Practice Free HPE7-A08 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exihibit.
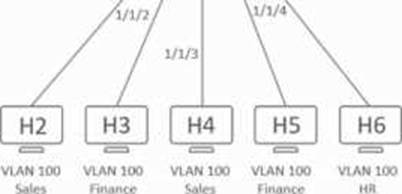

What is the expected behavior for ARP traffic sent from H1?
- A . A2 will send the ARP traffic out of ports 1/1/1 and 1/1/3.
- B . A2 will send the ARP traffic out of ports 1/1/1C1/1/4.
- C . A2 will drop the ARP traffic.
- D . A2 will flood the ARP traffic out of all interfaces.
Refer to the exhibit:
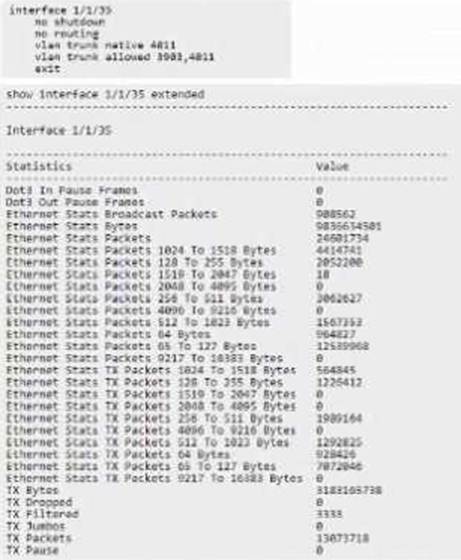
The interface is configured on an HPE Aruba Networking CX 8320 for a VMware server NIC, and the server admin reports that VMware vMotion traffic on VLAN 3903 fails, but the server can ping other ports with default settings.
What must be done to correct the issue based on the provided interface status and configuration?
- A . Configure jumbo on VLAN 3903
- B . Configure jumbo on interface 1/1/36
- C . Configure MTU 9198 on interface 1/1/36
- D . Configure MTU 9198 on VLAN 3903
A
Explanation:
The issue is VMware vMotion traffic on VLAN 3903 failing, while other VLANs work normally. vMotion traffic requires support for larger frame sizes (jumbo frames) because vMotion packets are large and benefit from increased MTU to improve performance and reduce fragmentation.
Configuring jumbo frames on VLAN 3903 ensures that frames on this VLAN can use an MTU larger than the default 1500 bytes.
Configuring jumbo on the interface alone may not be sufficient if the VLAN itself is not set to support jumbo frames.
Setting MTU on VLAN or interface might not work unless jumbo frames are enabled.
Reference: ArubaOS-CX VLAN and MTU Configuration Guide
VMware Best Practices for Networking on Aruba Switches
Aruba CX Switch Troubleshooting for VMware Environments
Refer to the exhibit:

The interface is configured on an HPE Aruba Networking CX 8320 for a VMware server NIC, and the server admin reports that VMware vMotion traffic on VLAN 3903 fails, but the server can ping other ports with default settings.
What must be done to correct the issue based on the provided interface status and configuration?
- A . Configure jumbo on VLAN 3903
- B . Configure jumbo on interface 1/1/36
- C . Configure MTU 9198 on interface 1/1/36
- D . Configure MTU 9198 on VLAN 3903
A
Explanation:
The issue is VMware vMotion traffic on VLAN 3903 failing, while other VLANs work normally. vMotion traffic requires support for larger frame sizes (jumbo frames) because vMotion packets are large and benefit from increased MTU to improve performance and reduce fragmentation.
Configuring jumbo frames on VLAN 3903 ensures that frames on this VLAN can use an MTU larger than the default 1500 bytes.
Configuring jumbo on the interface alone may not be sufficient if the VLAN itself is not set to support jumbo frames.
Setting MTU on VLAN or interface might not work unless jumbo frames are enabled.
Reference: ArubaOS-CX VLAN and MTU Configuration Guide
VMware Best Practices for Networking on Aruba Switches
Aruba CX Switch Troubleshooting for VMware Environments
You are troubleshooting a WLAN deployment with APs and gateways set up with an 802.1X tunneled SSID. End-users are complaining that they can’t connect to the enterprise SSID.
Which possible AP tunnel states could be the cause of the issue? (Select two.)
- A . SM_STATE_CONNECTING
- B . SM_STATE_SURVIVED
- C . SM_STATE_SURVIVING
- D . SM_STATE_CONNECTED
- E . SM_STATE_REKEYING
In an attempt to clear the switch configuration, you’ve issued the command erase all zeroize.
What is the result of this task?
- A . The switch clears all user credentials and retains the running configuration.
- B . The switch restores the factory-installed AOS-CX image to the switch.
- C . The switch runs a secure erase task, deleting the startup-config, and retains admin credential password.
- D . The switch runs a secure erase task, deleting all customer data, and may run up to an hour.
D
Explanation:
The command erase all zeroize performs a secure erase on the switch, which deletes all customer data including startup-config and stored credentials. This process can take up to an hour depending on the hardware and storage media.
It does not retain running config (Option A).
It does not restore the factory AOS-CX image (Option B).
Admin credentials are deleted as part of the secure erase (Option C is incorrect).
Therefore, this command securely wipes all data and resets the device.
Reference: ArubaOS-CX Secure Erase and Factory Reset Guide
HPE Aruba Switch Maintenance Procedures
Aruba CX Switch CLI Reference
You are remotely connected to an HPE Aruba Networking CX 6200F switch using SSH to change the Control Plane ACL, allowing only defined subnets to access the switch.
Which AOS-CX command allows you to roll back your change if the ACL change is wrongly formed and you can no longer log in to the switch?
- A . Use the checkpoint commit command after you commit the change.
- B . Use the checkpoint auto command before you commit the change.
- C . Use the checkpoint auto command after you commit the change.
- D . Use the checkpoint commit command before you commit the change.
B
Explanation:
When making changes remotely to critical configurations such as Control Plane ACLs on a CX switch, to protect against accidental lockout due to misconfiguration, you should enable checkpoint auto before committing the changes.
Checkpoint auto creates an automatic rollback timer. If the administrator loses connectivity (e.g., because of the ACL change), the system automatically rolls back the change after the timer expires, preventing lockout.
checkpoint commit is used after committing to save the checkpoint explicitly, but it does not provide automatic rollback.
Running checkpoint auto before committing is essential to have the rollback safety net.
Reference: ArubaOS-CX Configuration Rollback and Checkpoint Documentation
Aruba CLI User Guide C Checkpoint Commands
HPE Aruba Best Practices for Remote Configuration
DRAG DROP
You are tasked with developing a comprehensive, flexible, and survivable zero-trust wired access network using CX 6300 switching and HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Policy Manager. Match the scenario to the special roles to achieve your objectives.


Explanation:
What directly affects the MCS used by wireless stations? (Select two.)
- A . SNR
- B . Channel utilization
- C . Number of connected clients
- D . Retry rate
- E . Frequency band
A customer reports that their HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass Guest captive portal is not functioning. The page loads but they are unable to browse after pressing connect. They have uploaded a valid and publicly trusted *. aruba-training.com certificate.
Refer to the exhibit.
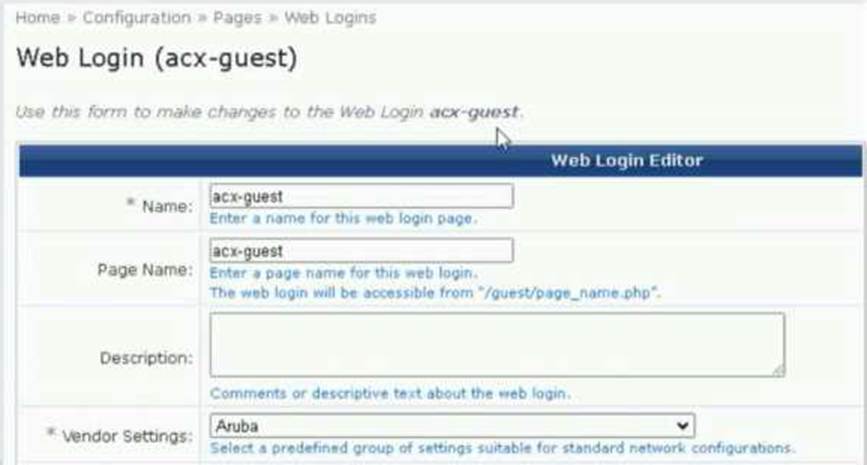
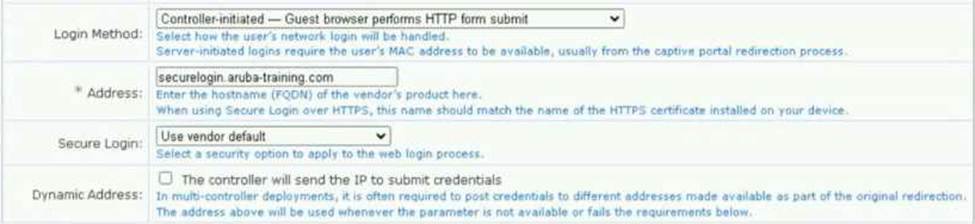
Which would explain this issue?
- A . aruba-training.com needs to be entered in the Address field for the ClearPass Guest
- B . captiveportal-login.aruba-training.com needs to be entered in the Address field for the ClearPass Guest
- C . HTTPS certificate is not required in ClearPass Guest
- D . HTTPS wildcard certificates are not supported
Refer to the exhibit:
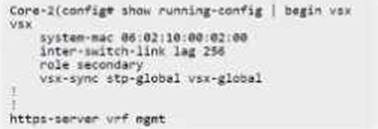
The primary VSX switch has a DHCP relay configured; however, the secondary switch does not display the DHCP relay configuration in the running configuration.
How can the VSX configuration be changed to have the same config on both nodes?
- A . On the secondary switch, add vsx-sync ip-helper under VSX configuration.
- B . On the primary switch, add vsx-sync ip-helper under VSX configuration.
- C . On the primary switch, add vsx-sync dhcp-relay under VSX configuration.
- D . On the secondary switch, add vsx-sync dhcp-relay under VSX configuration.
C
Explanation:
In a VSX cluster, certain configurations such as DHCP relay need to be synchronized between both nodes. To sync DHCP relay configuration from the primary to the secondary, the command:
vsx-sync dhcp-relay
must be added under the VSX configuration on the primary switch. This ensures that DHCP relay settings are pushed to the secondary member automatically.
Adding vsx-sync ip-helper relates to IP helper addresses, not DHCP relay specifically.
Adding the sync command on the secondary has no effect as synchronization originates from primary.
Reference: Aruba VSX Configuration Synchronization Guide
HPE Aruba DHCP Relay and VSX Documentation
ArubaOS-CX VSX Best Practices
