Practice Free JN0-460 Exam Online Questions
Click the Exhibit button.
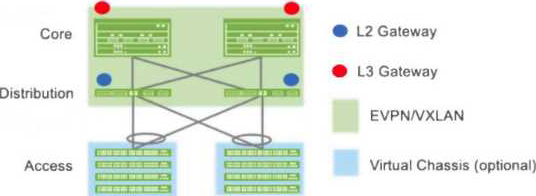
Which campus fabric architecture is shown in the exhibit?
- A . core-distribution C edge-routed bridging (ERB)
- B . 5-stage IP Clos
- C . 3-stage IP Clos
- D . core-distribution C centrally-routed bridging (CRB)
D
Explanation:
The exhibit shows:
L2 gateways (blue dots) positioned at the distribution layer.
L3 gateways (red dots) positioned at the core layer.
EVPN/VXLAN providing fabric connectivity between layers.
Access switches forwarding traffic into the fabric without acting as gateways.
This directly maps to the centrally-routed bridging (CRB) model, where:
Bridging occurs at the access/distribution layer.
Routing (L3 gateway) occurs centrally at the core layer.
“In the core-distribution CRB model, Layer 2 gateways are deployed at the distribution switches, and Layer 3 gateways are deployed centrally at the core switches.”
Option A (ERB) is incorrect because ERB places the L3 gateway at the edge/access. Option B (5-stage IP Clos) is incorrect ― that topology has a leaf/spine architecture, not core/distribution.
Option C (3-stage IP Clos) is incorrect ― that eliminates the distribution layer.
Option D (CRB) is correct, matching the diagram exactly.
Reference: Juniper Mist AI for Wired C Campus Fabric Architecture Guide
Juniper Validated Design C Campus Fabric EVPN-VXLAN Deployment Models Junos OS EVPN Campus Deployment Examples
Which routing protocol does EVPN utilize for the control plane?
- A . VXLAN
- B . IS-IS
- C . OSPF
- D . MP-BGP
What are two insights that Mist Wired can provide for third party devices? (Choose two)
- A . Inactive Wired VLANs
- B . Security Compliance
- C . Power Compliance
- D . Firmware Compliance
Which statement is correct about a 3-stage campus fabric IP Clos?
- A . The distribution layer is connected to the access layer.
- B . The distribution layer is connected to the core layer.
- C . The core layer is connected to the access layer.
- D . The core layer devices are connected to each other.
C
Explanation:
Juniper’s official Campus Fabric IP Clos design for Mist Wired Assurance defines that the 3-stage IP Clos topology eliminates the traditional distribution layer entirely. This architecture is intended for smaller campus environments that do not need an intermediate distribution layer between the access and core.
“Juniper’s Wired Assurance supports 3-Stage and 5-Stage IP Clos deployments. The 3-Stage IP Clos is targeted towards deployments that do not require a Distribution Layer and have smaller scale requirements.”
Because the distribution layer is not present, the only hierarchical connection in a 3-stage campus fabric is between the core and access layers. Traffic is routed directly at the access layer, and each access switch acts as a Layer-3 gateway (IRB) for its VLANs.
“In a campus fabric IP Clos architecture, Mist provisions Layer-3 (L3) integrated routing and bridging (IRB) interfaces on the access layer. All the access switches are configured with the same IP address for each L3 subnet.”
Additionally, the Juniper documentation explains that point-to-point links are configured between layers, and in the case of the 3-stage design (with no distribution), this means between the core and access devices:
“The point-to-point links between each layer utilize /31 addressing to conserve addresses.”
Therefore, the correct statement is C: The core layer is connected to the access layer.
Options A and B incorrectly mention a distribution layer that does not exist in this topology.
Option D is incorrect because core (spine) devices in a Clos fabric are not interconnected with each
other.
Reference: Juniper Mist AI for Wired C Campus Fabric IP Clos Architecture Guide Juniper Mist AI for Wired C Campus Fabric IP Clos Workflow Juniper Mist AI for Wired C Configure Campus Fabric IP Clos
Juniper Validated Design C Campus Fabric IP Clos Deployment Types
Which route types are associated with EVPN? (Select two)
- A . Ethernet Auto-Discovery (EAD)
- B . IP Prefix Route
- C . DHCP Route
- D . ARP Route
What information does Mist use to determine if the port is classified as an uplink? (Choose two.)
- A . if TX and RX are higher than the rest of the ports
- B . if the port has an MTU greater than 1500 configured
- C . if the port is an STP root port
- D . if the port has a description configured
A, C
Explanation:
Juniper Mist automatically classifies ports to simplify visibility and automation within Wired Assurance. The Mist cloud analyzes port telemetry and link behavior to determine port roles, including uplinks.
“Mist uses machine learning and switch telemetry to automatically detect uplinks by analyzing traffic behavior and topology information. Uplink ports typically exhibit higher TX/RX utilization and are identified as spanning-tree root or forwarding ports connecting upstream devices.”
Option A: Correct ― Mist examines traffic statistics. Ports with significantly higher TX/RX utilization relative to others are likely uplinks.
Option B: Incorrect ― MTU size is not a classification criterion.
Option C: Correct ― Mist uses STP information (root or designated port status) to identify uplinks.
Option D: Incorrect ― port description fields are for administrative purposes only and are not used
by Mist analytics.
Reference: Juniper Mist AI for Wired C Port Role Classification and Telemetry Juniper Mist AI for Wired C Automated Uplink Detection and Insights Juniper Wired Assurance Analytics Guide
What are two prereuisites for creating a campus fabric in Juniper Mist? (Choose two)
- A . Switches must be in the Connected state.
- B . Switches msut be claimed.
- C . Switches must be powered on.
- D . Switches must be assigned to the correct site.
Deploying Campus Fabric Architectures often requires:
- A . Guesswork and improvisation
- B . A disregard for best practices
- C . A comprehensive understanding of network design principles
- D . Sole reliance on outdated technologies
What information would be streamed through webhooks? (Choose two.)
- A . location coordinates of RFID tags
- B . alerts
- C . SLE metrics of clients
- D . audit logs
B, C
Explanation:
Mist webhooks provide real-time integration with external systems by streaming alerts and SLE (client) metrics.
They allow automation tools to react immediately to network health or performance changes.
Reference: Mist AI for Wired C Webhooks Integration and API Guide
Mist Cloud Automation and Telemetry Reference
What are three requirements for using ZTP during a Mist AI greenfield provisioning? (Choose three.)
- A . Junos Space
- B . Claim code
- C . SNMP server
- D . Internet access
- E . DHCP server
