Practice Free JN0-664 Exam Online Questions
168.1.1:455:10.1.1.0/24
You are examining an L3VPN route that includes the information shown in the exhibit
Which statement is correct in this scenario?
- A . The information shows a Type 1 route distinguisher.
- B . The information shows a Type 0 route distinguisher
- C . The information shows a Type 2 route distinguisher.
- D . The information shows a route target
A
Explanation:
The information shows a Type 0 route distinguisher, which is one of the three types of route distinguishers defined by RFC 4364. A route distinguisher is a 64-bit value that is prepended to an IPv4 address to create a VPN-IPv4 address, which is unique within a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) table. A Type 0 route distinguisher has two fields: an administrator subfield (2 bytes) and an assigned number subfield (6 bytes). The administrator subfield can be an AS number or an IP address, and the assigned number subfield can be any value assigned by the administrator. In this example, the administrator subfield is 65530 (an AS number) and the assigned number subfield is 1.
168.1.1:455:10.1.1.0/24
You are examining an L3VPN route that includes the information shown in the exhibit
Which statement is correct in this scenario?
- A . The information shows a Type 1 route distinguisher.
- B . The information shows a Type 0 route distinguisher
- C . The information shows a Type 2 route distinguisher.
- D . The information shows a route target
A
Explanation:
The information shows a Type 0 route distinguisher, which is one of the three types of route distinguishers defined by RFC 4364. A route distinguisher is a 64-bit value that is prepended to an IPv4 address to create a VPN-IPv4 address, which is unique within a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) table. A Type 0 route distinguisher has two fields: an administrator subfield (2 bytes) and an assigned number subfield (6 bytes). The administrator subfield can be an AS number or an IP address, and the assigned number subfield can be any value assigned by the administrator. In this example, the administrator subfield is 65530 (an AS number) and the assigned number subfield is 1.
Exhibit
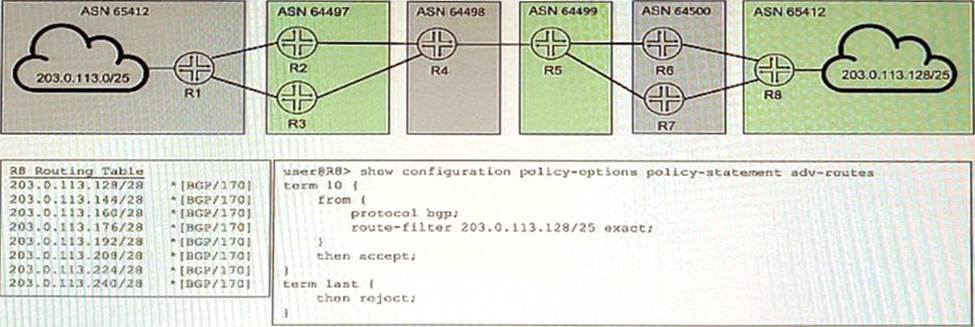
You are attempting to summarize routes from the 203.0.113.128/25 IP block on R8 to AS 64500. You implement the export policy shown in the exhibit and all routes from the routing table stop being advertised.
In this scenario, which two steps would you take to summarize the route in BGP? (Choose two.)
- A . Remove the from protocol bgp command from the export policy.
- B . Add the set protocols bgp family inet unicast add-path command to allow additional routes to the RIB tables.
- C . Add the set routing-options static route 203.0.113.123/25 discard command.
- D . Replace exact in the export policy with orlonger.
C,D
Explanation:
To summarize routes from the 203.0.113.128/25 IP block on R8 to AS 64500, you need to do the following:
✑ Add the set routing-options static route 203.0.113.128/25 discard command. This creates a static route for the summary prefix and discards any traffic destined to it. This is necessary because BGP can only advertise routes that are present in the routing table.
✑ Replace exact in the export policy with orlonger. This allows R8 to match and advertise any route that is equal or more specific than the summary prefix. The exact term only matches routes that are exactly equal to the summary prefix, which is not present in the routing table.
You must alter class-of-service values in packets on the outbound interface of an edge router.
In this scenario, which CoS component allows you to accomplish this task?
- A . output policer
- B . scheduler
- C . rewrite rules
- D . forwarding classes
C
Explanation:
Class of Service (CoS) in networking is used to manage traffic by classifying, scheduling, and sometimes modifying packets to ensure network performance and Quality of Service (QoS). Different CoS components are used to achieve these goals. Let’s analyze each option to determine which CoS component allows you to alter class-of-service values on the outbound interface of an edge router.
You are configuring a Layer 3 VPN between two sites. You are configuring the vrf-target target :
65100:100 statement in your routing instance.
In this scenario, which two statements describe the vrf-target configuration? (Choose two.)
- A . This value is used to identify BGP routes learned from the local CE device.
- B . This value is used to identify BGP routes learned from the remote PE device.
- C . This value is used to add a target community to BGP routes advertised to the local CE device.
- D . This value is used to add a target community to BGP routes advertised to the remote PE device.
BD
Explanation:
The `vrf-target` statement in a Layer 3 VPN configuration is used to control the import and export of VPN routes by attaching a target community to the routes. This helps in defining which VPN routes should be imported into or exported from a particular VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) instance.
You are configuring a Layer 3 VPN between two sites. You are configuring the vrf-target target :
65100:100 statement in your routing instance.
In this scenario, which two statements describe the vrf-target configuration? (Choose two.)
- A . This value is used to identify BGP routes learned from the local CE device.
- B . This value is used to identify BGP routes learned from the remote PE device.
- C . This value is used to add a target community to BGP routes advertised to the local CE device.
- D . This value is used to add a target community to BGP routes advertised to the remote PE device.
BD
Explanation:
The `vrf-target` statement in a Layer 3 VPN configuration is used to control the import and export of VPN routes by attaching a target community to the routes. This helps in defining which VPN routes should be imported into or exported from a particular VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) instance.
