Practice Free MB-820 Exam Online Questions
You create a page with the PageType property set to RoleCenter.
You navigate through the different sections of the page.
You need to add functionalities to the page.
What should you do?
- A . Define actions in the area (reporting) before actions in the area (creation).
- B . Define the navigation menu in the area(processing).
- C . Define the navigation bar in the area (embedding).
- D . Add a source table on the Role Center page.
C
Explanation:
When creating a page with the PageType property set to RoleCenter in Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, it’s essential to organize the functionalities and actions in a manner that enhances user experience and efficiency. The best practice is to define actions in the area (reporting) before actions in the area (creation) (A). This organization allows users to access reporting and analytical features quickly, which are commonly used in Role Centers for overview and insight purposes, before moving on to creation or transactional tasks. This logical flow aligns with typical user workflows, where analysis and review precede the creation of new records or transactions. The other options, such as defining the navigation menu in the area(processing) (B), defining the navigation bar in the area (embedding) (C), or adding a source table on the Role Center page (D), do not directly address the need to add functionalities to the Role Center page in a user-friendly manner.
You need to create the access modifier for IssueTotal.
Which variable declaration should you use?
- A . Protected vat IssueTotal: Decimal
- B . Internal var IssueTotal: Decimal
- C . Public var IssueTotal: Decimal
- D . Local var IssueTotal: Decimal
- E . Var IssueTotal; Decimal
B
Explanation:
In Business Central development using AL (the language for Business Central extensions), the use of access modifiers defines how variables and procedures are accessed within and outside of an object or codeunit.
Access Modifiers in AL:
Public: A public variable can be accessed from any object or codeunit within the same module or extension.
Protected: This restricts access to the current object and objects that inherit from the current object. However, in AL (at least in versions used for Business Central), the Protected access modifier is used with methods but not variables.
Internal: This modifier restricts the visibility to the current extension. This means that variables or methods declared as internal can only be accessed from within the same extension. This is appropriate when you want to provide functionality that is shared within the extension but not exposed externally.
Local: This restricts the variable or method to the current object or method where it is declared. It cannot be accessed from anywhere else, even within the same extension. Scenario Justification:
In the scenario for Contoso, Ltd., IssueTotal is a global variable in the ISSUE BASE extension, and the ISSUE EXT extension needs to access it. Therefore, the variable cannot be declared as Local, because this would restrict access to just the current object (or method).
Using Public would expose the variable outside of the extension, which is unnecessary because you only want other parts of the extension (specifically the ISSUE EXT extension) to have access.
The best choice in this case is Internal because it restricts access to the variable to within the same extension, which includes the base extension and any dependent extensions like ISSUE EXT. It strikes
the right balance between visibility and encapsulation.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
Reference: Access Modifiers in AL: Microsoft’s documentation on AL provides the details on access modifiers, where it is specified that internal variables can be accessed within the extension, and the public
variable is accessible across all extensions 【 source: Microsoft Learn on AL Programming 】 .
Best Practices for AL Development: Business Central development best practices suggest keeping variables internal unless they need to be accessed outside of the current extension 【 source: Microsoft Learn on AL development guidelines 】 .
DRAG DROP
A company is implementing Business Central.
The company has the following requirements for a report:
• The report must be loaded for users in a specific location only.
• Data entered in the request page must be validated before any further processing.
• A filter must be defined for users based on the Department field defined in user setup.
You need to implement the given requirements.
Which triggers should you use? To answer, move the appropriate triggers to the correct requirements. You may use each trigger once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to move the split bar between panes or scroll to view content. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Explanation:
Load the report for users in a specific location: OnInitReport
Validate data before processing: OnPreReport
Define filter based on Department field: OnPreDataItem
The requirements for the report are:
The report must be loaded for users in a specific location only.
Data entered in the request page must be validated before any further processing.
A filter must be defined for users based on the Department field defined in user setup.
Trigger Matching:
The report must be loaded for users in a specific location only.
The correct trigger for loading the report is OnInitReport.
This trigger runs when the report is initialized, and you can use it to define user-specific loading conditions, like location-based filtering.
Data entered in the request page must be validated before any further processing.
The correct trigger for validation before processing is OnPreReport.
This trigger occurs before the report is run and can be used for data validation before further processing begins.
A filter must be defined for users based on the Department field defined in user setup.
The correct trigger to define filters is OnPreDataItem.
This trigger occurs before data item processing begins and is used to apply filters such as those based on the Department field in the user setup.
A company has a Business Central online environment.
You need to create an HTTP GET request that connects to an external REST service.
Which solution should you use?
- A . HttpContent data type variable
- B . Codeunit 1299 "Web Request Helper"
- C . Codeunit S459 "JSON Management"
- D . Codeunit 1297 "Http Web Request Mgt”
- E . HttpClient data type variable
E
Explanation:
To create an HTTP GET request that connects to an external REST service in a Business Central online environment, the solution to use is the HttpClient data type variable (E). The HttpClient data type in AL language is designed for sending HTTP requests and receiving HTTP responses from a resource identified by a URI. This makes it the ideal choice for interfacing with external REST services, as it provides the necessary methods and properties to configure and execute HTTP GET requests, handle the responses, and process the data returned by the REST service. This approach is more direct and flexible compared to using specific codeunits like "Web Request Helper" (B) or "Http Web Request Mgt" (D), which might not provide the same level of control or specificity needed for RESTful interactions.
You have a decimal variable named AmountlCY.
You need to round up the variable to four decimal places.
Which result value should you use?
- A . Result: = Round (AmountLCY,A. ‘>"}:
- B . Result: = Round {AmountLCY. 0.0001. =’);
- C . Result: = Round (AmountLCY. 0.0001. ‘<‘):
- D . Result: = Round (AmountLCY, 0.0001, >’);
B
Explanation:
To round up a decimal variable to four decimal places in Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, you should use the Round function with specific parameters. The correct formula is Result: = Round (AmountLCY, 0.0001, ‘=’) (B). This function rounds the AmountLCY variable to the nearest value based on the second parameter, which is 0.0001 in this case, representing four decimal places. The third parameter, ‘=’, specifies that the function should round to the nearest value, which effectively rounds up the value when it’s halfway between two possible rounded values. This approach ensures that the AmountLCY variable is accurately rounded to four decimal places, which is essential for financial calculations and reporting to maintain precision.
HOTSPOT
A company plans to integrate tests with its build pipelines.
The company has two Docket sandbox environments: SandboxA and SandboxB.
You observe the following:
• SandboxA is configured without the Test Toolkit installed.
• SandboxB must be configured from scratch. The Test Toolkit must be installed in SandboxB during configuration.
You need to configure the sandbox environments.
How should you complete the cmdlets? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
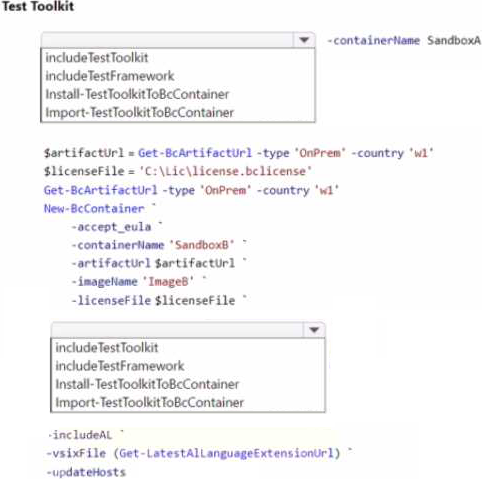
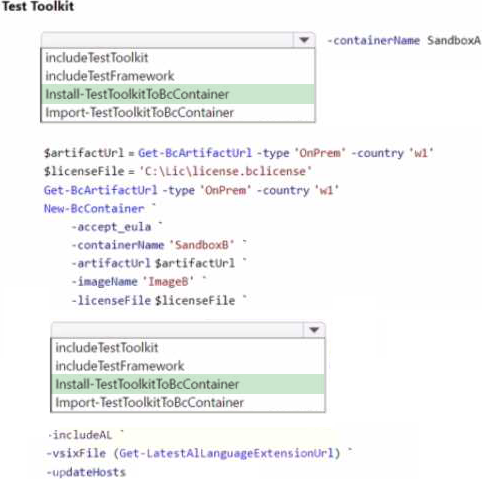
Explanation:
Based on the PowerShell script snippet you’ve provided and the scenario described, you need to configure Docker sandbox environments for a company with specific requirements for Test Toolkit installations.
For SandboxA, since it is configured without the Test Toolkit installed, you would typically use the PowerShell cmdlet Install-TestToolkitToBcContainer to install the Test Toolkit into the Business Central Docker container.
For SandboxB, which must be configured from scratch with the Test Toolkit installed during configuration, you would include the Test Toolkit as part of the New-BcContainer script block that creates the container.
The relevant cmdlets and parameters for SandboxB would include:
-includeTestToolkit: This parameter ensures that the Test Toolkit is included during the creation of the new container.
Given the limited context from the image, here’s how you should complete the cmdlets for SandboxB:
Add -includeTestToolkit in the New-BcContainer script to ensure the Test Toolkit is installed when creating SandboxB.
Since you are setting up SandboxB from scratch, you don’t need to run Install-TestToolkitToBcContainer separately as the toolkit will be included at the time of container creation with the -includeTestToolkit parameter.
For the New-BcContainer cmdlet, you would fill in the placeholders with the appropriate values for artifactUrl, imageName, and licenseFile if they are required for your specific setup.
A company uses Business Central.
You plan to help users through the installation process by using Assisted Setup.
You need to create a wizard page.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents a complete solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A . Set the PageType property to NavigatePage.
- B . For each step needed in the guide, add a group0 control to the root-level of the layout > area (Content) control
- C . Set the PageType property to Worksheet
- D . For each step needed in the guide, add a repeater!) control to the root-level of the layout > area (Content) control.
A, B
Explanation:
A: In Business Central, wizard pages are created using the NavigatePage type because it allows step-by-step navigation, which is perfect for wizard-like user experiences.
B: The group control organizes the content for each step in the guide, and it’s essential to add these controls to the layout’s Content area for each step of the wizard.
C: Worksheet is used for pages designed to handle larger datasets, not for wizard or step-by-step flows.
D: Repeater controls are used for displaying multiple records, not for guiding users through steps, so it’s incorrect for this scenario.
For more information, you can refer to Assisted Setup in Business Central.
A company uses Business Central.
The company plans to use the AL object model in Business Central to extend the Base Application.
You need to extend the objects.
Which two objects can you extend? Each correct answer presents a complete solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A . Codeunit
- B . Report
- C . Query
- D . API page
- E . Enum
B, E
Explanation:
You need to access the RoomsAPI API from the canvas app.
What should you do?
- A . Use the default API configuration in Business Central
- B . Enable the APIs for the Business Central online environment.
- C . Open the Web Services page and publish the RoomsAPI page as a web service.
- D . Include in the extension a codeunit of type Install that publishes RoomsAPI.
D
Explanation:
API Publishing for Extensions:
In Business Central, when creating custom APIs like RoomsAPI, it is important to ensure that they are automatically published during the installation or upgrade of the extension.
To achieve this, you can include a codeunit of type Install in the extension that explicitly publishes the custom API (RoomsAPI) as a web service. This ensures that it is available for use immediately after the extension is deployed without requiring manual intervention. Codeunit Type:
A codeunit of type Install runs when the extension is installed or upgraded. This type of codeunit can be used to perform setup tasks such as publishing web services or APIs like RoomsAPI.
Why Not Other Options?
Option A (default API configuration): This would not automatically publish the RoomsAPI. Default APIs do not cover custom APIs.
Option B (enable APIs for the environment): Enabling APIs in Business Central allows the standard APIs to be used, but custom APIs still need to be manually published.
Option C (publish via Web Services page): This would work but requires manual intervention to publish RoomsAPI, which does not fulfill the requirement of automatic publishing during installation.
DRAG DROP Documentation:
Publishing APIs in Extensions
Codeunit Types in Business Central
A company uses Business Central.
The company has sales orders that have a different location in the header than in the customer’s card. You plan to add a check on sales order posting.
The check must meet the following requirements.
• Sales Order must have the same Location Code as the Location Code set up on the customer’s card.
• Must not be run in preview mode.
• Must be run even if the user is only shipping items and not invoicing.
You create an event subscription for codeunit 80 "Sales-Post"
You need to identify which event to subscribe to
Which event should you identify?
A)
![]()
B)
![]()
C)
![]()
D)
![]()
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
A
Explanation:
This event occurs before posting a sales document.
PreviewMode is available in the parameters, which allows checking whether the process is being run in preview mode.
This event is typically used for sales order posting and can be used for both shipping and invoicing.
This event matches the requirements because:
You can check if PreviewMode is false.
It can run for both shipping and invoicing.
