcomes when FortiGate enters conserve mode? (Choose two.)
- A . FortiGate drops new sessions requiring inspection.
- B . Administrators must restart FortiGate to allow new sessions.
- C . Administrators cannot change the configuration.
- D . FortiGate skips quarantine actions.
Refer to the exhibit.
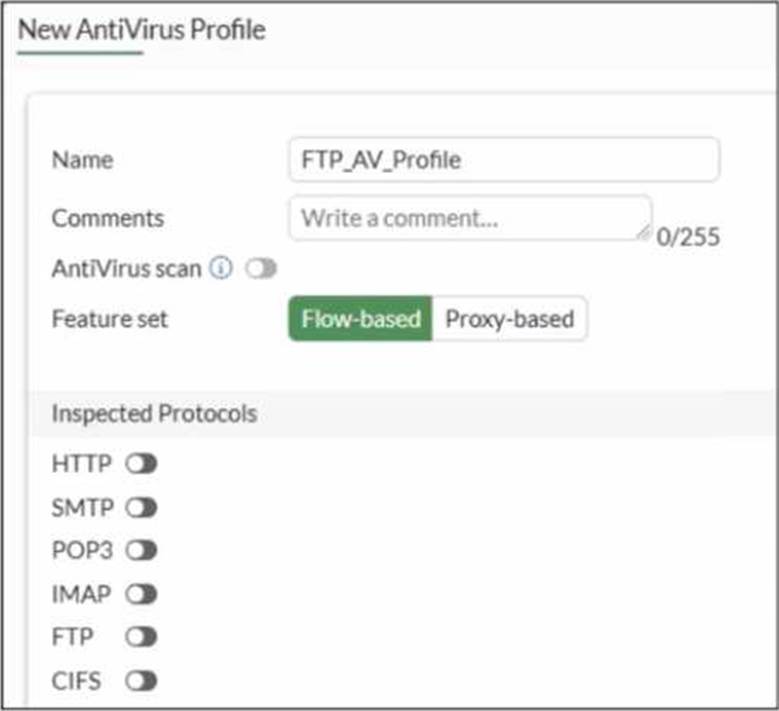
Why is the Antivirus scan switch grayed out when you are creating a new antivirus profile for FTP?
- A . Antivirus scan is disabled under System -> Feature visibility
- B . None of the inspected protocols are active in this profile.
- C . The Feature Set for the profile is Flow-based but it must be Proxy-based
- D . FortiGate. with less than 2 GB RAM. does not support the Antivirus scan feature.
B
Explanation:
In FortiOS 7.6, the Antivirus scan master switch in an antivirus profile becomes available only after at least one supported protocol is enabled for inspection.
What the exhibit shows
A new antivirus profile named FTP_AV_Profile Feature set: Flow-based
Antivirus scan switch is grayed out
All Inspected Protocols (HTTP, SMTP, POP3, IMAP, FTP, CIFS) are currently disabled
Why the Antivirus scan switch is grayed out
In FortiOS antivirus profiles:
The Antivirus scan toggle is a dependent control
It cannot be enabled unless at least one inspected protocol is selected This prevents enabling AV scanning when there is no traffic type to scan
This behavior is documented in the FortiOS 7.6 Antivirus Profile configuration section.
Once you enable a protocol (for example, FTP), the Antivirus scan switch becomes active and configurable.
Why option B is correct
B. None of the inspected protocols are active in this profile.
All protocol toggles are OFF
Therefore, FortiGate disables (grays out) the Antivirus scan option
This is expected and correct behavior
Why the other options are incorrect
Refer to the exhibit.
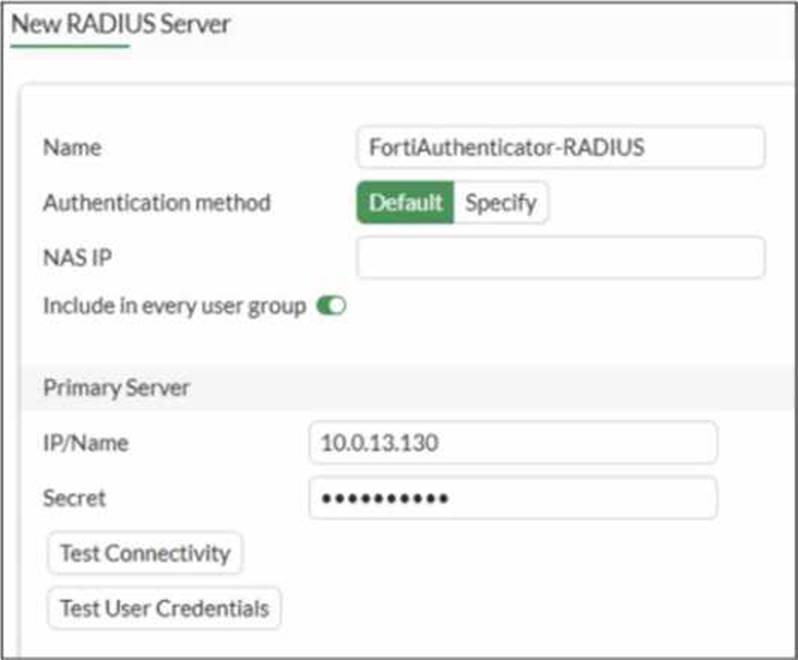
A RADIUS server configuration is shown.
An administrator added a configuration for a new RADIUS server While configuring, the administrator enabled Include in every user group.
What is the impact of enabling Include in every user group in a RADIUS configuration?
- A . This option places the RADIUS server, and all users who can authenticate against that server, into every FortiGate user group.
- B . This option places all FortiGate users and groups required to authenticate into the RADIUS server, which, in this case, is FortiAuthenticator.
- C . This option places the RADIUS server, and all users who can authenticate against that server, into every RADIUS group.
- D . This option places all users into every RADIUS user group, including groups that are used for the
LDAP server on FortiGate.
A
Explanation:
Based on the FortiOS 7.6 Authentication and User Group documentation, the correct answer is A.
Meaning of “Include in every user group” (FortiOS 7.6)
When configuring a RADIUS server on FortiGate, enabling Include in every user group has a very specific and documented effect:
The configured RADIUS server object is automatically added to all FortiGate user groups.
As a result, any user who successfully authenticates against that RADIUS server becomes a valid member of every FortiGate user group, unless additional group filtering (such as RADIUS attributes) is applied.
This simplifies configuration when the same external authentication source must be accepted across multiple firewall policies that reference different user groups.
This behavior is explicitly described in the FortiOS 7.6 Administrator Guide under RADIUS authentication servers and user groups.
Why Option A is Correct
FortiGate user groups can include:
Local users
LDAP servers
RADIUS servers
Enabling Include in every user group causes FortiGate to:
Insert the RADIUS server into all existing and future FortiGate user groups
Therefore, all users authenticating via this RADIUS server are implicitly allowed in every FortiGate user group.
This is exactly what option A describes.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
B: FortiGate does not push users or groups into the RADIUS server. Authentication is always initiated by FortiGate toward RADIUS.
C: FortiGate does not manage or modify RADIUS-side group definitions.
D: LDAP and RADIUS user groups are separate authentication mechanisms; this setting does not merge or affect LDAP groups.
An administrator wants to form an HA cluster using the FGCP protocol.
Which two requirements must the administrator ensure both members fulfill? (Choose two.)
- A . They must have the same hard drive configuration.
- B . They must have the same number of configured VDOMs.
- C . They must have the heartbeat interfaces in the same subnet
- D . They must have the same HA group ID.
B,D
Explanation:
According to the FortiOS 7.6 High Availability (HA) Administration Guide and FGCP (FortiGate Clustering Protocol) requirements, the correct answers are B and D.
FGCP HA Cluster Mandatory Requirements (FortiOS 7.6)
When forming an HA cluster using FGCP, FortiGate devices must meet several strict compatibility and configuration requirements. Among the options given, the following two are mandatory:
✅
B. They must have the same number of configured VDOMs
In FortiOS HA, all cluster members must have the same VDOM configuration.
This includes:
Same number of VDOMs
Same VDOM names
This is required so configuration synchronization can occur correctly between members.
If VDOM counts differ, HA formation will fail.
✔ This is explicitly required and documented.
✅
D. They must have the same HA group ID
The HA group ID uniquely identifies an HA cluster on the network.
All FortiGate units intended to join the same cluster must share the same HA group ID.
If the group IDs differ, devices will not recognize each other as cluster peers.
✔ This is a fundamental FGCP requirement.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
❌
Refer to the exhibit.

Which two statements about the FortiGuard connection are true? (Choose two.)
- A . The weight increases as the number of failed packets rises
- B . You can configure unreliable protocols to communicate with FortiGuard Server.
- C . FortiGate identified the FortiGuard Server using DNS lookup.
- D . FortiGate is using the default port for FortiGuard communication.
A,D
Explanation:
Based on the diagnose debug rating output provided in the exhibit and the standard behavior of the
FortiGuard connection mechanism in FortiOS 7.6:
Weight Calculation (Statement A is True):
In FortiOS, the rating server selection process uses a weight-based system.
According to official documentation, the weight increases with failed packets (lost responses) and decreases with successful packets.
This mechanism ensures that servers with poor reliability are penalized by having higher weights, effectively pushing them to the bottom of the preference list.
Default Port Communication (Statement D is True):
The exhibit explicitly shows the communication is using HTTPS on port 8888.
In FortiOS 7.6 (and legacy versions like 6.2/6.4), FortiGuard filtering supports specific protocols and ports: HTTPS on ports 443, 53, and 8888, where 8888 is considered a default port for FortiGuard queries.
Ports 53 and 8888 are standard for both UDP and TCP/HTTPS FortiGuard communications to avoid common firewall blocks on standard web ports.
Why other options are incorrect:
Statement B (Unreliable protocols): While you can configure UDP (which is unreliable), the exhibit specifically shows HTTPS is being used, which is a reliable (TCP-based) protocol.
Statement C (DNS lookup): In the "Flags" column of the server list, a server found via DNS lookup would be marked with the "D" flag. The exhibit shows the flag as "I" (indicating the last INIT request was sent to this server) and a numeric "2," but the "D" flag is absent. Additionally, the IP 10.0.1.241 is a private address, suggesting it is a manually configured FortiManager or local override server rather than a public server found via global DNS lookup.
Refer to the exhibit.
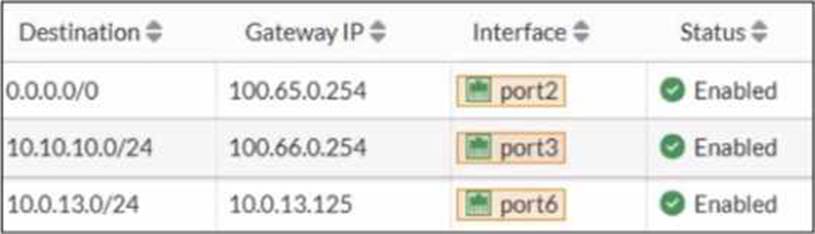
Based on the routing table shown in the exhibit, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
- A . A packet with the source IP address 10.0.13.10 arriving on port2 is allowed if strict RPF is disabled.
- B . A packet with the source IP address 10.100.110.10 arriving on port2 is allowed if strict RPF is enabled.
- C . A packet with the source IP address 10.100.110.10 arriving on port3 is allowed if strict RPF is disabled.
- D . A packet with the source IP address 10.10.10.10 arriving on port2 is allowed if strict RPF is enabled.
Refer to the exhibits.

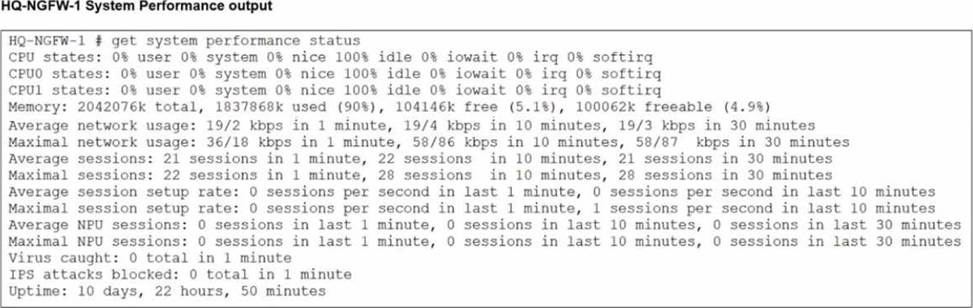
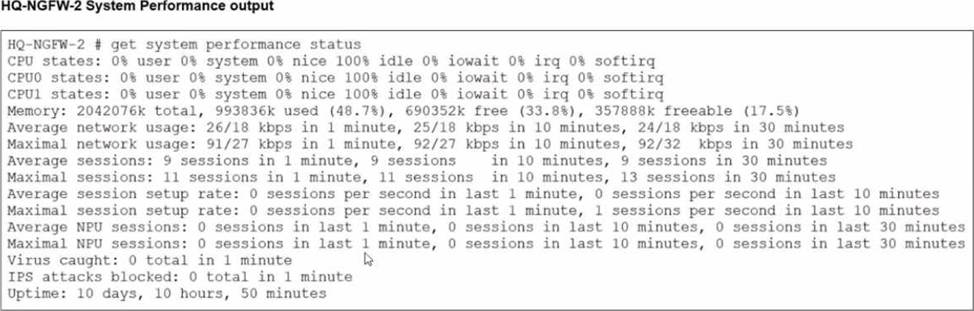
An administrator has observed the performance status outputs on an HA cluster for 55 seconds.
Which FortiGate is the primary?
- A . HQ-NGFW-1 with the parameter memory-failover-flip-timeout setting
- B . HQ-NGFW-2 with the parameter priority setting
- C . HQ-NGFW-1 with the parameter override setting
- D . HQ-NGFW-2 with the parameter memory-failover-threshold setting
D
Explanation:
From the HA configuration shown for HQ-NGFW-1:
set memory-based-failover enable
set memory-failover-threshold 70
set memory-failover-monitor-period 50
set memory-failover-sample-rate 10
set memory-failover-flip-timeout 60
set override disable
set priority 200
From the performance status outputs:
HQ-NGFW-1 memory used is 90% (well above the configured threshold of 70%)
HQ-NGFW-2 memory used is about 48.7% (well below the threshold)
What happens in FortiOS 7.6 with memory-based failover
When memory-based failover is enabled, FortiGate monitors memory utilization. If the unit’s memory usage stays above the configured memory-failover-threshold for the configured memory-failover-monitor-period, the cluster triggers a failover away from the unit under memory pressure.
Threshold = 70%
HQ-NGFW-1 is at 90%, so it violates the threshold.
Monitor period = 50 seconds.
The administrator observed for 55 seconds, which is longer than 50 seconds, so the condition is met for long enough to trigger failover.
The memory-failover-flip-timeout 60 is used to prevent rapid back-and-forth role changes (flapping) after a failover decision; it does not prevent the initial failover from occurring once the threshold breach persists for the monitor period.
What are two characteristics of HA cluster heartbeat IP addresses in a FortiGate device? (Choose two.)
- A . Heartbeat IP addresses are used to distinguish between cluster members.
- B . The heartbeat interface of the primary device in the cluster is always assigned IP address 169.254.0.1.
- C . A change in the heartbeat IP address happens when a FortiGate device joins or leaves the cluster.
- D . Heartbeat interfaces have virtual IP addresses that are manually assigned.
A,C
Explanation:
In FortiOS 7.6, HA cluster heartbeat IP addresses are automatically managed by FortiGate and play a critical role in cluster communication and synchronization.
Correct statements
What are two characteristics of HA cluster heartbeat IP addresses in a FortiGate device? (Choose two.)
- A . Heartbeat IP addresses are used to distinguish between cluster members.
- B . The heartbeat interface of the primary device in the cluster is always assigned IP address 169.254.0.1.
- C . A change in the heartbeat IP address happens when a FortiGate device joins or leaves the cluster.
- D . Heartbeat interfaces have virtual IP addresses that are manually assigned.
A,C
Explanation:
In FortiOS 7.6, HA cluster heartbeat IP addresses are automatically managed by FortiGate and play a critical role in cluster communication and synchronization.
Correct statements
