Practice Free MLA-C01 Exam Online Questions
An ML engineer decides to use Amazon SageMaker AI automated model tuning (AMT) for hyperparameter optimization (HPO). The ML engineer requires a tuning strategy that uses regression to slowly and sequentially select the next set of hyperparameters based on previous runs. The strategy must work across small hyperparameter ranges.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A . Grid search
- B . Random search
- C . Bayesian optimization
- D . Hyperband
C
Explanation:
Amazon SageMaker Automated Model Tuning supports several hyperparameter search strategies. Bayesian optimization is explicitly designed to model the relationship between hyperparameters and objective metrics using regression techniques. Based on results from previous training jobs, Bayesian optimization predicts which hyperparameter combinations are most likely to improve model performance and evaluates those next.
AWS documentation highlights Bayesian optimization as the preferred strategy when the hyperparameter search space is small to medium and when training jobs are expensive. Because the algorithm learns from prior runs, it avoids wasting resources on unpromising configurations and converges efficiently.
Grid search exhaustively evaluates all combinations and becomes inefficient even with moderately sized search spaces. Random search does not use information from prior runs and is less efficient. Hyperband focuses on aggressive early stopping and resource allocation, not regression-based sequential selection.
Therefore, Option C is the correct and AWS-verified solution.
HOTSPOT
An ML engineer is working on an ML model to predict the prices of similarly sized homes. The model will base predictions on several features.
The ML engineer will use the following feature engineering techniques to estimate the prices of the homes:
• Feature splitting
• Logarithmic transformation
• One-hot encoding
• Standardized distribution
Select the correct feature engineering techniques for the following list of features. Each feature engineering technique should be selected one time or not at all (Select three.)
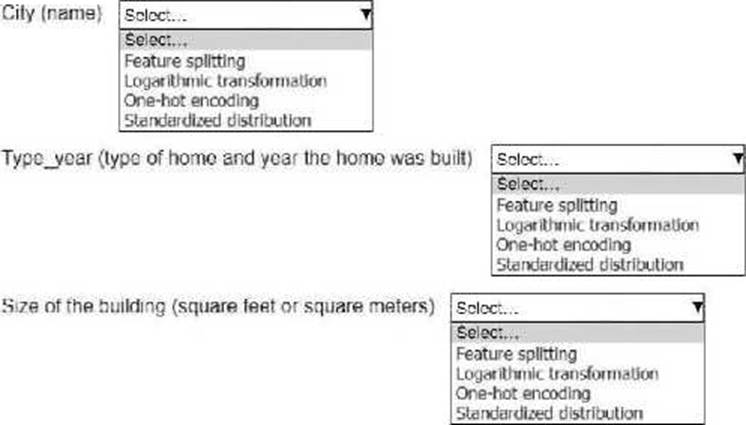
Explanation:
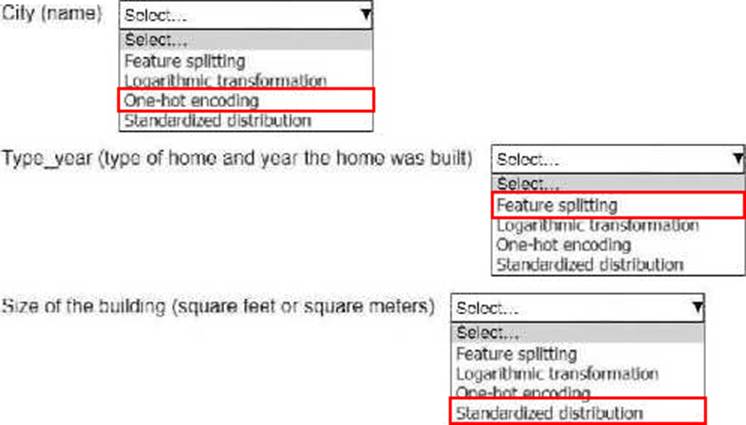
City (name): One-hot encoding
Type_year (type of home and year the home was built): Feature splitting
Size of the building (square feet or square meters): Standardized distribution
City (name): One-hot encoding
Why? The "City" is a categorical feature (non-numeric), so one-hot encoding is used to transform it into a numeric format. This encoding creates binary columns for each unique category (e.g., cities like "New York" or "Los Angeles"), which the model can interpret.
Type_year (type of home and year the home was built): Feature splitting
Why? "Type_year" combines two pieces of information into one column, which could confuse the model. Feature splitting separates this column into two distinct features: "Type of home" and "Year built," enabling the model to process each feature independently.
Size of the building (square feet or square meters): Standardized distribution
Why? Size is a continuous numerical variable, and standardization (scaling the feature to have a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1) ensures that the model treats it fairly compared to other features, avoiding bias from differences in feature scale.
By applying these feature engineering techniques, the ML engineer can ensure that the input data is correctly formatted and optimized for the model to make accurate predictions.
A company stores training data as a .csv file in an Amazon S3 bucket. The company must encrypt the data and must control which applications have access to the encryption key.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A . Create a new SSH access key and use the AWS Encryption CLI to encrypt the file.
- B . Create a new API key by using Amazon API Gateway and use it to encrypt the file.
- C . Create a new IAM role with permissions for kms: GenerateDataKey and use the role to encrypt the file.
- D . Create a new AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) key and use the AWS Encryption CLI with the KMS key to encrypt the file.
D
Explanation:
AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) is the recommended service for encryption and key access control. By creating a customer-managed KMS key, the company can define granular IAM policies that control which applications and roles can use the key.
The AWS Encryption CLI integrates directly with KMS and enables client-side encryption of files before storing them in Amazon S3. This approach ensures data is encrypted at rest and that only authorized principals can decrypt it.
SSH keys and API keys are not designed for data encryption. IAM roles alone do not create or manage encryption keys―they only grant permissions.
AWS documentation explicitly states that KMS customer-managed keys provide centralized key management, auditing, and access control.
Therefore, Option D is the correct and AWS-aligned solution.
