Practice Free H12-831_V1.0-ENU Exam Online Questions
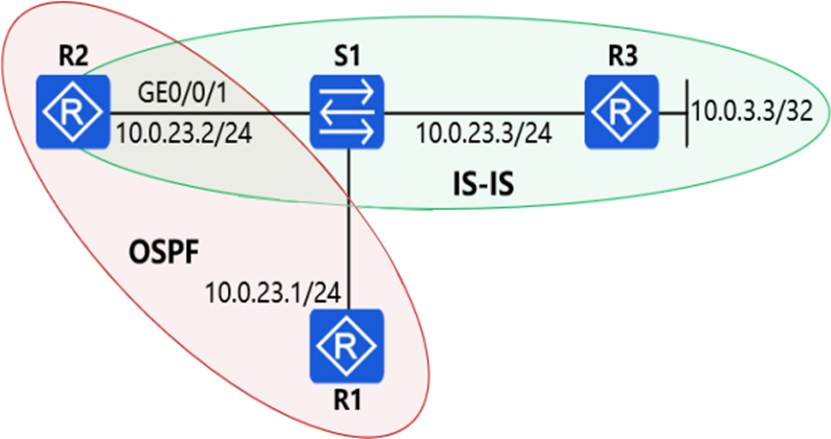
In the network shown in the figure, OSPF protocol is deployed between R2 and R1. IS-IS protocol is deployed between R2 and R3. In order for R1 to obtain the route to 10.0.3.3/32, IS-IS route is introduced into OSPF route on R2. Then, in R1’s routing table, the next hop address to 10.0.3.3/32 is ().
After port isolation is configured on a switch, hosts in the same VLAN cannot communicate with each other at Layer 2 or Layer 3 by default.
- A . TRUE
- B . FALSE
On the IS-IS IPv6 network shown in the figure, multi-topology is enabled on all routers. The IPv6 address of Loopback0 on R4 is 2000::/128. The IPv6 summary 2000::/64 level-1-2 command is configured in the IS-IS processes of R2 and R1.
Which of the following statements is false?
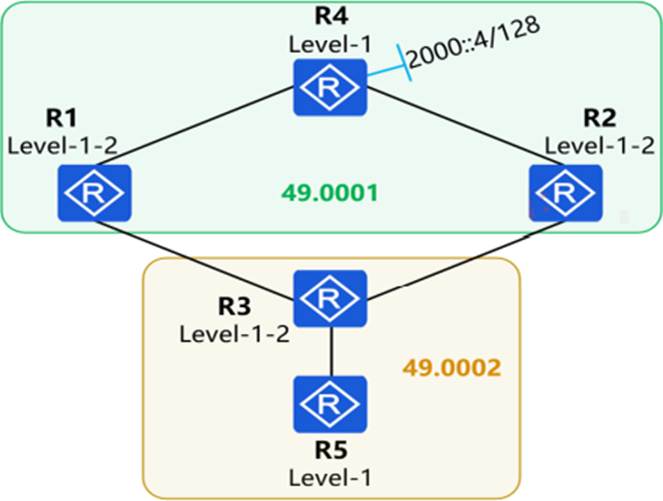
- A . The routing table of R1 contains the route 2000::/64.
- B . The routing table of R2 contains the route 2000::/64.
- C . The routing table of R3 contains the route 2000::/128.
- D . The routing table of R2 contains the route 2000::/128.
C
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed In-Depth
To determine which statement is false, we need to analyze the IS-IS topology, the role of multi-topology, the IPv6 summary configuration, and the level-1-2 behavior of IS-IS routers. Let’s break it down step by step:
Understanding the IS-IS Topology and Levels:
IS-IS supports multiple levels: Level-1 (L1) for intra-area routing, Level-2 (L2) for inter-area routing,
and Level-1-2 (L1-2) routers that can operate in both levels and connect L1 and L2 areas.
In the figure, R1 and R2 are configured as Level-1-2 routers, R3 is a Level-1-2 router, R4 is a Level-1
router, and R5 is a Level-1 router. The area borders are indicated by the system IDs (49.0001 for R4’s area and 49.0002 for R3 and R5’s area).
R4’s Loopback0 has the IPv6 address 2000::/128, which is a host route (a /128 prefix, representing a single address).
Multi-Topology IS-IS for IPv6:
Multi-topology IS-IS allows separate topologies for IPv4 and IPv6, ensuring that IPv6 routes are
handled independently. Since multi-topology is enabled on all routers, IPv6 routes (like 2000::/128
on R4) are advertised and processed within the IPv6 topology.
This means that IPv6 routes, including the Loopback0 address of R4 (2000::/128), can be advertised across the IS-IS domain, subject to the level and summary configurations.
IPv6 Summary Configuration (2000::/64 level-1-2):
The command ipv6 summary 2000::/64 level-1-2 is configured in the IS-IS processes of R1 and R2. This command instructs R1 and R2 (as Level-1-2 routers) to summarize the IPv6 prefix 2000::/64 and advertise it to both Level-1 and Level-2 areas.
Summarization means that instead of advertising the more specific route (e.g., 2000::/128 from R4), R1 and R2 advertise the less specific summary route 2000::/64. This summary route covers the 2000::/128 address of R4’s Loopback0.
Since R1 and R2 are Level-1-2 routers, they can advertise this summary to both their Level-1 neighbors (like R4 and R3) and Level-2 neighbors (across areas).
Analyzing Each Statement:
In the OSPF network shown in the figure, R1 and R2 achieve intercommunication through Loopback0 interface through OSPF.
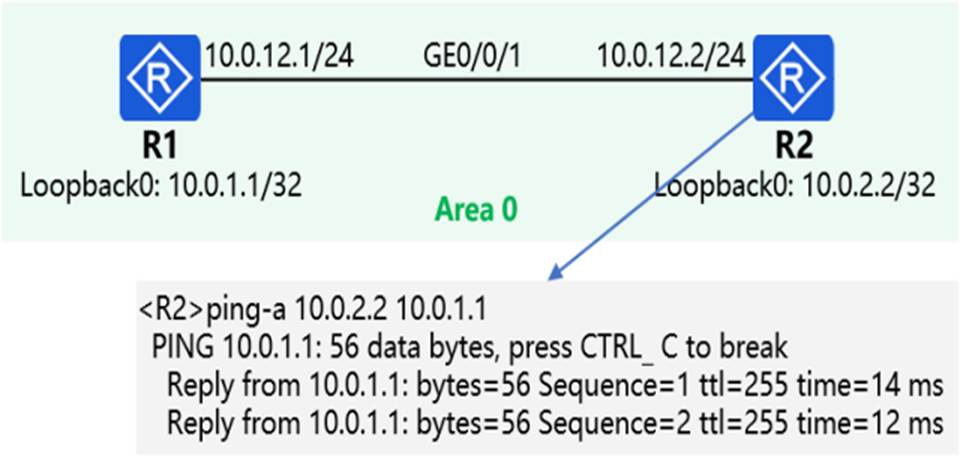
At the same time, R1 and R2 have enabled the MPLS LDP function, and the LDP transmission address is the IP address of the Loopback0 interface. The network engineer found that R1 and R2 could not establish an LDP session, so he first executed the command shown in the figure on R2.
Based on this, which of the following reasons may cause the failure of establishing an LDP session between R1 and R2? (Multiple choice)
- A . R2 GE0/0/1 interface refuses to receive packets with a destination IP address of 224.0.0.2
- B . R1 GE0/0/1 interface refuses to receive packets with a destination IP address of 224.0.0.5
- C . R2 GE0/0/1 interface refuses to receive packets with source IP address 10.0.12.1
- D . R1 GE0/0/1 interface refuses to receive packets with TCP destination port 646
Which of the following descriptions about OSPFv3 are correct? (Multiple choice)
- A . OSPFv3 Router LSA and Network LSA do not contain IP addresses
- B . The LSA flooding range is added to the OSPFv3 LSA message
- C . In broadcast, NBMA, and P2MP networks, neighbors are no longer identified by IP addresses, but only by Router IDs.
- D . OSPFv3 supports multiple processes on a link
