Practice Free MLA-C01 Exam Online Questions
Case Study
A company is building a web-based AI application by using Amazon SageMaker. The application will provide the following capabilities and features: ML experimentation, training, a central model registry, model deployment, and model monitoring.
The application must ensure secure and isolated use of training data during the ML lifecycle. The training data is stored in Amazon S3.
The company must implement a manual approval-based workflow to ensure that only approved models can be deployed to production endpoints.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
- A . Use SageMaker Experiments to facilitate the approval process during model registration.
- B . Use SageMaker ML Lineage Tracking on the central model registry. Create tracking entities for the approval process.
- C . Use SageMaker Model Monitor to evaluate the performance of the model and to manage the
approval. - D . Use SageMaker Pipelines. When a model version is registered, use the AWS SDK to change the approval status to "Approved."
D
Explanation:
To implement a manual approval-based workflow ensuring that only approved models are deployed to production endpoints, Amazon SageMaker provides integrated tools such as SageMaker Pipelines and the SageMaker Model Registry.
SageMaker Pipelines is a robust service for building, automating, and managing end-to-end machine learning workflows. It facilitates the orchestration of various steps in the ML lifecycle, including data preprocessing, model training, evaluation, and deployment. By integrating with the SageMaker Model Registry, it enables seamless tracking and management of model versions and their approval statuses.
Implementation Steps:
Define the Pipeline:
Create a SageMaker Pipeline encompassing steps for data preprocessing, model training, evaluation, and registration of the model in the Model Registry.
Incorporate a Condition Step to assess model performance metrics. If the model meets predefined criteria, proceed to the next step; otherwise, halt the process.
Register the Model:
Utilize the RegisterModel step to add the trained model to the Model Registry.
Set the ModelApprovalStatus parameter to PendingManualApproval during registration. This status indicates that the model awaits manual review before deployment.
Manual Approval Process:
Notify the designated approver upon model registration. This can be achieved by integrating Amazon EventBridge to monitor registration events and trigger notifications via AWS Lambda functions.
The approver reviews the model’s performance and, if satisfactory, updates the model’s status to Approved using the AWS SDK or through the SageMaker Studio interface.
Deploy the Approved Model:
Configure the pipeline to automatically deploy models with an Approved status to the production endpoint. This can be managed by adding deployment steps conditioned on the model’s approval status.
Advantages of This Approach:
Automated Workflow: SageMaker Pipelines streamline the ML workflow, reducing manual interventions and potential errors.
Governance and Compliance: The manual approval step ensures that only thoroughly evaluated models are deployed, aligning with organizational standards.
Scalability: The solution supports complex ML workflows, making it adaptable to various project requirements.
By implementing this solution, the company can establish a controlled and efficient process for deploying models, ensuring that only approved versions reach production environments.
Reference: Automate the machine learning model approval process with Amazon SageMaker Model Registry and Amazon SageMaker Pipelines
Update the Approval Status of a Model – Amazon SageMaker
A company is developing an application that reads animal descriptions from user prompts and generates images based on the information in the prompts. The application reads a message from an Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) queue. Then the application uses Amazon Titan Image Generator on Amazon Bedrock to generate an image based on the information in the message. Finally, the application removes the message from SQS queue.
Which IAM permissions should the company assign to the application’s IAM role? (Select TWO.)
- A . Allow the bedrock:InvokeModel action for the Amazon Titan Image Generator resource.
- B . Allow the bedrock:Get* action for the Amazon Titan Image Generator resource.
- C . Allow the sqs:ReceiveMessage action and the sqs:DeleteMessage action for the SQS queue resource.
- D . Allow the sqs:GetQueueAttributes action and the sqs:DeleteMessage action for the SQS queue resource.
- E . Allow the sagemaker:PutRecord* action for the Amazon Titan Image Generator resource.
A,C
Explanation:
To generate images, the application must invoke a foundation model hosted on Amazon Bedrock. Invoking the Amazon Titan Image Generator requires the bedrock:InvokeModel permission. Read-only permissions such as bedrock:Get* do not allow inference execution and are insufficient.
The application also interacts with Amazon Simple Queue Service. To process messages, the
application must be able to receive messages from the queue and delete them after successful processing. These actions require sqs:ReceiveMessage and sqs:DeleteMessage.
sqs:GetQueueAttributes alone does not allow message consumption. SageMaker permissions are unrelated because Bedrock is a separate service.
Therefore, permissions to invoke the model and receive/delete SQS messages are required.
A company is using an Amazon S3 bucket to collect data that will be used for ML workflows. The company needs to use AWS Glue DataBrew to clean and normalize the data.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A . Create a DataBrew dataset by using the S3 path. Clean and normalize the data by using a DataBrew profile job.
- B . Create a DataBrew dataset by using the S3 path. Clean and normalize the data by using a DataBrew recipe job.
- C . Create a DataBrew dataset by using a JDBC driver to connect to the S3 bucket. Use a profile job.
- D . Create a DataBrew dataset by using a JDBC driver to connect to the S3 bucket. Use a recipe job.
B
Explanation:
AWS Glue DataBrew supports datasets sourced directly from Amazon S3 paths. To clean and normalize data, AWS documentation specifies using DataBrew recipes, which define transformation steps such as standardization, deduplication, and formatting.
A profile job is used only for data analysis and statistics generation, not for transformation. A recipe job applies actual transformations to the data and writes the output to Amazon S3.
JDBC connections are used for relational databases, not S3 buckets.
Therefore, options C and D are invalid.
AWS clearly documents that the correct workflow is:
Create a DataBrew dataset from an S3 path
Define transformations using a recipe
Run a recipe job to produce cleaned data
Thus, Option B is the correct and AWS-aligned answer.
A company has a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) application that uses a vector database to store embeddings of documents. The company must migrate the application to AWS and must implement a solution that provides semantic search of text files. The company has already migrated the text repository to an Amazon S3 bucket.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A . Use an AWS Batch job to process the files and generate embeddings. Use AWS Glue to store the embeddings. Use SQL queries to perform the semantic searches.
- B . Use a custom Amazon SageMaker notebook to run a custom script to generate embeddings. Use SageMaker Feature Store to store the embeddings. Use SQL queries to perform the semantic searches.
- C . Use the Amazon Kendra S3 connector to ingest the documents from the S3 bucket into Amazon Kendra. Query Amazon Kendra to perform the semantic searches.
- D . Use an Amazon Textract asynchronous job to ingest the documents from the S3 bucket. Query Amazon Textract to perform the semantic searches.
C
Explanation:
Amazon Kendra is an AI-powered search service designed for semantic search use cases. It allows ingestion of documents from an Amazon S3 bucket using the Amazon Kendra S3 connector. Once the documents are ingested, Kendra enables semantic searches with its built-in capabilities, removing the need to manually generate embeddings or manage a vector database. This approach is efficient, requires minimal operational effort, and meets the requirements for a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) application.
A company is building an enterprise AI platform. The company must catalog models for production, manage model versions, and associate metadata such as training metrics with models. The company needs to eliminate the burden of managing different versions of models.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A . Use the Amazon SageMaker Model Registry to catalog the models. Create unique tags for each model version. Create key-value pairs to maintain associated metadata.
- B . Use the Amazon SageMaker Model Registry to catalog the models. Create model groups for each model to manage the model versions and to maintain associated metadata.
- C . Create a separate Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) repository for each model. Use the repositories to catalog the models and to manage model versions and associated metadata.
- D . Create a separate Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) repository for each model.
Create unique tags for each model version. Create key-value pairs to maintain associated metadata.
B
Explanation:
AWS enterprise ML best practices recommend using Amazon SageMaker Model Registry to manage models throughout their lifecycle. The Model Registry is designed specifically to catalog models, track versions, and associate metadata such as training metrics, approval status, and deployment history.
Model Registry introduces the concept of model groups, which act as logical containers for different versions of the same model. Each model version within a group automatically inherits versioning, metadata tracking, and governance controls. This eliminates the operational burden of manually managing model versions and ensures consistent lineage and traceability across development, testing, and production environments.
Option A is less optimal because manually tagging model versions increases operational complexity and does not take full advantage of the built-in version management features provided by model groups.
Options C and D are incorrect because Amazon ECR is a container image repository, not a model governance or lifecycle management service. Using ECR to manage ML model versions would require custom tooling and manual metadata handling, significantly increasing operational overhead.
By using model groups within SageMaker Model Registry, the company gains a centralized, scalable, and AWS-native solution for enterprise AI governance. This approach directly aligns with AWS documentation for managing model catalogs, version control, and metadata association while minimizing manual intervention.
A company is building a deep learning model on Amazon SageMaker. The company uses a large amount of data as the training dataset. The company needs to optimize the model’s hyperparameters to minimize the loss function on the validation dataset.
Which hyperparameter tuning strategy will accomplish this goal with the LEAST computation time?
- A . Hyperbaric!
- B . Grid search
- C . Bayesian optimization
- D . Random search
A
Explanation:
Hyperband is a hyperparameter tuning strategy designed to minimize computation time by adaptively allocating resources to promising configurations and terminating underperforming ones early. It efficiently balances exploration and exploitation, making it ideal for large datasets and deep learning models where training can be computationally expensive.
An ML engineer needs to use an ML model to predict the price of apartments in a specific location.
Which metric should the ML engineer use to evaluate the model’s performance?
- A . Accuracy
- B . Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC)
- C . F1 score
- D . Mean absolute error (MAE)
D
Explanation:
Predicting apartment prices is a regression problem, where the target variable is continuous. AWS documentation states that classification metrics such as accuracy, AUC, and F1 score are not appropriate for regression tasks.
Mean Absolute Error (MAE) measures the average absolute difference between predicted values and actual values. MAE is easy to interpret because it is expressed in the same units as the target variable (for example, dollars), making it especially useful for business-facing problems like price prediction.
AWS best practices recommend MAE for evaluating regression models when understanding average prediction error magnitude is important and when robustness to outliers is desired.
Therefore, Option D is the correct and AWS-aligned answer.
An ML engineer develops a neural network model to predict whether customers will continue to subscribe to a service. The model performs well on training data. However, the accuracy of the model decreases significantly on evaluation data.
The ML engineer must resolve the model performance issue.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
- A . Penalize large weights by using L1 or L2 regularization.
- B . Remove dropout layers from the neural network.
- C . Train the model for longer by increasing the number of epochs.
- D . Capture complex patterns by increasing the number of layers.
A
Explanation:
This scenario clearly describes an overfitting problem. The neural network performs well on training data but fails to generalize to evaluation data. According to AWS Machine Learning and deep learning best practices, overfitting occurs when a model learns noise or overly specific patterns in the training data instead of generalizable relationships.
L1 and L2 regularization are well-established techniques to combat overfitting. They work by penalizing large weight values during optimization, effectively constraining the model’s complexity. L1 regularization encourages sparsity, while L2 regularization (weight decay) smooths the weight distribution. AWS documentation recommends regularization as a primary method for improving generalization when a model shows a large gap between training and evaluation performance.
Option B is incorrect because removing dropout layers would increase overfitting, not reduce it.
Dropout is itself a regularization technique.
Option C would likely worsen overfitting, as training for more epochs allows the model to memorize the training data even further.
Option D increases model complexity, which again exacerbates overfitting rather than resolving it.
Therefore, penalizing large weights using L1 or L2 regularization is the correct solution.
A company has trained and deployed an ML model by using Amazon SageMaker. The company needs to implement a solution to record and monitor all the API call events for the SageMaker endpoint. The solution also must provide a notification when the number of API call events breaches a threshold.
Use SageMaker Debugger to track the inferences and to report metrics. Create a custom rule to provide a notification when the threshold is breached.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A . Use SageMaker Debugger to track the inferences and to report metrics. Create a custom rule to provide a notification when the threshold is breached.
- B . Use SageMaker Debugger to track the inferences and to report metrics. Use the tensor_variance built-in rule to provide a notification when the threshold is breached.
- C . Log all the endpoint invocation API events by using AWS CloudTrail. Use an Amazon CloudWatch dashboard for monitoring. Set up a CloudWatch alarm to provide notification when the threshold is breached.
- D . Add the Invocations metric to an Amazon CloudWatch dashboard for monitoring. Set up a CloudWatch alarm to provide notification when the threshold is breached.
D
Explanation:
Amazon SageMaker automatically tracks the Invocations metric, which represents the number of API calls made to the endpoint, in Amazon CloudWatch. By adding this metric to a CloudWatch dashboard, you can monitor the endpoint’s activity in real-time. Setting up a CloudWatch alarm allows the system to send notifications whenever the API call events exceed the defined threshold, meeting both the monitoring and notification requirements efficiently.
HOTSPOT
A company has built more than 50 models and deployed the models on Amazon SageMaker Al as real-time inference endpoints. The company needs to reduce the costs of the SageMaker Al inference endpoints. The company used the same ML framework to build the models. The company’s customers require low-latency access to the models.
Select and order the correct steps from the following list to reduce the cost of inference and keep latency low. Select each step one time or not at all. (Select and order FIVE.)
・ Create an endpoint configuration that Reference a multi-model container.
. Create a SageMaker Al model with multi-model endpoints enabled.
. Deploy a real-time inference endpoint by using the endpoint configuration.
. Deploy a serverless inference endpoint configuration by using the endpoint configuration.
・ Spread the existing models to multiple different Amazon S3 bucket paths.
. Upload the existing models to the same Amazon S3 bucket path.
. Update the models to use the new endpoint ID. Pass the model IDs to the new endpoint.
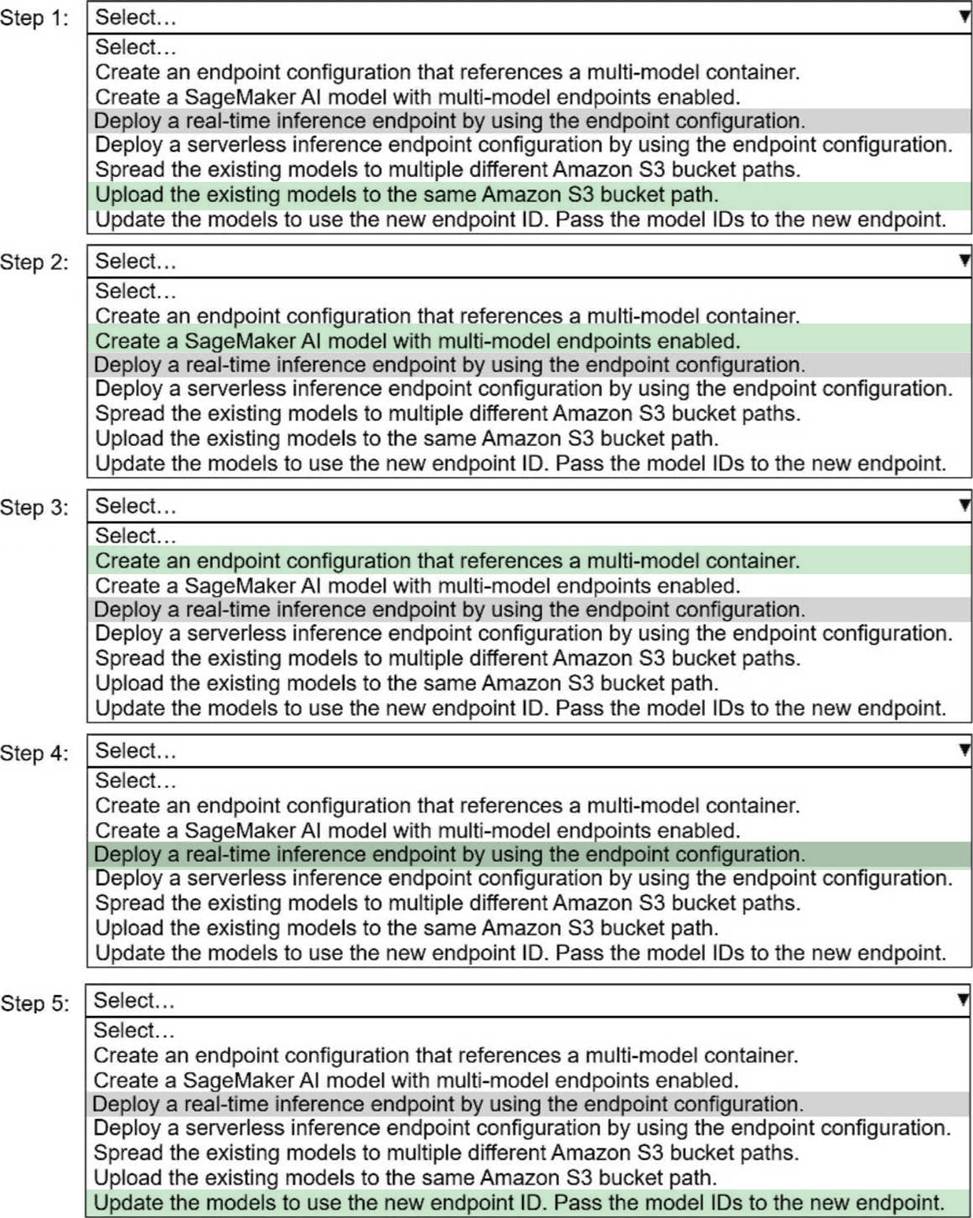
Explanation:
Step 1
Upload the existing models to the same Amazon S3 bucket path.
Multi-model endpoints require all models to be stored under a single S3 prefix so SageMaker can dynamically load them on demand.
Step 2
Create a SageMaker AI model with multi-model endpoints enabled.
This creates a SageMaker model resource that uses a multi-modelCcapable container (for example, XGBoost, PyTorch, or TensorFlow MME-compatible containers).
Step 3
Create an endpoint configuration that Reference a multi-model container.
The endpoint configuration defines:
Instance type
Initial instance count
The multi-model container reference
Step 4
Deploy a real-time inference endpoint by using the endpoint configuration.
Real-time endpoints ensure low-latency inference, which is a strict customer requirement.
Step 5
Update the models to use the new endpoint ID. Pass the model IDs to the new endpoint.
Each inference request specifies a model ID so SageMaker knows which model to load from S3.
