Practice Free HPE6-A84 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the scenario.
A customer is migrating from on-prem AD to Azure AD as its sole domain solution. The customer also manages both wired and wireless devices with Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune).
The customer wants to improve security for the network edge. You are helping the customer design a ClearPass deployment for this purpose. Aruba network devices will authenticate wireless and wired clients to an Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) cluster (which uses version 6.10).
The customer has several requirements for authentication. The clients should only pass EAP-TLS authentication if a query to Azure AD shows that they have accounts in Azure AD. To further refine the clients’ privileges, ClearPass also should use information collected by Intune to make access control decisions.
You are planning to use Azure AD as the authentication source in 802.1X services.
What should you make sure that the customer understands is required?
- A . An app registration on Azure AD that references the CPPM’s FQDN
- B . Windows 365 subscriptions
- C . CPPM’s RADIUS certificate was imported as trusted in the Azure AD directory
- D . Azure AD Domain Services
Refer to the scenario.
This customer is enforcing 802.1X on AOS-CX switches to Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM). The customer wants switches to download role settings from CPPM.
The “reception-domain” role must have these settings:
― Assigns clients to VLAN 14 on switch 1, VLAN 24 on switch 2, and so on.
― Filters client traffic as follows:
― Clients are permitted full access to 10.1.5.0/24 and the Internet
― Clients are denied access to 10.1.0.0/16
The switch topology is shown here:
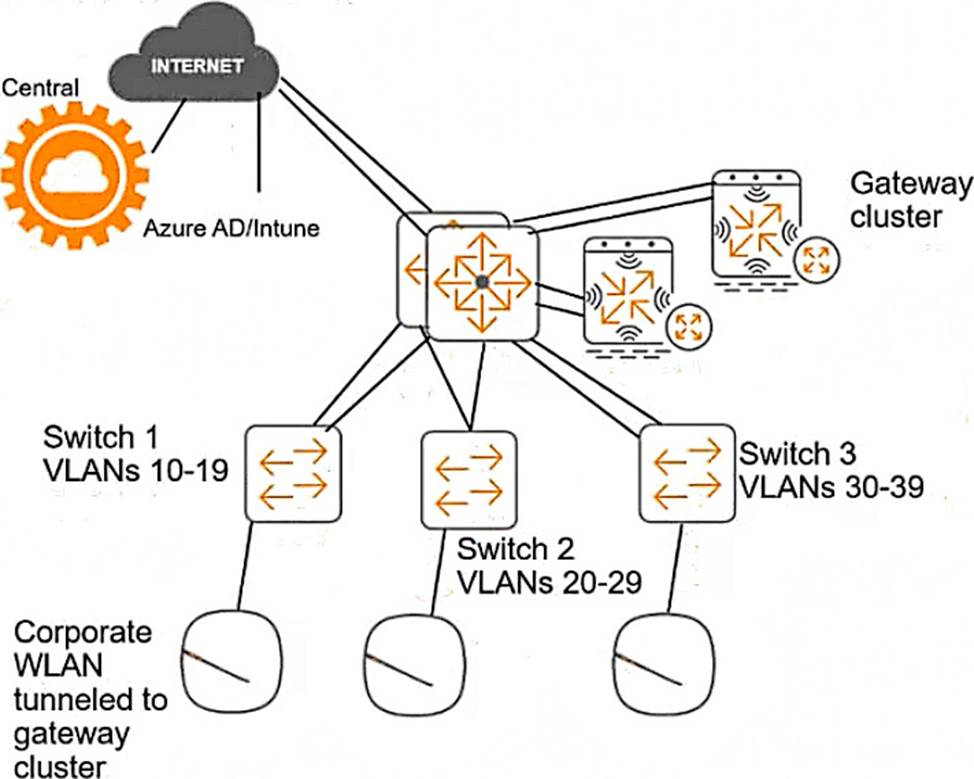
How should you configure the VLAN setting for the reception role?
- A . Assign a consistent name to VLAN 14, 24, or 34 on each access layer switch and reference that name in the enforcement profile VLAN settings.
- B . Configure the enforcement profile as a downloadable role, but specify only the role name and leave the VLAN undefined. Then define a “reception” role with the correct VLAN setting on each individual access layer switch.
- C . Assign a number-based ID to the access layer switches. Then use this variable in the enforcement profile VLAN settings: %(NAS-ID}4.
- D . Create a separate enforcement profile with a different VLAN ID for each switch. Add all profiles to the profile list in the appropriate enforcement policy rule.
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network infrastructure devices.
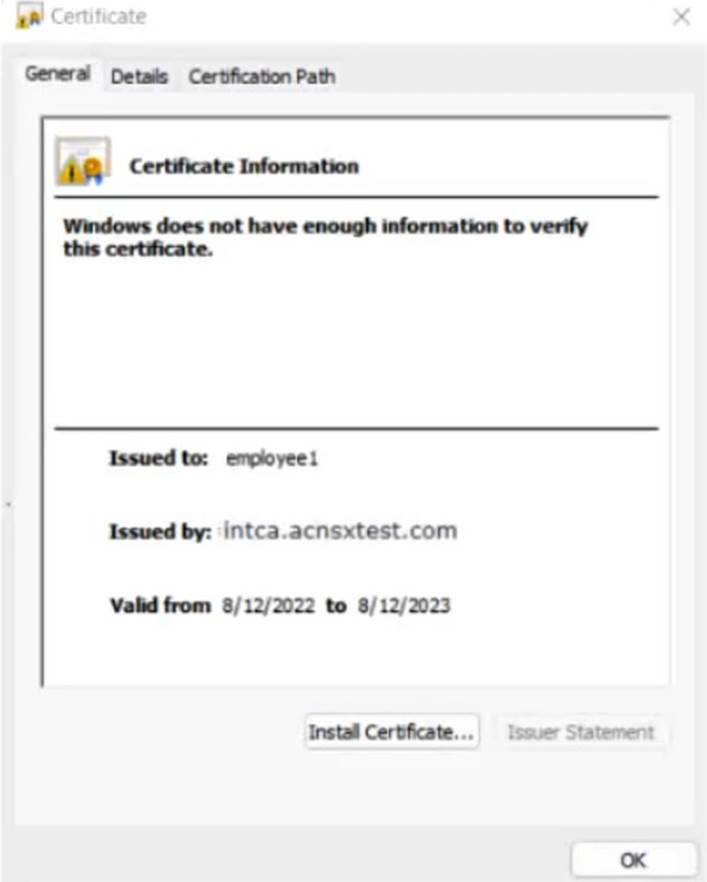
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows CA. The Window CA issues certificates to domain computers, domain users, and servers such as domain controllers. An example of a certificate issued by the Windows CA is shown here.
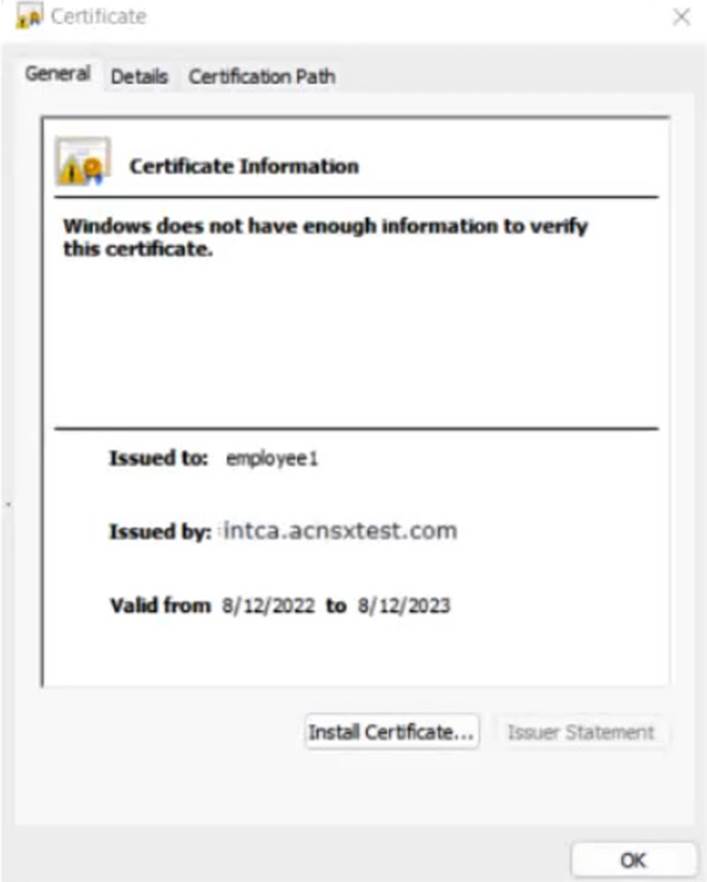
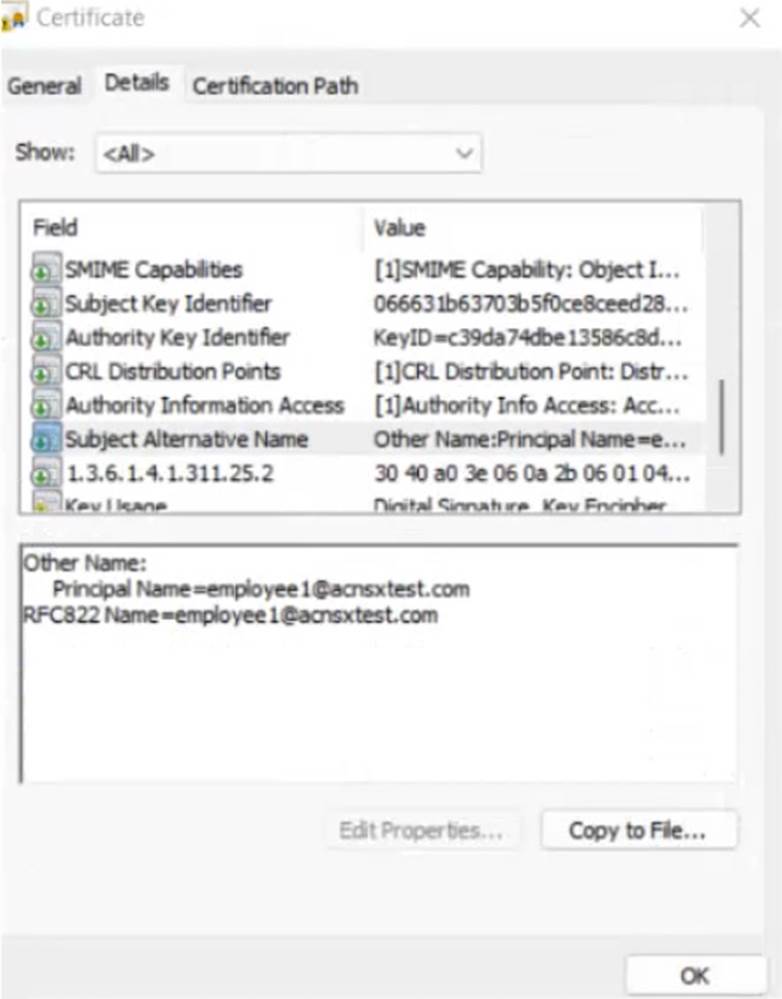
The company is in the process of adding Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune) to manage its mobile clients. The customer is maintaining the on-prem AD for now and uses Azure AD Connect to sync with Azure AD.
# Requirements for issuing certificates to mobile clients
The company wants to use ClearPass Onboard to deploy certificates automatically to mobile clients enrolled in Intune. During this process, Onboard should communicate with Azure AD to validate the clients. High availability should also be provided for this scenario; in other words, clients should be able to get certificates from Subscriber 2 if Subscriber 1 is down.
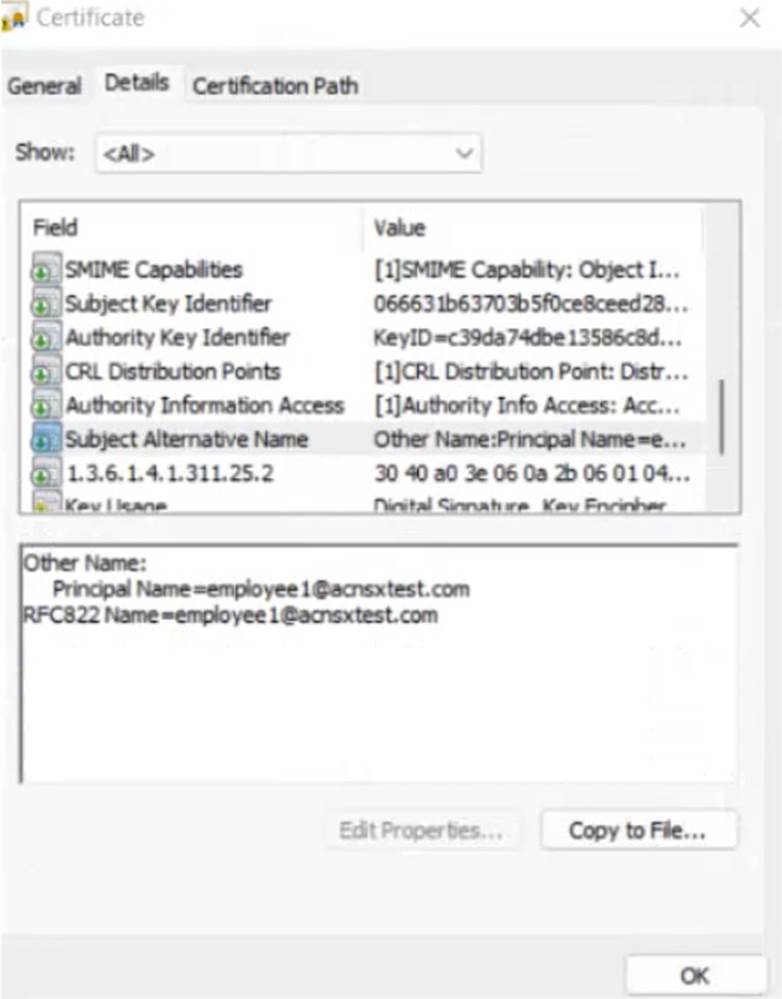
The Intune admins intend to create certificate profiles that include a UPN SAN with the UPN of the user who enrolled the device.
# Requirements for authenticating clients
The customer requires all types of clients to connect and authenticate on the same corporate SSID.
The company wants CPPM to use these authentication methods:
EAP-TLS to authenticate users on mobile clients registered in Intune
TEAR, with EAP-TLS as the inner method to authenticate Windows domain computers and the users on them
To succeed, EAP-TLS (standalone or as a TEAP method) clients must meet these requirements:
Their certificate is valid and is not revoked, as validated by OCSP
The client’s username matches an account in AD
# Requirements for assigning clients to roles
After authentication, the customer wants the CPPM to assign clients to ClearPass roles based on the following rules:
Clients with certificates issued by Onboard are assigned the “mobile-onboarded” role
Clients that have passed TEAP Method 1 are assigned the “domain-computer” role
Clients in the AD group “Medical” are assigned the “medical-staff” role
Clients in the AD group “Reception” are assigned to the “reception-staff” role
The customer requires CPPM to assign authenticated clients to AOS firewall roles as follows:
Assign medical staff on mobile-onboarded clients to the “medical-mobile” firewall role
Assign other mobile-onboarded clients to the “mobile-other” firewall role
Assign medical staff on domain computers to the “medical-domain” firewall role
All reception staff on domain computers to the “reception-domain” firewall role
All domain computers with no valid user logged in to the “computer-only” firewall role
Deny other clients access –
# Other requirements
Communications between ClearPass servers and on-prem AD domain controllers must be encrypted.
# Network topology
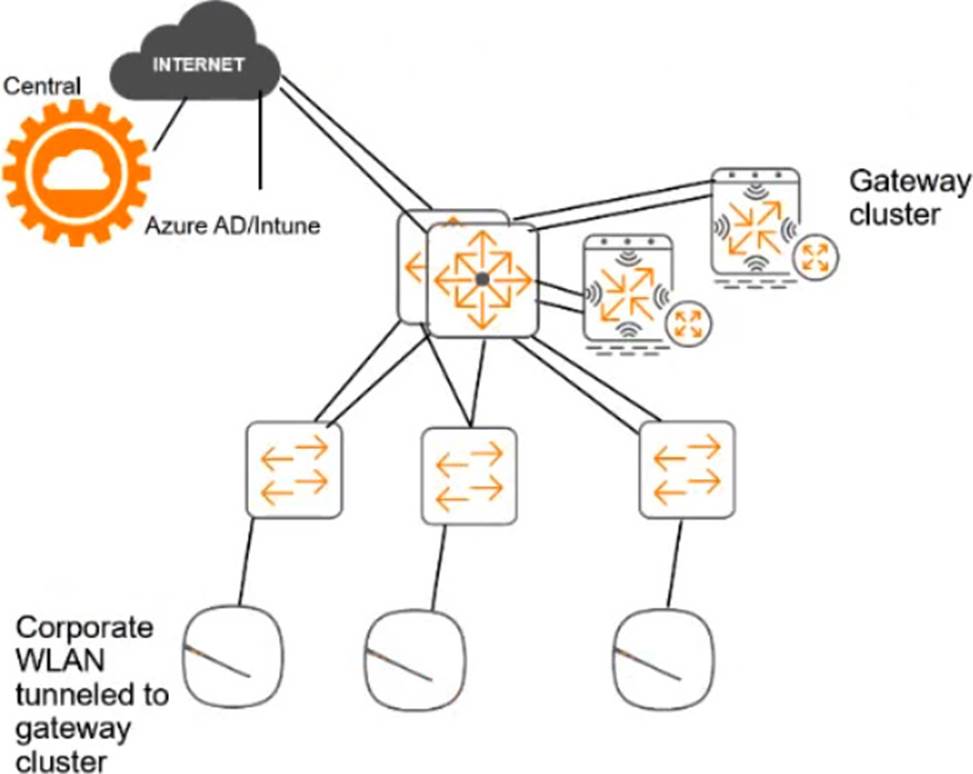
For the network infrastructure, this customer has Aruba APs and Aruba gateways, which are managed by Central. APs use tunneled WLANs, which tunnel traffic to the gateway cluster. The customer also has AOS-CX switches that are not managed by Central at this point.
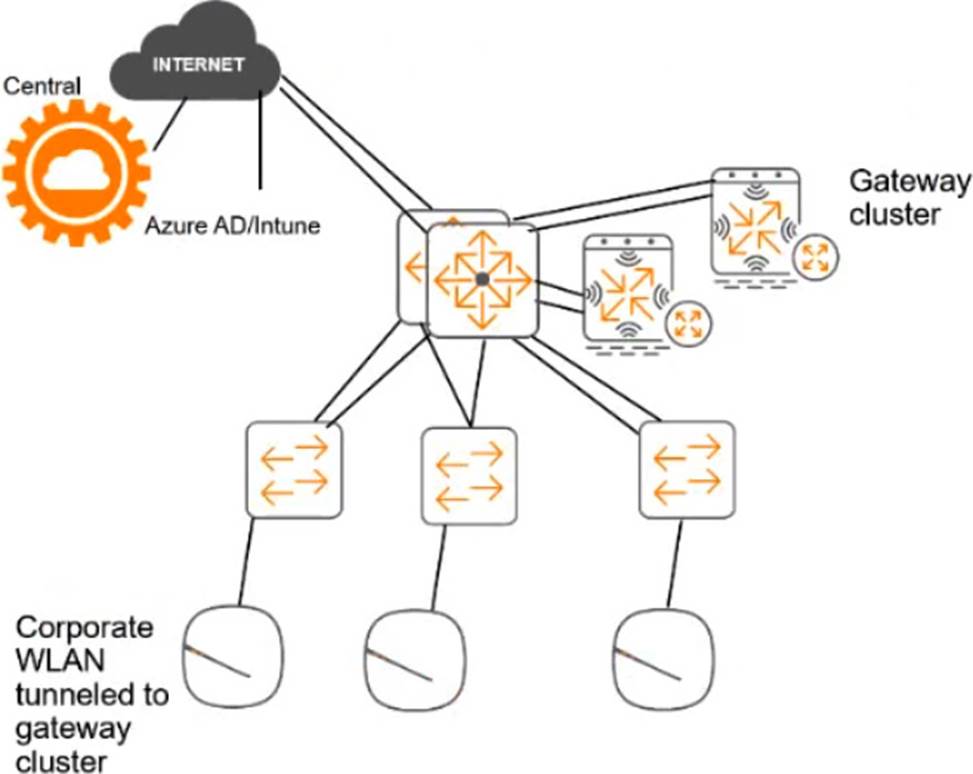
# ClearPass cluster IP addressing and hostnames
A customer’s ClearPass cluster has these IP addresses:
Publisher = 10.47.47.5 –
Subscriber 1 = 10.47.47.6 –
Subscriber 2 = 10.47.47.7 –
Virtual IP with Subscriber 1 and Subscriber 2 = 10.47.47.8
The customer’s DNS server has these entries
cp.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.5
cps1.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.6
cps2.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.7
radius.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.8
onboard.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.8
You cannot see flow attributes for wireless clients.
What should you check?
- A . Deep packet inspection is enabled on the role to which the Aruba APs assign the wireless clients.
- B . Firewall application visibility is enabled on the Aruba gateways, and the gateways have been rebooted.
- C . Gateway IDS/IPS is enabled on the Aruba gateways, and the gateways have been rebooted.
- D . Deep packet inspection is enabled on the Aruba Aps, and the APs have been rebooted.
What is a common characteristic of a beacon between a compromised device and a command and control server?
- A . Use of IPv6 addressing instead of IPv4 addressing
- B . Lack of encryption
- C . Use of less common protocols such as SNAP
- D . Periodic transmission of small, identically sized packets
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows CA. The Window CA issues certificates to domain computers, domain users, and servers such as domain controllers. An example of a certificate issued by the Windows CA is shown here.
The company is in the process of adding Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune) to manage its mobile clients. The customer is maintaining the on-prem AD for now and uses Azure AD Connect to sync with Azure AD.
# Requirements for issuing certificates to mobile clients
The company wants to use ClearPass Onboard to deploy certificates automatically to mobile clients enrolled in Intune. During this process, Onboard should communicate with Azure AD to validate the clients. High availability should also be provided for this scenario; in other words, clients should be able to get certificates from Subscriber 2 if Subscriber 1 is down.
The Intune admins intend to create certificate profiles that include a UPN SAN with the UPN of the user who enrolled the device.
# Requirements for authenticating clients
The customer requires all types of clients to connect and authenticate on the same corporate SSID.
The company wants CPPM to use these authentication methods:
EAP-TLS to authenticate users on mobile clients registered in Intune
TEAR, with EAP-TLS as the inner method to authenticate Windows domain computers and the users on them
To succeed, EAP-TLS (standalone or as a TEAP method) clients must meet these requirements:
Their certificate is valid and is not revoked, as validated by OCSP
The client’s username matches an account in AD
# Requirements for assigning clients to roles
After authentication, the customer wants the CPPM to assign clients to ClearPass roles based on the following rules:
Clients with certificates issued by Onboard are assigned the “mobile-onboarded” role
Clients that have passed TEAP Method 1 are assigned the “domain-computer” role
Clients in the AD group “Medical” are assigned the “medical-staff” role
Clients in the AD group “Reception” are assigned to the “reception-staff” role
The customer requires CPPM to assign authenticated clients to AOS firewall roles as follows:
Assign medical staff on mobile-onboarded clients to the “medical-mobile” firewall role
Assign other mobile-onboarded clients to the “mobile-other” firewall role
Assign medical staff on domain computers to the “medical-domain” firewall role
All reception staff on domain computers to the “reception-domain” firewall role
All domain computers with no valid user logged in to the “computer-only” firewall role
Deny other clients access –
# Other requirements
Communications between ClearPass servers and on-prem AD domain controllers must be encrypted.
# Network topology
For the network infrastructure, this customer has Aruba APs and Aruba gateways, which are managed by Central. APs use tunneled WLANs, which tunnel traffic to the gateway cluster. The customer also has AOS-CX switches that are not managed by Central at this point.
# ClearPass cluster IP addressing and hostnames
A customer’s ClearPass cluster has these IP addresses:
Publisher = 10.47.47.5 –
Subscriber 1 = 10.47.47.6 –
Subscriber 2 = 10.47.47.7 –
Virtual IP with Subscriber 1 and Subscriber 2 = 10.47.47.8
The customer’s DNS server has these entries
cp.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.5
cps1.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.6
cps2.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.7
radius.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.8
onboard.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.8
The customer has now decided that it needs CPPM to assign certain mobile-onboarded devices to a “nurse-call” AOS user role. These are mobile-onboarded devices that are communicating with IP address 10.1.18.12 using port 4343.
What are the prerequisites for fulfilling this requirement?
- A . Setting up traffic classes and role mapping rules within Central’s global settings
- B . Creating server-based role assignment rules on APs that apply roles to clients based on traffic destinations
- C . Creating server-based role assignment rules on gateways that apply roles to clients based on traffic destinations
- D . Creating a tag on Central to select the proper destination connection and integrating CPPM with Device Insight
A customer’s admins have added RF Protect licenses and enabled WIDS for a customer’s AOS 8-based solution. The customer wants to use the built-in capabilities of APs without deploying dedicated air monitors (AMs). Admins tested rogue AP detection by connecting an unauthorized wireless AP to a switch. The rogue AP was not detected even after several hours.
What is one point about which you should ask?
- A . Whether APs’ switch ports support all the VLANs that are accessible at the edge
- B . Whether admins enabled wireless containment
- C . Whether admins set at least one radio on each AP to air monitor mode
- D . Whether the customer is using non-standard Wi-Fi channels in the deployment
You are configuring gateway IDS/IPS settings in Aruba Central.
For which reason would you set the Fail Strategy to Bypass?
- A . To permit traffic if the IPS engine falls to inspect It
- B . To enable the gateway to honor the allowlist settings configured in IDS/IPS policies
- C . To tell gateways to stop enforcing IDS/IPS policies if they lose connectivity to the Internet
- D . To avoid wasting IPS engine resources on filtering traffic for unauthenticated clients
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows CA. The Window CA issues certificates to domain computers, domain users, and servers such as domain controllers. An example of a certificate issued by the Windows CA is shown here.
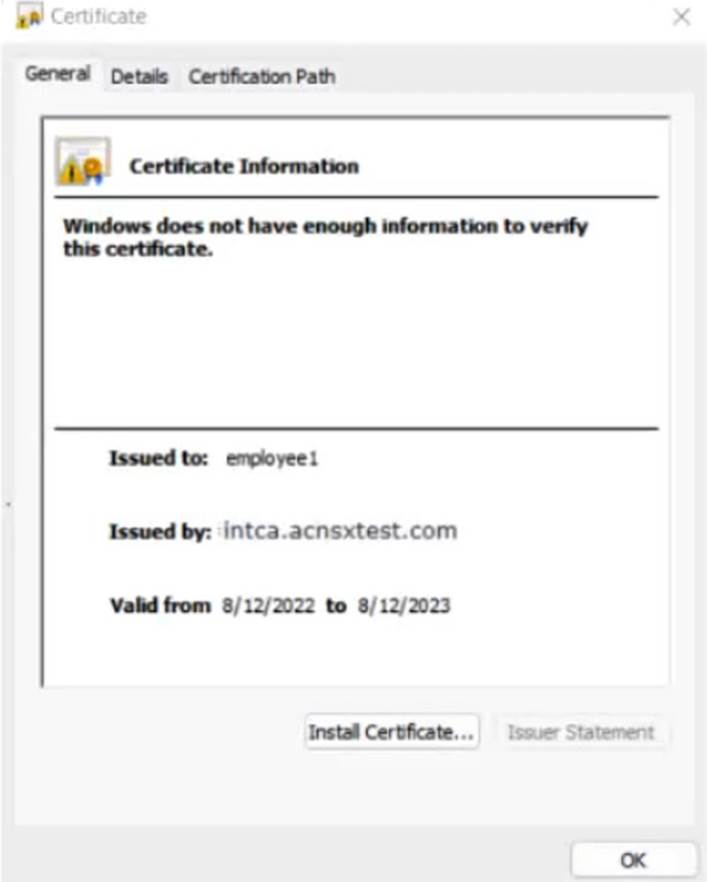
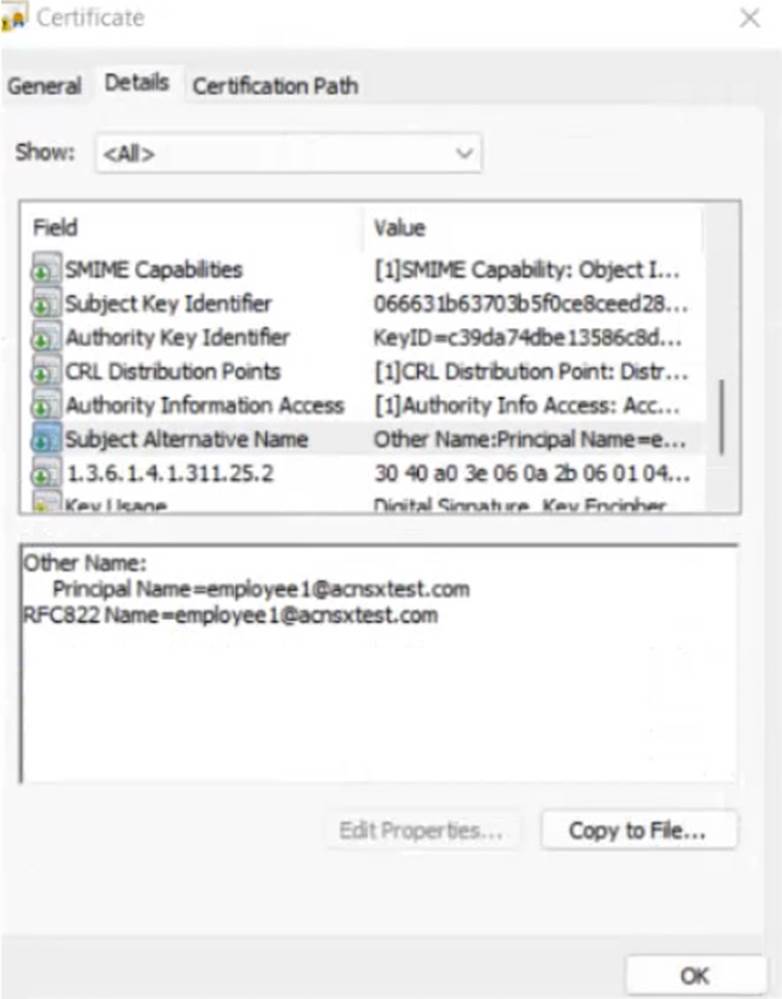
The company is in the process of adding Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune) to manage its mobile clients. The customer is maintaining the on-prem AD for now and uses Azure AD Connect to sync with Azure AD.
# Requirements for issuing certificates to mobile clients
The company wants to use ClearPass Onboard to deploy certificates automatically to mobile clients enrolled in Intune. During this process, Onboard should communicate with Azure AD to validate the clients. High availability should also be provided for this scenario; in other words, clients should be able to get certificates from Subscriber 2 if Subscriber 1 is down.
The Intune admins intend to create certificate profiles that include a UPN SAN with the UPN of the user who enrolled the device.
# Requirements for authenticating clients
The customer requires all types of clients to connect and authenticate on the same corporate SSID.
The company wants CPPM to use these authentication methods:
EAP-TLS to authenticate users on mobile clients registered in Intune
TEAR, with EAP-TLS as the inner method to authenticate Windows domain computers and the users on them
To succeed, EAP-TLS (standalone or as a TEAP method) clients must meet these requirements:
Their certificate is valid and is not revoked, as validated by OCSP
The client’s username matches an account in AD
# Requirements for assigning clients to roles
After authentication, the customer wants the CPPM to assign clients to ClearPass roles based on the following rules:
Clients with certificates issued by Onboard are assigned the “mobile-onboarded” role
Clients that have passed TEAP Method 1 are assigned the “domain-computer” role
Clients in the AD group “Medical” are assigned the “medical-staff” role
Clients in the AD group “Reception” are assigned to the “reception-staff” role
The customer requires CPPM to assign authenticated clients to AOS firewall roles as follows:
Assign medical staff on mobile-onboarded clients to the “medical-mobile” firewall role
Assign other mobile-onboarded clients to the “mobile-other” firewall role
Assign medical staff on domain computers to the “medical-domain” firewall role
All reception staff on domain computers to the “reception-domain” firewall role
All domain computers with no valid user logged in to the “computer-only” firewall role
Deny other clients access –
# Other requirements
Communications between ClearPass servers and on-prem AD domain controllers must be encrypted.
# Network topology
For the network infrastructure, this customer has Aruba APs and Aruba gateways, which are managed by Central. APs use tunneled WLANs, which tunnel traffic to the gateway cluster. The customer also has AOS-CX switches that are not managed by Central at this point.
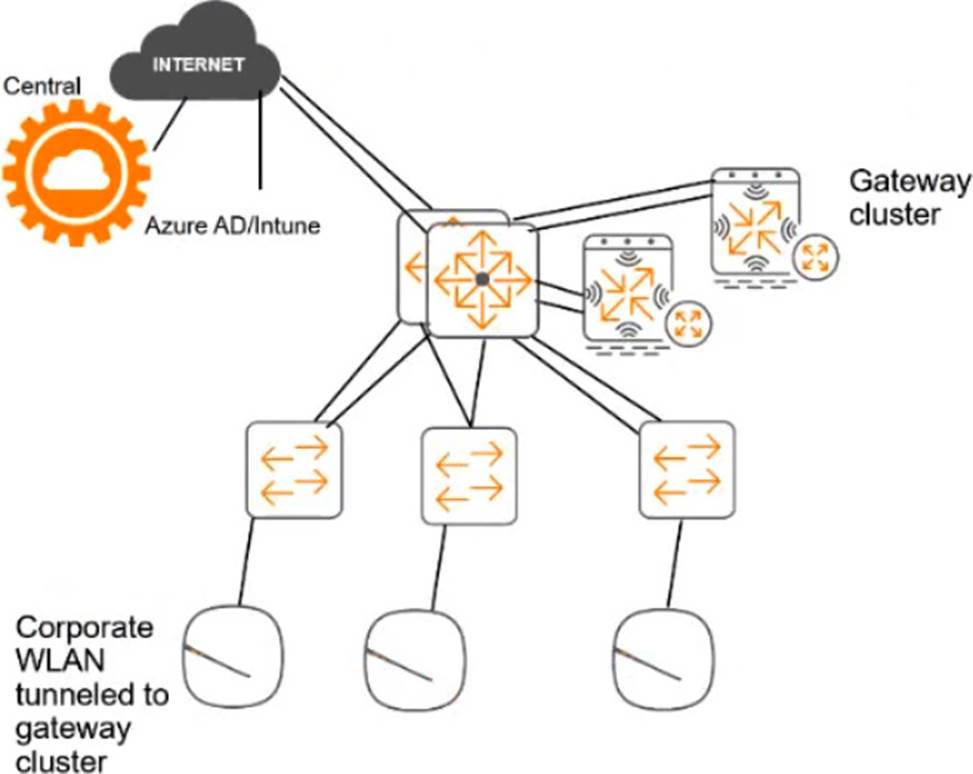
# ClearPass cluster IP addressing and hostnames
A customer’s ClearPass cluster has these IP addresses:
Publisher = 10.47.47.5 –
Subscriber 1 = 10.47.47.6 –
Subscriber 2 = 10.47.47.7 –
Virtual IP with Subscriber 1 and Subscriber 2 = 10.47.47.8
The customer’s DNS server has these entries
cp.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.5
cps1.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.6
cps2.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.7
radius.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.8
onboard.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.8
On CPPM, you are creating the authentication method shown in the exhibit below:
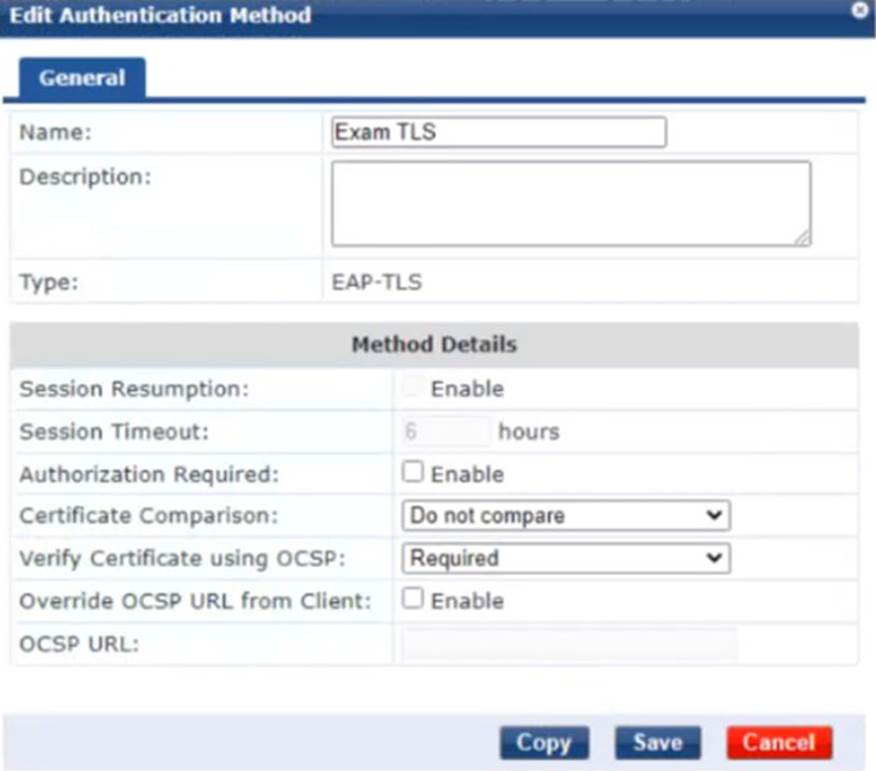
You will use the method for standalone EAP-TLS and for inner methods in TEAP.
What should you do?
- A . Configure OCSP override and set the OCSP URL to localhost/onboard/mdps_ocsp.php/2
- B . Enable certificate comparison.
- C . Enable authorization.
- D . Configure OCSP override and leave the OCSP URL blank.
