Practice Free H12-831_V1.0-ENU Exam Online Questions
Which of the following TLVs is added to IS-IS to support multi-topology?
- A . TLV229
- B . TLV232
- C . TLV236
- D . TLV129
In the OSPF network shown in the figure, R1 and R2 achieve intercommunication through Lopback0 interface through OSPF.
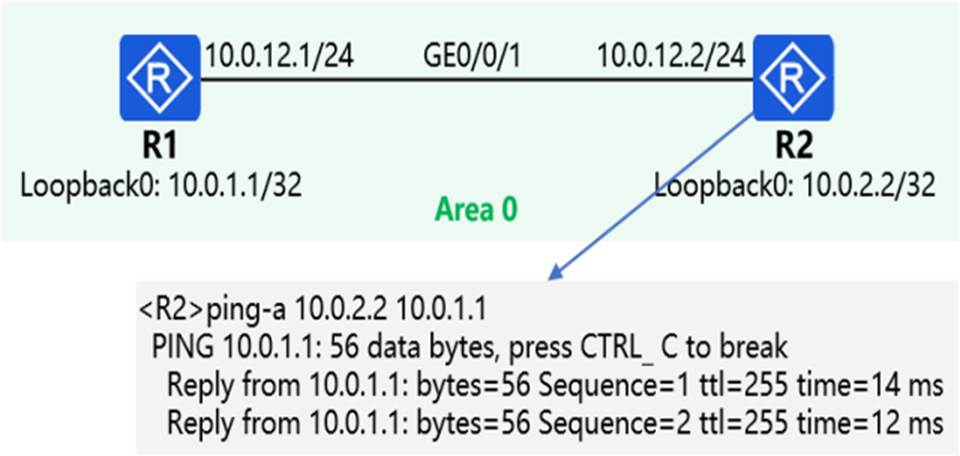
At the same time, R1 and R2 have enabled the MPLS LDP function, and the LDP transmission address is the IP address of the Loopback0 interface. The network engineer found that R1 and R2 could not establish an LDP session, so he first executed the command shown in the figure on R2.
Based on this, which of the following reasons may cause the failure of establishing an LDP session between R1 and R2? (Multiple choice)
- A . R1 GE0/0/1 interface refuses to receive packets with a destination IP address of 10.0.2.2
- B . R2 GE0/0/1 interface refuses to receive ICP packets with destination port 646
- C . MPLS LDP is not enabled on R2 GE0/0/1 interface
- D . R1 GE0/0/1 interface refuses to receive packets with UDP destination port 646
In the IS-IS IPv6 network shown in the figure, all routers have multi-topology enabled. The IPv6 address of the R4 Loopback0 interface is 2000::4/128.

By default, which of the following routers does not have a route to 2000::4/128 in its routing table?
- A . R3
- B . R2
- C . R1
- D . R5
On an MPLS network, an LSR ID uniquely identifies an LSR. An LSR ID defaults to the IP address of a physical interface on a device and can be manually set to a loopback interface address.
- A . TRUE
- B . FALSE
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
LSR ID (Label Switch Router ID) uniquely identifies an MPLS router in the network.
By default, the LSR ID is the IP address of a physical interface on the router.
Best Practice: Manually configuring the LSR ID to use a loopback interface address improves stability and reachability in MPLS networks.
The loopback interface is always up, ensuring that the LSR ID remains accessible even if physical interfaces go down.
Reference: HCIP-Datacom Advanced Routing & Switching Technology C MPLS LSR ID Configuration
Trap information is a notification generated by the system when a fault is detected. It mainly records system status information such as faults. If the network administrator wants to view Trap information through the command line, the SNMP agent function must be enabled first.
- A . True
- B . False
When the administrator enters the command label advertise explicit-null on the egress device in the MPLS network, which of the following labels is assigned to the penultimate hop device?
- A . 0
- B . 15
- C . 18
- D . 3
On the network shown in the figure, IS-IS runs on R1, R2, R4, and R5, and the area ID is 49.0001. IS-IS runs on R3 and R6, and the area ID is 49.0002. The import-route isis level-2 into level-1 command is configured on R2.
In AS 65000, R1, R3, R4, and R6 each establish iBGP peer relationships with R2 and R5. R2 and R5 are Route Reflectors (RRs), and R1, R4, R3, and R6 are clients.
The iBGP peer relationships are established using Loopback0. The IP address of Loopback0 on each router is 10.0.X.X/32, and the router ID is 10.0.X.X, where X is the number of the router.
R1 and R4 import the external route 192.168.1.0/24 to BGP through the import-route command, and R3 and R6 import the external route 192.168.2.0/24 to BGP through the import-route command.
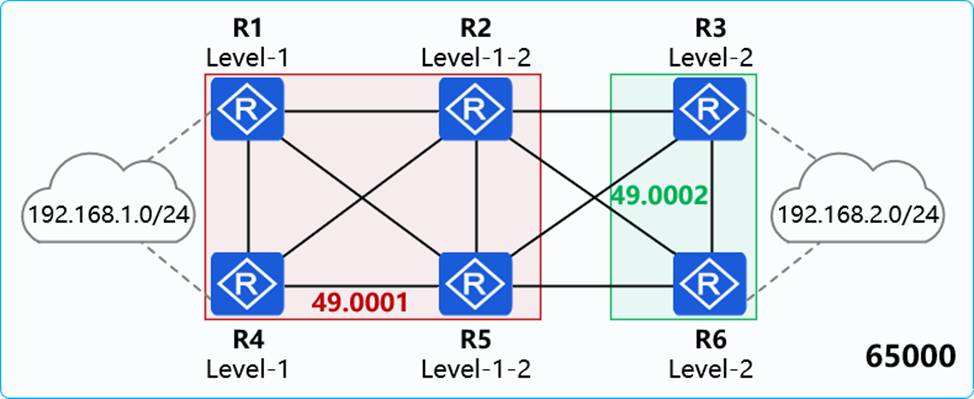
Which of the following statements are true?
- A . The route 192.168.2.0/24 in the routing table of R4 has two next hops.
- B . The routing table of R1 contains two equal-cost default routes.
- C . The routing table of R4 contains two equal-cost default routes.
- D . The routing table of R1 contains the route 192.168.2.0/24.
A, D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
Understanding the BGP and IS-IS Network Topology in the Question:
IS-IS Areas:
Area 49.0001 (Level-1 IS-IS): Contains R1, R2, R4, R5.
Area 49.0002 (Level-2 IS-IS): Contains R3, R6.
R2 acts as an ABR (Area Border Router) and redistributes routes between Level-1 and Level-2 using import-route isis level-2 into level-1.
BGP Route Reflection & Peering:
R2 and R5 are Route Reflectors (RRs).
iBGP peering is established among all routers (R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6).
R1 and R4 import 192.168.1.0/24 into BGP, meaning this prefix will be advertised to all iBGP peers.
R3 and R6 import 192.168.2.0/24 into BGP, meaning this prefix will also be advertised to all iBGP peers.
Route Distribution Analysis:
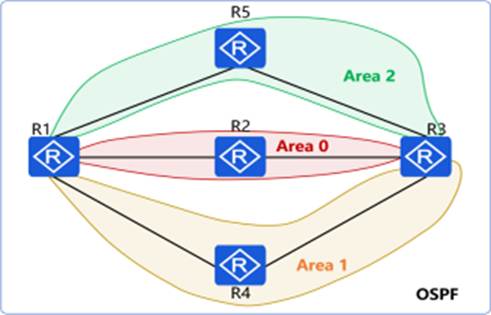
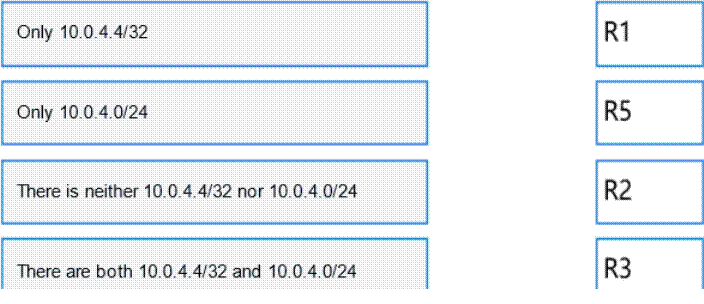
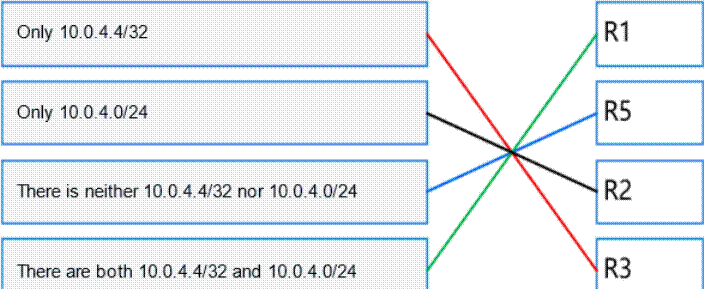
In the OSPF network shown in the figure, area 1 is the MS5A area, area 2 is the Stub area, and R4 imports the external route 10.0.4.4/32. The Router ID of each device is 10.0.X.X, where X is the device number. The "asbr-summary 10.0.4.0 255.255.255.0" command is configured in the OSPF process of R1 and R3. Please match the route entries in the following routing table with the routers.
When the administrator enables the MPLS LDP function of the device, which of the following commands must be configured first?
- A . [Huawei] mpls 1sr-id 1.1.1. 1
- B . [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] mpls ldp
- C . [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] mpls
- D . [Huawei] mpls ldp
When the administrator enables the MPLS LDP function of the device, which of the following commands must be configured first?
- A . [Huawei] mpls 1sr-id 1.1.1. 1
- B . [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] mpls ldp
- C . [Huawei-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] mpls
- D . [Huawei] mpls ldp
