Practice Free JN0-105 Exam Online Questions
What will the request system configuration rescue save command do?
- A . It saves the most recently committed configuration as the rescue configuration.
- B . It saves the candidate configuration as the rescue configuration.
- C . It saves a configuration version prior to the configuration most recently committed as the rescue configuration.
- D . It activates the rescue configuration.
A
Explanation:
The request system configuration rescue save command in Junos OS saves the most recently committed configuration as the rescue configuration. This rescue configuration can be used to recover the device if future configurations cause issues. It ensures there is a stable, known-good configuration to fall back on, which is crucial in network management and troubleshooting.
Reference: "rescue: save configurations as the rescue: request system configuration save ……………..(saves the current configs as a rescue configs)" from Useful Juniper Commands.txt.
Juniper official documentation: Configuring and Activating a Rescue Configuration.
Which two common routing policy actions affect the flow of policy evaluation? (Choose two.)
- A . next policy
- B . community
- C . next term
- D . next hop
AC
Explanation:
In Junos OS routing policy evaluation, "next policy" (A) and "next term" (C) are common actions that affect the flow of policy evaluation. "Next policy" directs the evaluation to the next policy in the sequence, whereas "next term" moves the evaluation to the next term within the current policy, allowing for granular control over routing decisions.
Exhibit
policy-options { policy-statement Load-Balance-Policy { term Load-Balance { then { load-balance per-flow; accept;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
router-id 192.168.100.11; autonomous-system 65201; forwarding-table {
export Load-Balance-Policy;
Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
- A . The policy enables equal cost load balancing in the forwarding table.
- B . The policy must be applied under the protocols hierarchy.
- C . The policy enables per-packet load balancing.
- D . The policy enables flow-based load balancing.
AD
Explanation:
The load-balance per-flow statement in the Junos OS policy-options configuration enables flow-based load balancing in the forwarding table. This means that the traffic is distributed across multiple paths based on flows, where a flow is typically identified by attributes such as source and destination IP addresses, and possibly layer 4 information like TCP/UDP ports. This allows for more granular and efficient utilization of available paths, avoiding overloading a single path. The policy does not enable per-packet load balancing, which would send individual packets of the same flow over different paths, potentially causing out-of-order delivery issues. The policy’s placement in the forwarding-table export suggests it’s intended to influence forwarding behavior, not just routing protocol decisions, and does not necessarily have to be applied under the protocols hierarchy.
Click the Exhibit button.
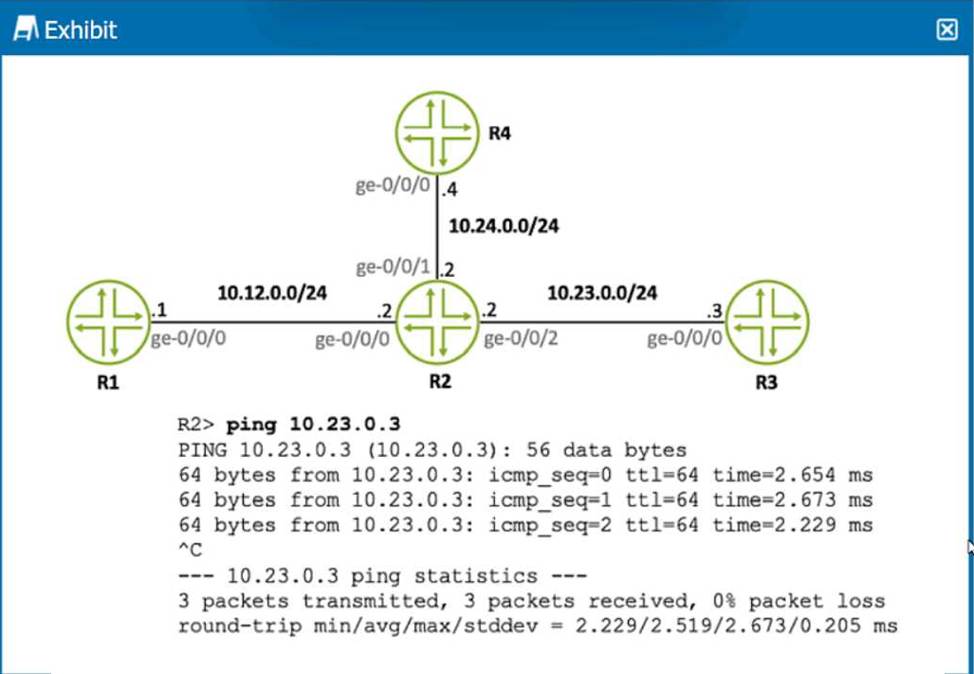
Referring to the exhibit, what is the source IP a ddress of the ping that was executed?
- A . 10.12.0.2
- B . 10.23.0.2
- C . 10.23.0.3
- D . 10.24.0.4
B
Explanation:
The exhibit shows a ping test being executed from router R2 to the IP address 10.23.0.3. Since the ping command is issued on R2 and we see successful replies from 10.23.0.3, it means the source of the ping must be an interface on R2. Given the network diagram and the IP address scheme, the source IP address of the ping is on the interface ge-0/0/2 of R2, which is in the subnet 10.23.0.0/24. The only logical IP address for R2’s interface in this subnet, based on standard networking practices and the given options, would be 10.23.0.2. The other addresses provided in the options belong to different subnets or are the destination of the ping itself.
You issue the monitor traffic interface ge-0/0/0 command.
What will this command accomplish?
- A . It displays real-time statistics for interface ge-0/0/0.
- B . It displays an operational summary of ge-0/0/0.
- C . It displays the MTU and MAC address for ge-0/0/0.
- D . It displays a packet capture on interface ge-0/0/0.
D
Explanation:
The command "monitor traffic interface ge-0/0/0" (D) initiates a packet capture on the specified interface, allowing you to view the actual packets being transmitted and received. This is useful for troubleshooting and analyzing the traffic passing through the interface in real time.
In the Junos OS, which keyboard shortcut allows you to move to the start of the line?
- A . Ctrl+a
- B . Ctrl+e
- C . Ctrl+w
- D . Ctrl+k
A
Explanation:
In the Junos OS command-line interface (CLI), the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+a is used to move the cursor to the start of the line. This is a common convention in many command-line environments and text editors, providing a quick way to navigate to the beginning of the current command or line of text without having to use the arrow keys. This can be particularly useful for making quick edits to commands or for navigating long lines of text more efficiently.
You want to find out the chassis serial number of a Junos device.
Which command would display this information?
- A . show chassis environment
- B . show chassis hardware
- C . show chassis routing-engine
- D . show chassis location
B
Explanation:
The show chassis hardware command in Junos OS displays detailed information about the hardware installed in the device, including the chassis itself. This command provides a list of all hardware components, their serial numbers, part numbers, and version information. When looking for the chassis serial number specifically, this command is the most direct and comprehensive way to retrieve that information, as it includes the serial number of the chassis among the details provided.
You are asked to view the real-time usage statistics for the busiest interfaces on a device running Junos OS.
Which command will achieve this task?
- A . monitor traffic absolute-sequence
- B . monitor interface traffic
- C . monitor traffic
- D . show interfaces extensive
B
Explanation:
To view real-time usage statistics for the busiest interfaces on a device running Junos OS, the correct command is B, "monitor interface traffic." This command provides a dynamic, real-time view of the traffic flowing through the interfaces, allowing administrators to quickly identify and monitor the busiest interfaces on the device.
Which two statements apply to the Routing Engine functions? (Choose two.)
- A . It responds to ping and traceroute commands.
- B . It maintains the routing tables.
- C . It does not process routing updates.
- D . It processes the transit traffic.
A, B
Explanation:
The Routing Engine (RE) in Juniper Networks devices plays a critical role in the control plane operations. One of its functions includes responding to network utility commands like ping and traceroute, which are essential for diagnosing network connectivity and path issues. Furthermore, the RE is responsible for maintaining the routing tables, which contain information about network paths and destinations. These tables are vital for making forwarding decisions but are distinct from the actual forwarding of packets, which is handled by the Packet Forwarding Engine (PFE).
What are two attributes of the UDP protocol? (Choose two.)
- A . UDP is more reliable than TCP.
- B . UDP is always slower than TCP.
- C . UDP is best effort.
- D . UDP is connectionless.
CD
Explanation:
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is known for being connectionless (D) and providing best-effort delivery without the reliability mechanisms present in TCP (C). This means that UDP does not establish a connection before sending data and does not guarantee delivery, order, or error checking, making it faster but less reliable than TCP.
