Practice Free NCP-MCA Exam Online Questions
An administrator need to remove an application from Self-Service (formerly Calm). However, the VM needs to the kept up and running in the environment as it hosts important data.
How can the administrator accomplish this tasks in the simplest way?
- A . Export the VM and then delete the application and re-deploy the VM.
- B . Go to the Manage tab of the application and select the Delete action.
- C . Go to the Manage tab of the application and select the Delete action.
- D . Create a snapshots of the VMs and re-deploy it with a new name.
B
Explanation:
To remove an application from Self-Service (formerly Calm) while keeping the VM up and running, the administrator should:
Go to the Manage tab of the application in Self-Service.
Select the Delete action.
By doing this, the application will be removed from the management of Self-Service, but the VM will remain running in the environment.
Reference: Nutanix documentation on Managing Applications.
Nutanix Best Practices for Application Deletion.
Exhibit.
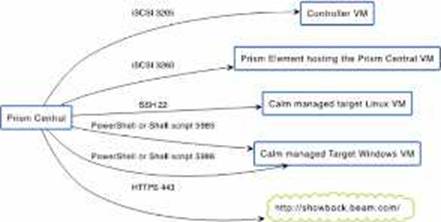
What ports should be opened? (Choose two.)
- A . TCP 22
- B . UDP 5985 and 5986
- C . TC 5985 and 5986
- D . UDP 22
AC
Explanation:
From the exhibit, it is clear that Prism Central needs to communicate with Calm managed target Linux VMs via SSH and with Calm managed target Windows VMs via PowerShell or Shell scripts.
The appropriate ports to open for these communications are:
TCP 22: This port is used for SSH, which is necessary for managing Linux VMs.
TCP 5985 and 5986: These ports are used for PowerShell remoting, which is essential for managing Windows VMs.
Reference: Nutanix Calm documentation on Network Ports.
Best practices for Nutanix Network Configuration.
What is the benefit of defining service dependencies in a Nutanix Calm blueprint?
- A . Accelerates the deployment process
- B . Reduces the cost of operations
- C . Ensures correct startup sequence of services
- D . Provides enhanced security between services
An administrator needs to add AWS as a usable destination for application deployments.
Where would the administrator perform the task?
- A . Marketplace
- B . Projects
- C . Blueprints
- D . Providers
D
Explanation:
The administrator needs to add AWS as a provider in Calm. A provider is a cloud platform or infrastructure that hosts the application VMs or services. Calm supports various providers such as Nutanix, AWS, Azure, GCP, VMware, and Kubernetes. To add a provider, the administrator needs to go to the Providers page in the Calm UI and click on the +Create Provider button. Then, the administrator needs to select the AWS provider type and enter the required information such as name, access key, secret key, and regions.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional – Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) Exam Blueprint Guide, page 11; Nutanix Calm User Guide, section 3.1.
Reference: https://portal.nutanix.com/page/documents/solutions/details?targetId=RA-2093-Nutanix-Calm:RA-2093-Nutanix-Calm
When creating a Playbook using alerts, which types of actions can be executed?
- A . Task alert end communication actions
- B . VM, alert and communication actions
- C . VM, notification, and report actions
- D . Task notification. and report actions
B
Explanation:
Playbooks are a feature of X-Play that allow you to automate tasks based on events or alerts. You can use the actions gallery to select from a variety of actions that can be executed by a playbook. These actions are categorized into three types: VM, alert, and communication1. VM actions allow you to perform operations on virtual machines, such as power on, power off, snapshot, clone, etc. Alert actions allow you to create, update, or close alerts in Prism Central. Communication actions allow you to send messages to various channels, such as email, Slack, or Microsoft Teams2. Therefore, the correct answer is B.
Reference:
1: Nutanix Certified Professional – Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) Exam Blueprint Guide
2: Playbooks C Nutanix.dev
Which statement best describes Categories in Self-Service (formerly Calm)?
- A . Categories provide a way to access the values of variables that are set on entities.
- B . Categories are metadata labels that are assigned to cloud resources.
- C . Categories are part of a templating language for Self-Service scripts.
- D . Categories are the VM instances existing machines or bare-metal machines.
B
Explanation:
Categories in Self-Service (formerly Calm) are metadata labels that are assigned to cloud resources. These categories help organize and manage resources by tagging them with specific attributes, making it easier to apply policies and manage the infrastructure.
Reference: Nutanix Calm documentation on Using Categories.
Nutanix Best Practices for Category Management.
An administrator has built a Playbook to run a Powershell script in a VM when a specific alert is generated. Several days later, the alert is generated, but the script does not execute and there are no Plays recorded for the Playbook.
What is causing this issue?
- A . The Playbook was never enabled.
- B . The version of Playbooks is not correct for the version of Prism Central.
- C . The script executed, but closed with an error code.
- D . The path to the script was not correct.
A
Explanation:
A Playbook is a set of actions that are triggered by an event or a schedule. To run a Playbook, it must be enabled first. If a Playbook is not enabled, it will not respond to any events or schedules, and no Plays will be recorded for it. Therefore, the most likely cause of the issue is that the administrator forgot to enable the Playbook after building it.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional – Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) Exam Blueprint Guide, page 13, section 3.2. Nutanix Multicloud Automation Administration (NMCAA) course, module 4, lesson 2.
Reference: https://portal.nutanix.com/page/documents/details?targetId=Prism-Central-Guide-Prism-v6_0:Prism-Central-Guide-Prism-v6_0
Which are valid entity types to be associated with a playbook using a manual trigger?
- A . VM, Host, Prism Central
- B . VM, Host, Cluster
- C . VM, Category, Prism Element
- D . VM, Category, Cluster
B
Explanation:
Reference: https://portal.nutanix.com/page/documents/details?targetId=Prism-Central-Guide-Prism-v6_0:mul-playbooks-create-manual-triggers-pc-t.html#suppression-rules-add-aws-sc-t
A blueprint service needs to use scaling. The requirements are:
Windows 2019 VM (12 vCPU, 24 GB memory, 500 GB volume)
Minimum VMs needed at any time and at time of deployment is 2 VMs
VMs should not exceed the project quota of 100 vCPUs or 300 GB of memory
There are no other services in use within the project
Which scaling VM replica settings meet all requirements?
- A . MIN: 2, MAX: 11, Default: 2
- B . MIN: 2, MAX: 7, Default: 2
- C . MIN: 2, MAX: 10, Default: 1
- D . MIN: 2, MAX: 8, Default: 1
B
Explanation:
Scaling VM replica settings allow you to specify the minimum, maximum, and default number of VMs that can be created from a blueprint service. The minimum and default values must be equal to or greater than the number of VMs needed at any time and at time of deployment, which is 2 in this case. The maximum value must be equal to or less than the project quota divided by the VM resources, which is 100/12 = 8 for vCPUs and 300/24 = 12 for memory. The lowest of these two values is the limit for the maximum value, which is 8. Therefore, the only option that meets all the requirements is B. MIN: 2, MAX: 7, Default: 2.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional – Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) Exam Blueprint Guide, page 10, Objective 3.1: Given a scenario, create a blueprint to deploy infrastructure and applications using Self-Service
Nutanix Multicloud Automation Administration (NMCAA), Module 5: Self-Service, Lesson 5.2: Blueprint Design, slide 23: Scaling VM Replica Settings
Nutanix Certified Professional Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) 6 Exam, page 10, Objective 3.1: Given a scenario, create a blueprint to deploy infrastructure and applications using Self-Service
How can an administrator ensure that a Nutanix Calm blueprint is only deployed after manual approval?
- A . Use runtime variables
- B . Integrate an approval system via external hooks
- C . Configure a delay task at the beginning of the blueprint
- D . Enable the approval policy in project settings
