Practice Free Mule-Arch-202 Exam Online Questions
What is a fundamental security measure for Mule applications to protect against data breaches and intrusions?
- A . Frequent application redesign to confuse potential attackers.
- B . Ensuring all data transmissions are encrypted.
- C . Using only proprietary protocols for data transmission.
- D . Limiting application functionality to reduce attack surfaces.
What is a critical practice for securing access to the Anypoint Platform control plane?
- A . Using default login credentials for ease of access.
- B . Implementing strong, role-based access control mechanisms.
- C . Limiting access to within corporate network only.
- D . Regularly changing the platform’s URL for security.
Refer to the exhibit.
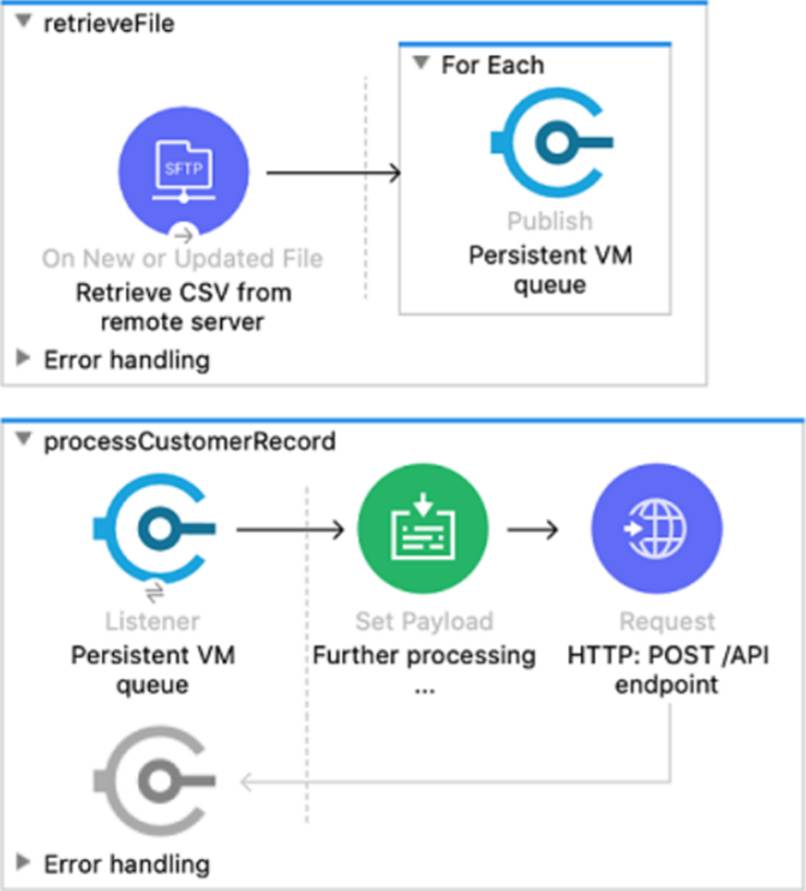
In this Mule application, the retrieveFile flow’s event source reads a CSV file from a remote SFTP server and then publishes each record in the CSV file to a VM queue.
The processCustomerRecord flow’s VM Listener receives messages from the same VM queue and then processes each message separately. This Mule application is deployed to multiple CloudHub workers with persistent queues enabled.
How are messages routed to the CloudHub workers as messages are received by the VM Listener?
- A . Each message is routed to the same CloudHub worker that retrieved the file, thereby binding all messages to only that one CloudHub worker
- B . Each message is duplicated to all of the CloudHub workers, thereby sharing each message with all the CloudHub workers
- C . Each message is routed to one of the available CloudHub workers in a non-deterministic, non-round-robin fashion, thereby approximately balancing messages among the CloudHub workers
- D . Each message is routed to one of the CloudHub workers in a deterministic round-robin fashion, thereby exactly balancing messages among the CloudHub workers
Refer to the exhibit.
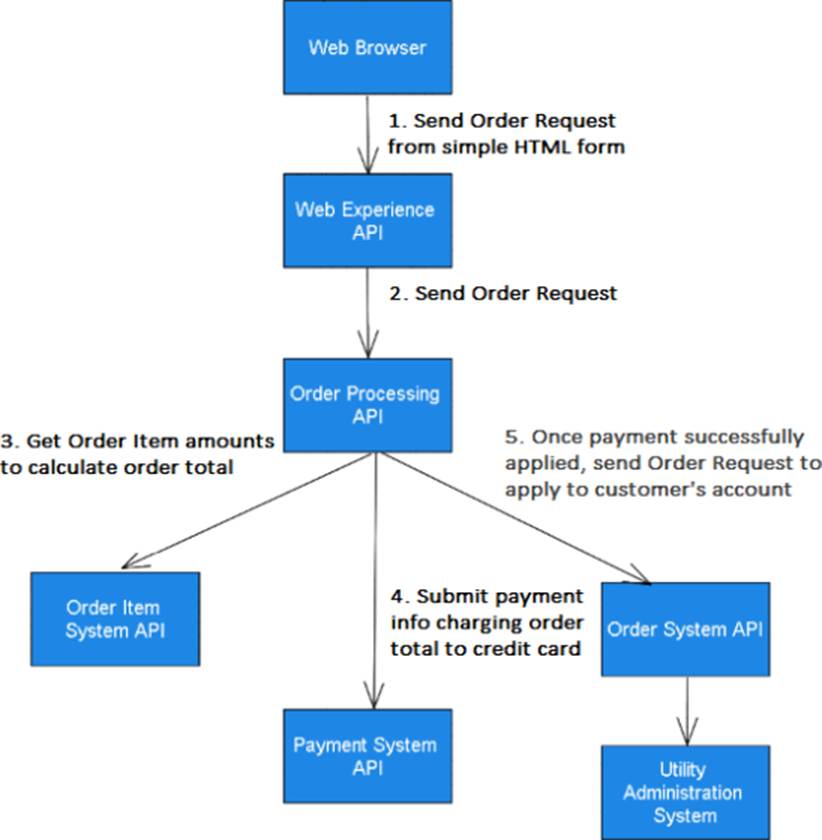
A telecommunications company receives orders (bill payments) from customers who submit a simple HTML form (no JavaScript or Web Assembly). Currently the process is synchronous and the customer is notified after everything is complete.
The requirement is that the customer is notified of payment (charging the customer’s credit card) through the response to the browser, but the customer can also be notified when the order is applied to the customer’s account at a later time. Due to an increase in customers, the system has been unable to handle the load and the solution has been experiencing performance and reliability issues.
Which request point could be replaced with an event-driven API using a JMS queue to help mitigate the performance issues, increase the fault tolerance, and meet the requirements?
- A . 5
- B . 4
- C . 1
- D . 2
Select the core router that would be used to process multiple routes concurrently in a Mule application.
- A . Scatter-Gather
- B . Round Robin
- C . First Successful
- D . All
Refer to the exhibit.
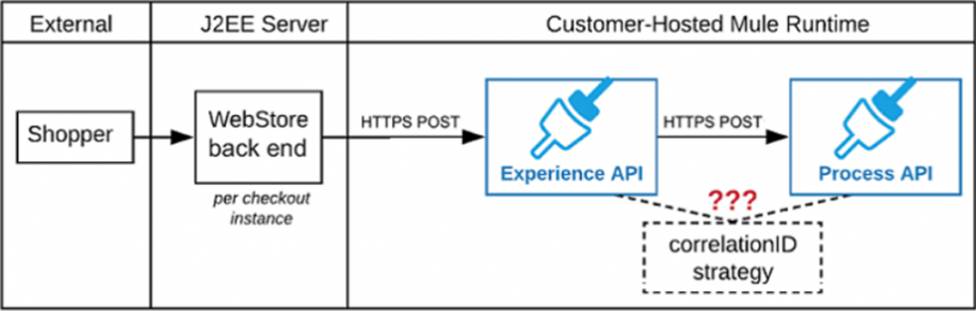
A shopping cart checkout process consists of a web store back end that sends a sequence of HTTPS POST requests to an Experience API, which in turn invokes a Process API using HTTPS. The web store back end executes in a Java EE application server. All API implementations are Mule applications executing in a customer-hosted Mule runtime.
End-to-end correlation of all HTTP requests and responses belonging to each checkout instance is required. This is to be done through a common correlation ID so that all log entries written by the web store back end, Experience API implementation, and Process API implementation include the same correlation ID for all requests and responses belonging to the same checkout instance.
What is the most efficient way (using the least amount of custom coding or configuration) for the web store back end and the implementations of the Experience API and Process API to participate in end-to-end correlation of the API invocations for each checkout instance?
- A . The Experience API implementation generates a correlation ID for each incoming HTTP request and passes it to the web store back end in the HTTP response, which includes it in all subsequent API invocations to the Experience API.
The Experience API implementation must also be coded to propagate the correlation ID to the Process API in a suitable HTTP request header. - B . The web store back end sends a correlation ID value in the HTTP request body in the way required by the Experience API.
The Experience API and Process API implementations must be coded to receive the custom correlation ID in the HTTP requests and propagate it in suitable HTTP request headers. - C . The web store back end, being a Java EE application, automatically uses the thread-local correlation ID generated by the Java EE application server and automatically transmits that to the Experience API using standard HTTP headers.
No special code or configuration is included in the web store back end, Experience API implementation, or Process API implementation to generate and manage the correlation ID. - D . The web store back end generates a new correlation ID value at the start of checkout and sets it on the X-Correlation-ID HTTP request header in each API invocation belonging to that checkout.
No special code or configuration is included in the Experience API or Process API implementations to generate and manage the correlation ID.
An automation engineer must write scripts to automate the steps of the API lifecycle, including steps to create, publish, deploy, and manage APIs and their implementations in Anypoint Platform.
Which Anypoint Platform feature can be most easily used to automate the execution of all these actions in scripts without needing to directly invoke the Anypoint Platform REST APIs?
- A . Mule Maven plugin
- B . Anypoint CLI
- C . Custom-developed Postman scripts
- D . GitHub actions
In a Mule application, a flow contains two JMS Consume operations that are used to connect to a JMS broker and consume messages from two JMS destinations. The Mule application then joins the two consumed JMS messages together.
The JMS broker does not implement high availability and periodically experiences scheduled outages of up to 10 minutes for routine maintenance.
How should the Mule flow be built so it can recover from the expected outages?
- A . Enclose the two JMS operations in a Try scope with an On Error Continue error handler
- B . Configure a reconnection strategy for the JMS connector
- C . Enclose the two JMS operations in an Until Successful scope
- D . Configure a transaction for the JMS connector
Refer to the exhibit.
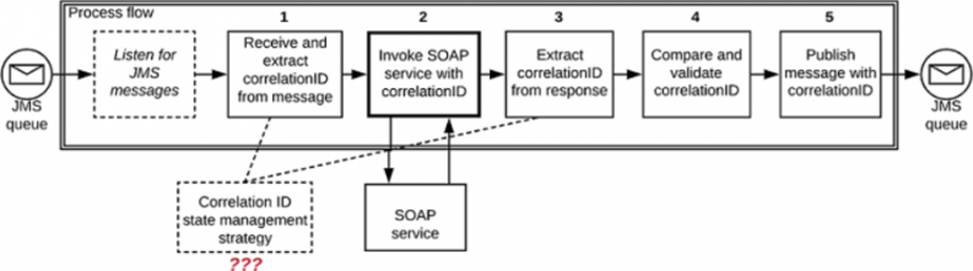
A Mule application is deployed to a multi-node Mule runtime cluster. The Mule application uses the Competing Consumers pattern among its cluster replicas to receive JMS messages from a JMS queue. To process each received JMS message, the following steps are performed in a flow.
Step 1: The JMS Correlation ID header is read from the received JMS message.
Step 2: The Mule application invokes an idempotent SOAP web service over HTTPS, passing the JMS Correlation ID as one parameter in the SOAP request.
Step 3: The response from the SOAP web service also returns the same JMS Correlation ID.
Step 4: The JMS Correlation ID received from the SOAP web service is validated to be identical to the JMS Correlation ID received in Step 1.
Step 5: The Mule application creates a response JMS message, setting the JMS Correlation ID message header to the validated JMS Correlation ID and publishes that message to a response JMS queue.
Where should the Mule application store the JMS Correlation ID values received in Step 1 and Step 3 so that the validation in Step 4 can be performed and the overall Mule application can be highly available, fault-tolerant, performant, and maintainable?
- A . The Correlation ID value in Step 1 should be stored in a persistent Object Store The Correlation ID value in Step 3 should be stored as Mule event variables or attributes
- B . Both Correlation ID values should be stored in a persistent Object Store
- C . Both Correlation ID values should be stored as Mule event variables or attributes
- D . Both Correlation ID values should be stored in a nonpersistent Object Store
How does the Scatter-Gather router benefit Mule application design?
- A . It simplifies transaction management.
- B . It collects responses from multiple routes and aggregates them.
- C . It guarantees the order of message processing.
- D . It routes each message to the first successful route only.
