Practice Free IIA-CIA-Part2 Exam Online Questions
The engagement supervisor would like lo change the audit program’s scope poor to beginning fieldwork According to IIA guidance before any change is implemented what is the most important action that should be undertaken?
- A . Document in the engagement workpapers the rationale for changing the scope.
- B . Confirm that the scope change would align to the organization’s objectives and goals
- C . Confirm that the internal audit activity continues to have the necessary knowledge and skills
- D . Seek approval from the chief audit executive for the proposed scope change
An internal auditor was reviewing the procurement department’s tender documentation for completeness He documented all discrepancies but the procurement manager disagreed with his findings Upon further review, the internal auditor noted that all discrepancies had been corrected in the tender database.
Which of the following courses of action would have prevented this situation?
- A . The auditor should have ensured the preservation of audit evidence by taking screenshots or extracting tender documents
- B . The auditor should have extracted a list of logs and identified any actions that were executed in the database during the audit
- C . The auditor should have instructed procurement workers that changes to the database during the course of the audit were strictly forbidden
- D . The internal auditor should have created a more thorough work program, which would address audit criteria and potential causes in more detail
An internal auditor was reviewing the procurement department’s tender documentation for completeness He documented all discrepancies but the procurement manager disagreed with his findings Upon further review, the internal auditor noted that all discrepancies had been corrected in the tender database.
Which of the following courses of action would have prevented this situation?
- A . The auditor should have ensured the preservation of audit evidence by taking screenshots or extracting tender documents
- B . The auditor should have extracted a list of logs and identified any actions that were executed in the database during the audit
- C . The auditor should have instructed procurement workers that changes to the database during the course of the audit were strictly forbidden
- D . The internal auditor should have created a more thorough work program, which would address audit criteria and potential causes in more detail
Acceding to IIA guidance, when of the Mowing is an assurance service commonly performed by the internal audit activity?
- A . Proposing fine item recommendation lot the annual financial budget of the accounting department
- B . Making recommendations regarding financial approval authority limits for the operations department
- C . Validating whether employees are following established policies and procedures in the procurement department
- D . Generating expense report metrics for employees in the finance department
In the following risk control map risks have been categorized based on the level of significance and the associated level of control.
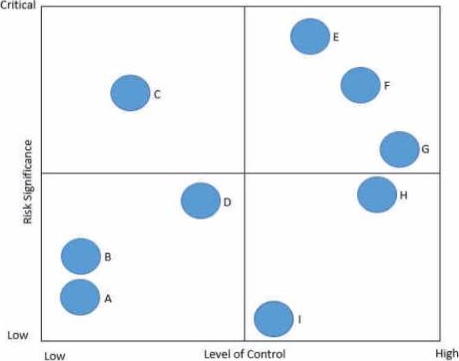
Which of the following statements is true regarding Risk C?
- A . The level of control is appropriate given the level of risk
- B . The level of control is excessive given the level of risk
- C . The level of control is inadequate given the level of risk
- D . There is not enough of information to determine whether the controls are appropriate or not
According to HA guidance, which of the following is the Key planning step internal auditors should perform to establish appropriate engagement objectives prior to starting an audit engagement?
- A . Review the organizational structure, management roles and responsibilities and operating procedures
- B . Evaluate management’s risk assessment and the internal audit activity’s risk assessment
- C . Assess process How and control documents used to meet regulatory requirements
- D . Review meeting notes from discussions involving management of the area to be reviewed.
Flowcharts are useful during audit planning because they contain information that may help internal auditors with which of the following?
- A . Understanding management’s risk tolerance.
- B . Understanding business processes.
- C . Determining the size of the audit team needed to perform the review.
- D . Understanding organizational objectives.
B
Explanation:
Flowcharts are a valuable tool in internal auditing, particularly during the audit planning phase. They provide a visual representation of business processes, which helps internal auditors gain a comprehensive understanding of how these processes function .
Detailed Explanation
Understanding Business Processes:
Flowcharts are used to depict the steps in a process, illustrating how inputs are transformed into outputs, the sequence of activities, and the points where decisions are made. This visual representation makes it easier for auditors to understand the flow of transactions, identify potential control points, and recognize areas where risks may arise. IIA Standard 2201 C Planning Considerations:
According to this standard, internal auditors must consider the objectives, scope, and risks associated with the audit engagement during the planning phase. Understanding business processes is crucial for this, and flowcharts are an effective way to achieve this understanding. IIA Practice Advisory 2210.A1-1:
This advisory suggests using various tools, including flowcharts, to enhance understanding of the area under review. Flowcharts help auditors see the process as a whole and identify where controls should be in place.
Why Not Other Options?
Option A (Understanding management’s risk tolerance): Flowcharts focus on processes, not on management’s subjective risk tolerance.
Option C (Determining the size of the audit team): While flowcharts provide process insights, they do not directly inform team size decisions.
Option D (Understanding organizational objectives): Flowcharts focus on specific processes rather than high-level organizational objectives.
Conclusion: Option B is correct as it aligns with the purpose of flowcharts in audit planning, which is to understand business processes effectively.
Management has taken immediate action to address an observation received during an audit of the organization’s manufacturing process.
Which of the following is true regarding the validity of the observation closure?
- A . Valid closure requires evidence that ensures the corrected process will function as expected in the future
- B . Valid closure requires the client lo address not only the condition, but also the cause of the condition
- C . Valid closure of an observation ensures it will be included in the final engagement report
- D . Valid closure requires assurance from management that the original problem will not recur in the future
An internal auditor developed a list of internal and external risk considerations across the organization’s processes, developed a scale to assess each risk and allocated the relative importance of each risk. When of the following approaches did the auditor take?
- A . Top-down approach
- B . Process-Metrix approach
- C . Risk-factor approach
- D . Bottom up approach
According to IIA guidance, which of the following statements is true regarding engagement planning?
- A . For both assurance and consulting engagements, planning typically occurs after the engagement objectives and scope have already been determined.
- B . The expectations and objectives of an assurance engagement are usually determined by, or in conjunction with, the engagement client.
- C . Internal auditors may not need to complete a preliminary risk assessment for a consulting engagement as they would when planning an assurance engagement.
- D . For both consulting and assurance engagements, internal auditors usually form the engagement objectives prior to completing the preliminary risk assessment.
C
Explanation:
According to IIA guidance, internal auditors are typically required to conduct a preliminary risk assessment when planning an assurance engagement to identify key areas of focus. However, for consulting engagements, the need for a preliminary risk assessment is not as stringent, as these engagements are often more flexible and driven by the specific needs of the client. Consulting engagements may not follow the same structured approach as assurance engagements, and the scope may evolve based on the client’s requirements. IIA
Reference: IIA Standard 2201: Planning Considerations requires internal auditors to consider significant risks when planning engagements. However, this standard is more rigidly applied to assurance engagements.
The Practice Advisory 2201-2: Consulting Engagements notes that consulting engagements might not require the same level of preliminary risk assessment, depending on the nature of the engagement and the needs of the client.
